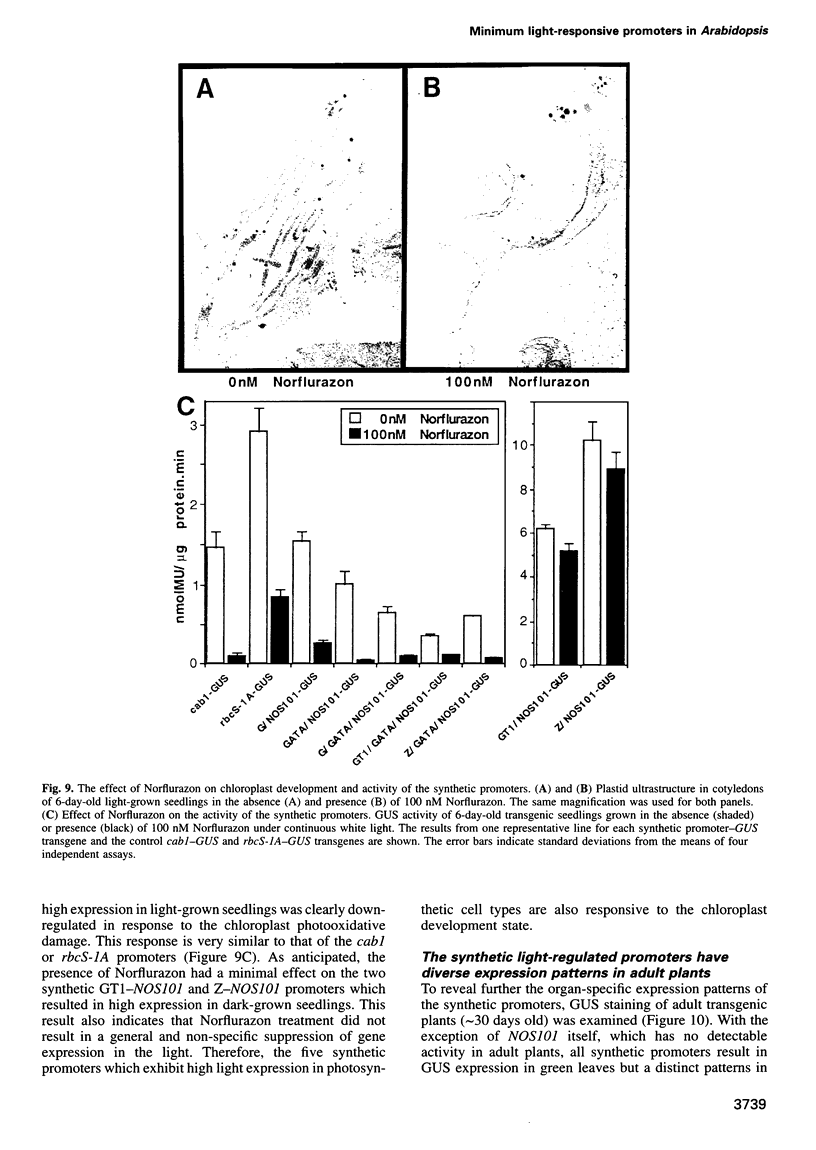
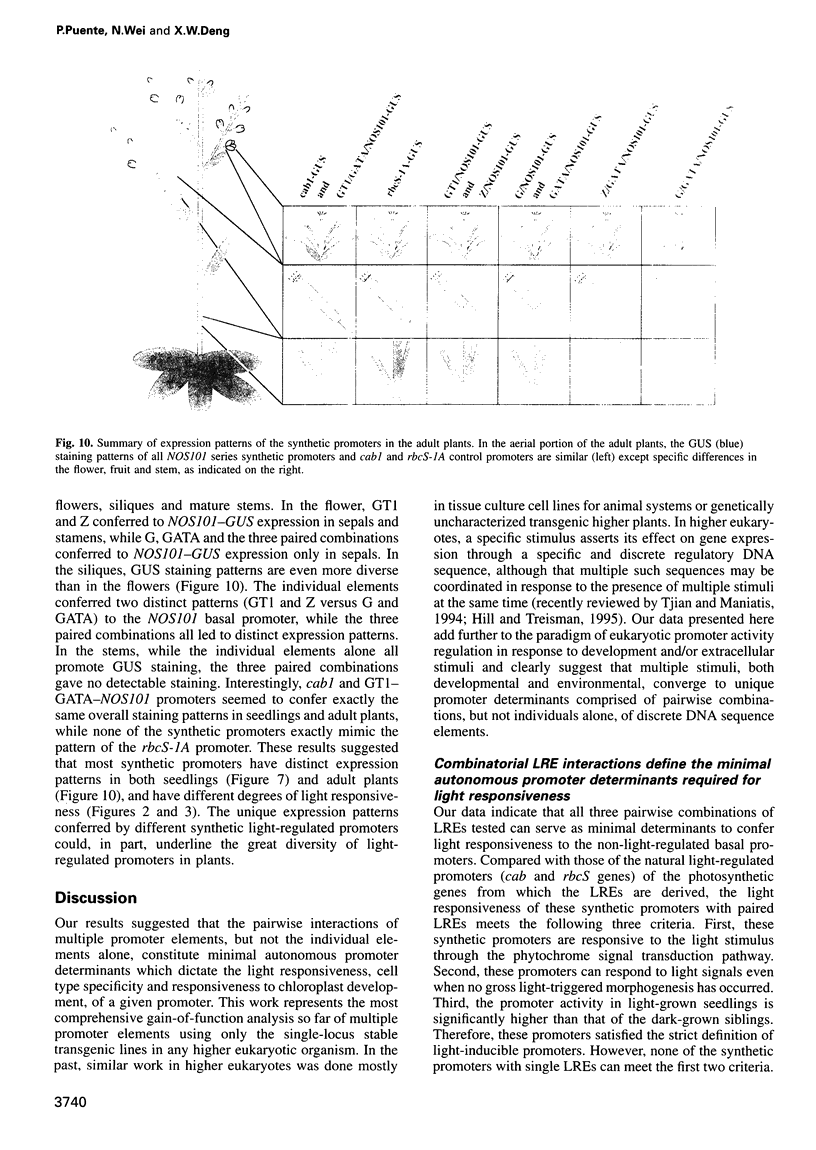
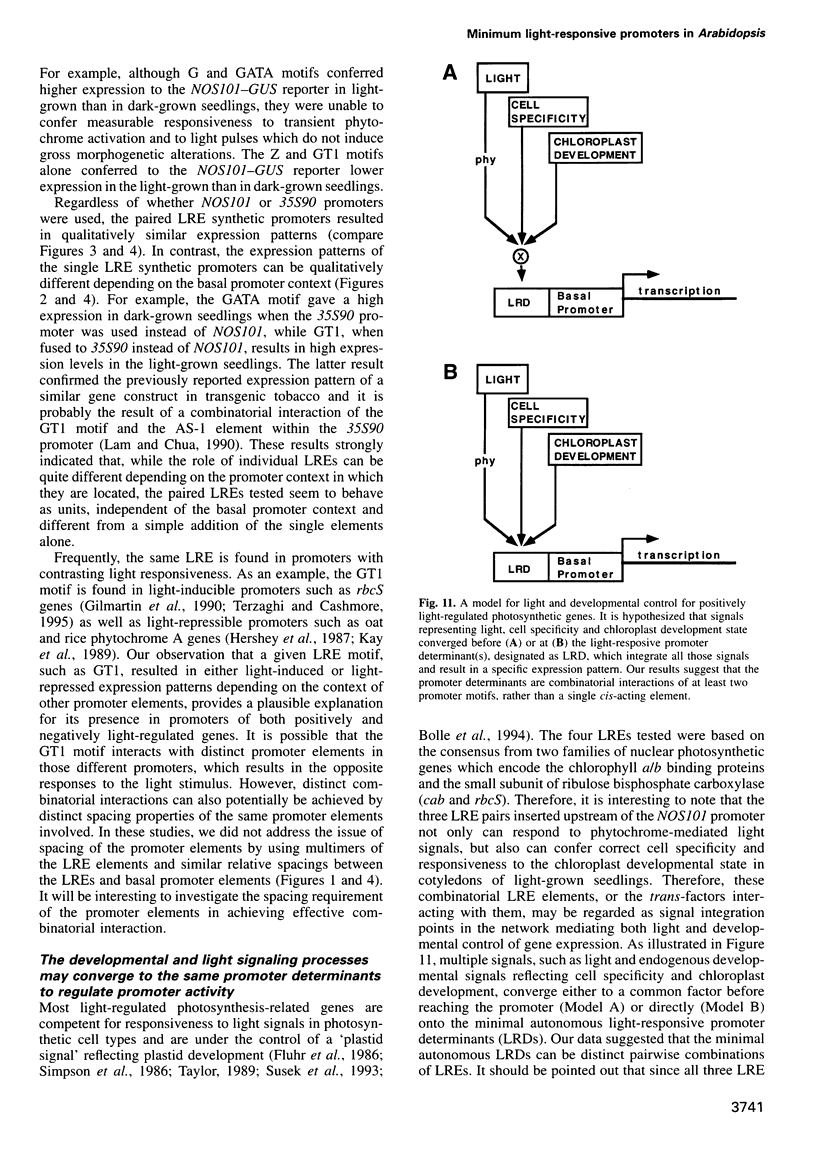
Abstract
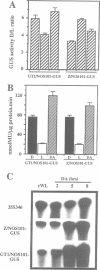
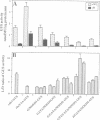
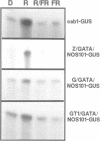
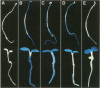
Higher plants are able to integrate environmental and endogenous signals to regulate gene expression for optimal development. To define the minimal sequence requirement sufficient to integrate light and developmental signals in controlling promoter activity, we carried out a systematic analysis of the roles of four well-conserved 'light-responsive elements (LREs)' common to many nuclear-encoded photosynthetic genes. A gain-of-function assay using basal promoter-reporter fusions in stable transgenic Arabidopsis was employed to demonstrate that pairwise combinations of the LREs, but not the individual elements alone, can confer light-inducible expression to the reporter gene independently of the basal promoter context and the light-triggered morphological changes. The activity of the synthetic promoters with the paired LREs can be modulated at least by the phytochrome system. Further, those synthetic light-regulated promoters confer a photosynthetic cell-specific expression pattern and respond to the chloroplast development state. Our data suggest that distinct combinatorial interactions of LREs can serve as minimal autonomous promoter determinants which integrate light and developmental signals and modulate promoter activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. L., Teakle G. R., Martino-Catt S. J., Kay S. A. Circadian clock- and phytochrome-regulated transcription is conferred by a 78 bp cis-acting domain of the Arabidopsis CAB2 promoter. Plant J. 1994 Oct;6(4):457–470. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1994.6040457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolle C., Sopory S., Lubberstedt T., Klosgen R. B., Herrmann R. G., Oelmuller R. The Role of Plastids in the Expression of Nuclear Genes for Thylakoid Proteins Studied with Chimeric [beta]-Glucuronidase Gene Fusions. Plant Physiol. 1994 Aug;105(4):1355–1364. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.4.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler C., Chua N. H. Emerging themes of plant signal transduction. Plant Cell. 1994 Nov;6(11):1529–1541. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.11.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castresana C., Garcia-Luque I., Alonso E., Malik V. S., Cashmore A. R. Both positive and negative regulatory elements mediate expression of a photoregulated CAB gene from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamovitz D., Pecker I., Hirschberg J. The molecular basis of resistance to the herbicide norflurazon. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):967–974. doi: 10.1007/BF00016069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley T. R., Park S. C., Kwon H. B., Peng H. P., Shih M. C. Characterization of cis-acting elements in light regulation of the nuclear gene encoding the A subunit of chloroplast isozymes of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2525–2533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Caspar T., Quail P. H. cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W. Fresh view of light signal transduction in plants. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Cashmore A. R. Mutation of either G box or I box sequences profoundly affects expression from the Arabidopsis rbcS-1A promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1717–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob U., Stüber K. Discrimination of phytochrome dependent light inducible from non-light inducible plant genes. Prediction of a common light-responsive element (LRE) in phytochrome dependent light inducible plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9957–9973. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha S. B., An G. Identification of upstream regulatory elements involved in the developmental expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana cab1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8017–8021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey H. P., Barker R. F., Idler K. B., Murray M. G., Quail P. H. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a gene encoding the phytochrome polypeptide from Avena. Gene. 1987;61(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Treisman R. Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Sun L., Tobin E. M. Expression of Light-Harvesting Chlorophyll a/b-Protein Genes Is Phytochrome-Regulated in Etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1323–1331. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Keith B., Shinozaki K., Chye M. L., Chua N. H. The rice phytochrome gene: structure, autoregulated expression, and binding of GT-1 to a conserved site in the 5' upstream region. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):351–360. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe D. M., Degenhardt J., Winicov I., Tobin E. M. Two 10-bp regions are critical for phytochrome regulation of a Lemna gibba Lhcb gene promoter. Plant Cell. 1994 Aug;6(8):1123–1134. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.8.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Chua N. H. ASF-2: a factor that binds to the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and a conserved GATA motif in Cab promoters. Plant Cell. 1989 Dec;1(12):1147–1156. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.12.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Chua N. H. GT-1 binding site confers light responsive expression in transgenic tobacco. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):471–474. doi: 10.1126/science.2330508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Carrasco P., Gruissem W. Developmental and organ-specific changes in promoter DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS gene family. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1305–1316. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNellis T. W., Deng X. W. Light control of seedling morphogenetic pattern. Plant Cell. 1995 Nov;7(11):1749–1761. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNellis T. W., von Arnim A. G., Deng X. W. Overexpression of Arabidopsis COP1 results in partial suppression of light-mediated development: evidence for a light-inactivable repressor of photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell. 1994 Oct;6(10):1391–1400. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.10.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra A., An G. Three distinct regulatory elements comprise the upstream promoter region of the nopaline synthase gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):294–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00339731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quail P. H. Photosensory perception and signal transduction in plants. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Oct;4(5):652–661. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90131-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo M. A., Freed D. D., Carrington J. C. Nuclear transport of plant potyviral proteins. Plant Cell. 1990 Oct;2(10):987–998. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.10.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., VAN Montagu M., Herrera-Estrella L. Photosynthesis-associated gene families: differences in response to tissue-specific and environmental factors. Science. 1986 Jul 4;233(4759):34–38. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4759.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susek R. E., Ausubel F. M., Chory J. Signal transduction mutants of Arabidopsis uncouple nuclear CAB and RBCS gene expression from chloroplast development. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):787–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonkyn J. C., Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Regulation of Plastid Gene Expression during Photooxidative Stress. Plant Physiol. 1992 Aug;99(4):1406–1415. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens D., Van Montagu M., Van Lijsebettens M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5536–5540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei N., Deng X. W. COP9: a new genetic locus involved in light-regulated development and gene expression in arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1992 Dec;4(12):1507–1518. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.12.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei N., Kwok S. F., von Arnim A. G., Lee A., McNellis T. W., Piekos B., Deng X. W. Arabidopsis COP8, COP10, and COP11 genes are involved in repression of photomorphogenic development in darkness. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):629–643. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Ma H., Bowman J. L., Drews G. N., Feldmann K. A., Meyerowitz E. M. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):35–39. doi: 10.1038/346035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]