Abstract
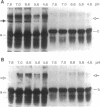
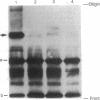
The apolipoprotein E (apoE) type 4 allele (APOE4) is a susceptibility gene for late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer disease. ApoE is found in some neurofibrillary tangle-bearing neurons, one of the major pathologic hallmarks of the disease. Neurofibrillary tangles contain paired helical filaments formed from hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein tau. In vitro, tau binds avidly to apoE3, but not to apoE4, forming a bimolecular complex. Tau phosphorylated with a brain extract does not bind either isoform. ApoE3 binds to the microtubule-binding repeat region of tau, which is also the region that is thought to cause self-assembly into the paired helical filament. Binding studies with fragments of ApoE demonstrate that the tau-binding region of apoE3 corresponds to its receptor-binding domain and is distinct from the region that binds lipoprotein particles or beta/A4 peptide. Isoform-specific interactions of apoE with tau may regulate intraneuronal tau metabolism in Alzheimer disease and alter the rate of formation of paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arriagada P. V., Growdon J. H., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Hyman B. T. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992 Mar;42(3 Pt 1):631–639. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanas V., Alvarez R. B., Engel W. K. beta-Amyloid precursor epitopes in muscle fibers of inclusion body myositis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Oct;34(4):551–560. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanas V., Engel W. K., Bilak M., Alvarez R. B., Selkoe D. J. Twisted tubulofilaments of inclusion body myositis muscle resemble paired helical filaments of Alzheimer brain and contain hyperphosphorylated tau. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jan;144(1):177–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askanas V., Mirabella M., Engel W. K., Alvarez R. B., Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactive deposits in inclusion-body muscle diseases. Lancet. 1994 Feb 5;343(8893):364–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biernat J., Mandelkow E. M., Schröter C., Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Steiner B., Berling B., Meyer H., Mercken M., Vandermeeren A., Goedert M. The switch of tau protein to an Alzheimer-like state includes the phosphorylation of two serine-proline motifs upstream of the microtubule binding region. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1593–1597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. A., Gilliam E. B., Gotto A. M., Jr, Gianturco S. H. Apolipoprotein-E degradation in human very low density lipoproteins by plasma protease(s): chemical and biological consequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1360–1367. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91927-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Risch N. J., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Rimmler J. B., Locke P. A., Conneally P. M., Schmader K. E. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2):180–184. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Olesen O. F., Jakes R., Goedert M. The microtubule binding repeats of tau protein assemble into filaments like those found in Alzheimer's disease. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 7;309(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R., Crowther R. A., Six J., Lübke U., Vandermeeren M., Cras P., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. The abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein at Ser-202 in Alzheimer disease recapitulates phosphorylation during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R. Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4225–4230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Cairns N. J., Crowther R. A. Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90117-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M. Tau protein and the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Nov;16(11):460–465. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90078-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Stark D., Wilson D., Brewer H. B., Jr Abnormal in vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein E4 in humans. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):815–821. doi: 10.1172/JCI112645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Wong J. S., Guo L. S., Krisans S., Havel R. J. Apolipoprotein E localization in rat hepatocytes by immunogold labeling of cryothin sections. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1589–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S. H., Hulette C., Saunders A. M., Einstein G., Pericak-Vance M., Strittmatter W. J., Roses A. D., Schmechel D. E. Apolipoprotein E is present in hippocampal neurons without neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and in age-matched controls. Exp Neurol. 1994 Jul;128(1):13–26. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Morishima-Kawashima M., Takio K., Suzuki M., Titani K., Ihara Y. Protein sequence and mass spectrometric analyses of tau in the Alzheimer's disease brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17047–17054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Friedlander E. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Binding of apolipoprotein E fragments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12341–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Hess M., May P. C., Finch C. E. Astrocytic apolipoprotein E mRNA and GFAP mRNA in hippocampus after entorhinal cortex lesioning. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Sep;11(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90111-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of apolipoprotein E. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:273–287. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Schmader K., Breitner J. C., Benson M. D., Brown W. T., Goldfarb L., Goldgaber D., Manwaring M. G., Szymanski M. H., McCown N. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):710–711. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Crain B. J., Hulette C. M., Joo S. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Goedert M., Saunders A. M., Huang D., Corder E. H., Dong L. M., Jakes R., Alberts M. J., Gilbert J. R. Hypothesis: microtubule instability and paired helical filament formation in the Alzheimer disease brain are related to apolipoprotein E genotype. Exp Neurol. 1994 Feb;125(2):163–174. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Huang D. Y., Dong L. M., Salvesen G. S., Pericak-Vance M., Schmechel D., Saunders A. M., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Binding of human apolipoprotein E to synthetic amyloid beta peptide: isoform-specific effects and implications for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8098–8102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Schmidt M. L., Shin R. W., Bramblett G. T., Rao D., Lee V. M. Altered tau and neurofilament proteins in neuro-degenerative diseases: diagnostic implications for Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementias. Brain Pathol. 1993 Jan;3(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1993.tb00725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E distribution among human plasma lipoproteins: role of the cysteine-arginine interchange at residue 112. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1503–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H. Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationships. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:249–302. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60642-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Apoprotein (E--A-II) complex of human plasma lipoproteins. I. Characterization of this mixed disulfide and its identification in a high density lipoprotein subfraction. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6281–6288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9077–9083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Shinto L. H. Identification of the disulfide-linked homodimer of apolipoprotein E3 in plasma. Impact on receptor binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12029–12034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund J. A., Weisgraber K. H. Discrete carboxyl-terminal segments of apolipoprotein E mediate lipoprotein association and protein oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15745–15750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille H., Drewes G., Biernat J., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments and antiparallel dimers formed from microtubule-associated protein tau in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):573–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]