Abstract
A large variety of different RNA species that are replicated by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from bacteriophage T7 have been generated by incubating high concentrations of this enzyme with substrate for extended time periods. The products differed from sample to sample in molecular weight and sequence, their chain lengths ranging from 60 to 120. The mechanism of autocatalytic amplification of RNA by T7 RNA polymerase proved to be analogous to that observed with viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (replicases): only single-stranded templates are accepted and complementary replica strands are synthesized. With enzyme in excess, exponential growth was observed; linear growth resulted when the enzyme was saturated by RNA template. The plus strands, present at 90% of the replicating RNA species, were found to have GG residues at both termini. Consensus sequences were not found among the sequences of the replicating RNA species. The secondary structures of all species sequenced turned out to be hairpins. The RNA species were specifically replicated by T7 RNA polymerase; they were not accepted as templates by the RNA polymerases from Escherichia coli or bacteriophage SP6 or by Qbeta replicase; T3 RNA polymerase was partially active. Template-free production of RNA was completely suppressed by addition of DNA to the incubation mixture. When both DNA and RNA templates were present, transcription and replication competed, but T7 RNA polymerase preferred DNA as a template. No replicating RNA species were detected in vivo in cells expressing T7 RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K., Rensing U., August J. T. Replication of RNA viruses. X. Replication of a natural 6 s RNA by the Q-beta RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
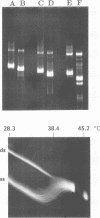
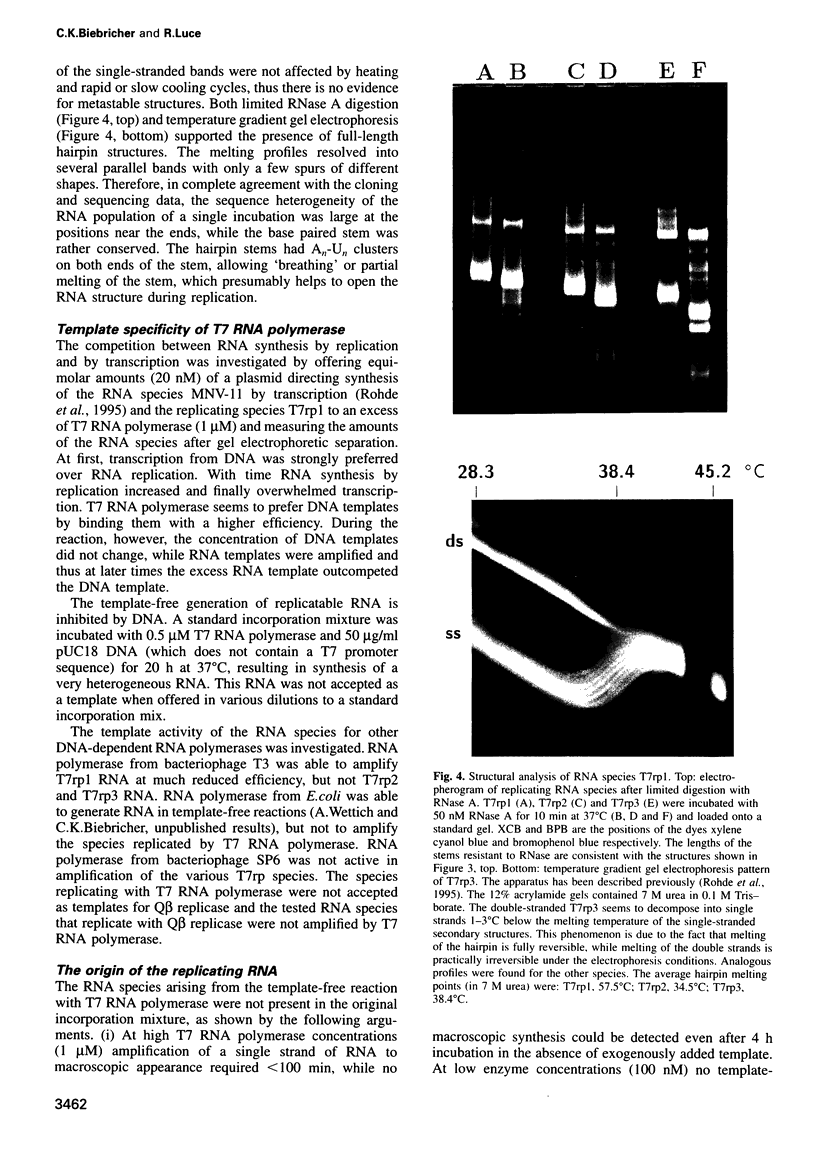
- Biebricher C. K., Diekmann S., Luce R. Structural analysis of self-replicating RNA synthesized by Qbeta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 5;154(4):629–648. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Eigen M., Luce R. Kinetic analysis of template-instructed and de novo RNA synthesis by Q beta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):391–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Eigen M., Luce R. Product analysis of RNA generated de novo by Q beta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):369–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Eigen M., Luce R. Template-free RNA synthesis by Q beta replicase. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):89–91. doi: 10.1038/321089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Eigen M., McCaskill J. S. Template-directed and template-free RNA synthesis by Q beta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):175–179. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Luce R. In vitro recombination and terminal elongation of RNA by Q beta replicase. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5129–5135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Luce R. Sequence analysis of RNA species synthesized by Q beta replicase without template. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4848–4854. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K., Orgel L. E. An RNA that multiplies indefinitely with DNA-dependent RNA polymerase: selection from a random copolymer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):934–938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K. Replication and evolution of short-chained RNA species replicated by Q beta replicase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:299–306. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breaker R. R., Joyce G. F. Emergence of a replicating species from an in vitro RNA evolution reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6093–6097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O., Owens R. A., Hammond R. W. Viroids: the smallest and simplest agents of infectious disease. How do they make plants sick? Intervirology. 1993;35(1-4):186–195. doi: 10.1159/000150309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen E. D., Durbin R. K., Risman S. S., McAllister W. T. Specific contacts between the bacteriophage T3, T7, and SP6 RNA polymerases and their promoters. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Replication of RNA by the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of phage T7. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90917-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Structure of RNAs replicated by the DNA-dependent T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90456-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Synthesis of small RNAs using T7 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:51–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Peterson R. L., Spiegelman S. An extracellular Darwinian experiment with a self-duplicating nucleic acid molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):217–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. D., Burg J. L., DiFrancesco R., Lovern D., Stanick W., Lin-Goerke J., Mahdavi K., Wu Y., Farrell M. P. Evolution of host cell RNA into efficient template RNA by Q beta replicase: the origin of RNA in untemplated reactions. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13836–13847. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. E., Klement J. F., McAllister W. T. Cloning and expression of the bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase gene. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde N., Daum H., Biebricher C. K. The mutant distribution of an RNA species replicated by Q beta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 16;249(4):754–762. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick C., Martin C. T. Tests of a model of specific contacts in T7 RNA polymerase-promoter interactions. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 17;34(2):666–672. doi: 10.1021/bi00002a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M., Luce R. Evidence for de novo production of self-replicating and environmentally adapted RNA structures by bacteriophage Qbeta replicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):162–166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C. The making of a phage. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 23;40(0):suppl–suppl:S18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80684-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamora H., Luce R., Biebricher C. K. Design of artificial short-chained RNA species that are replicated by Q beta replicase. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 31;34(4):1261–1266. doi: 10.1021/bi00004a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]