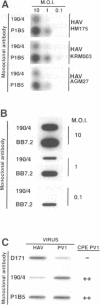
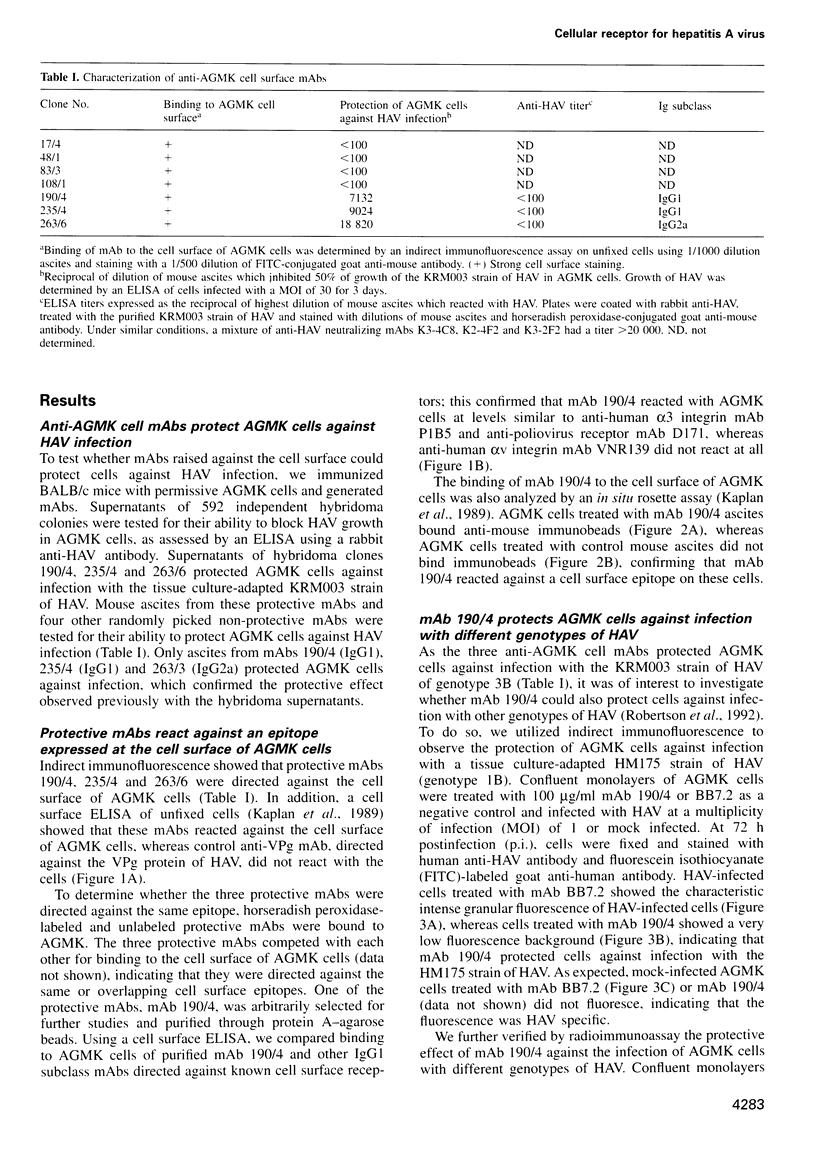
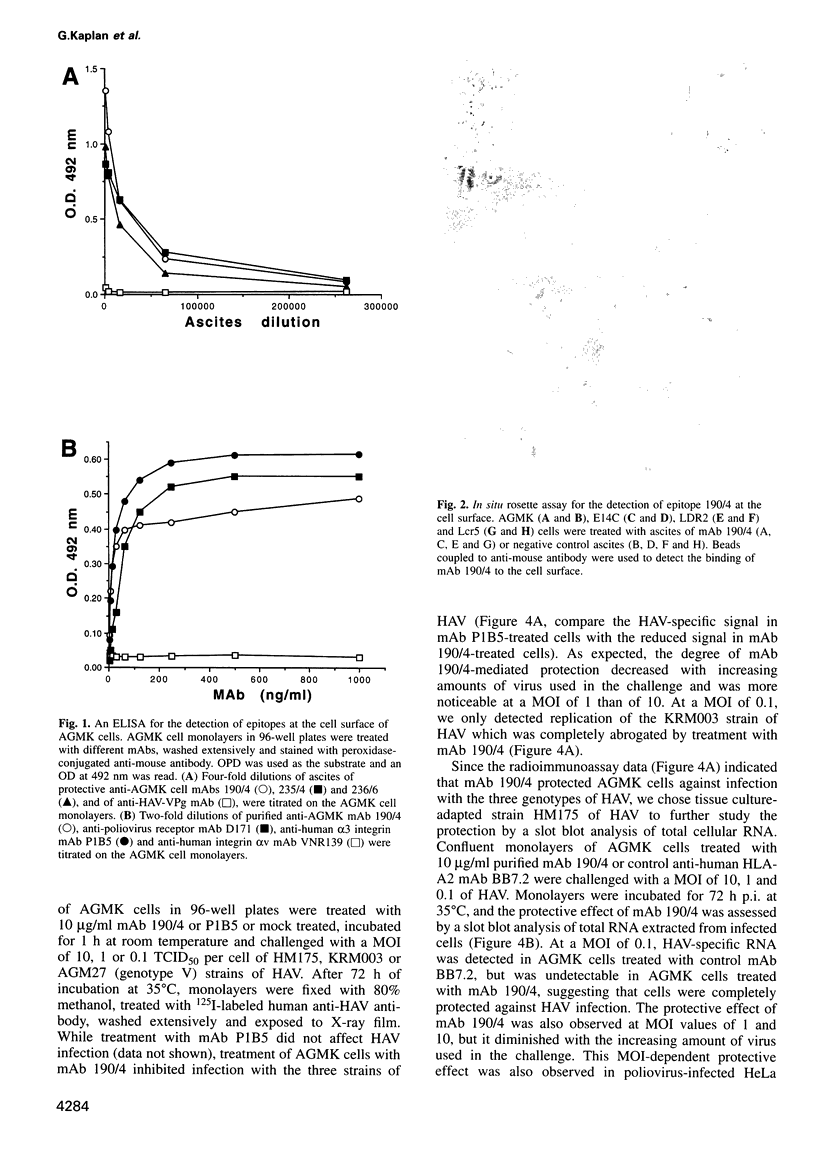
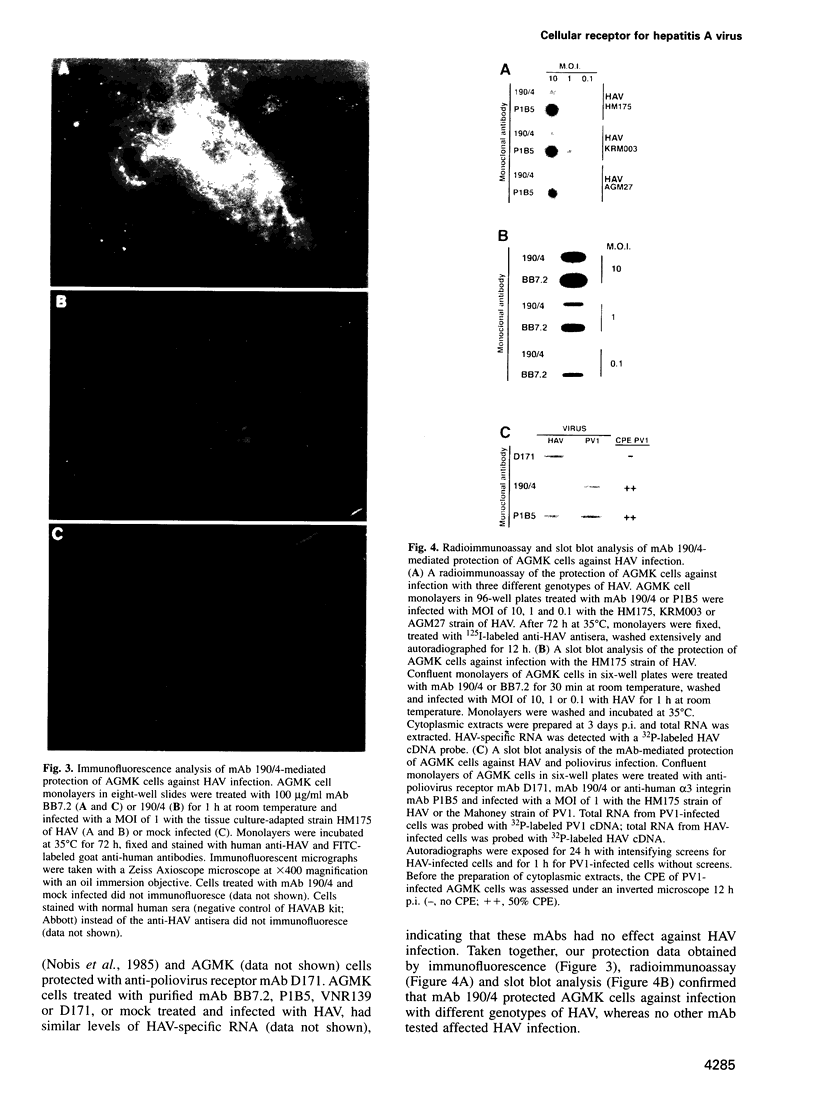
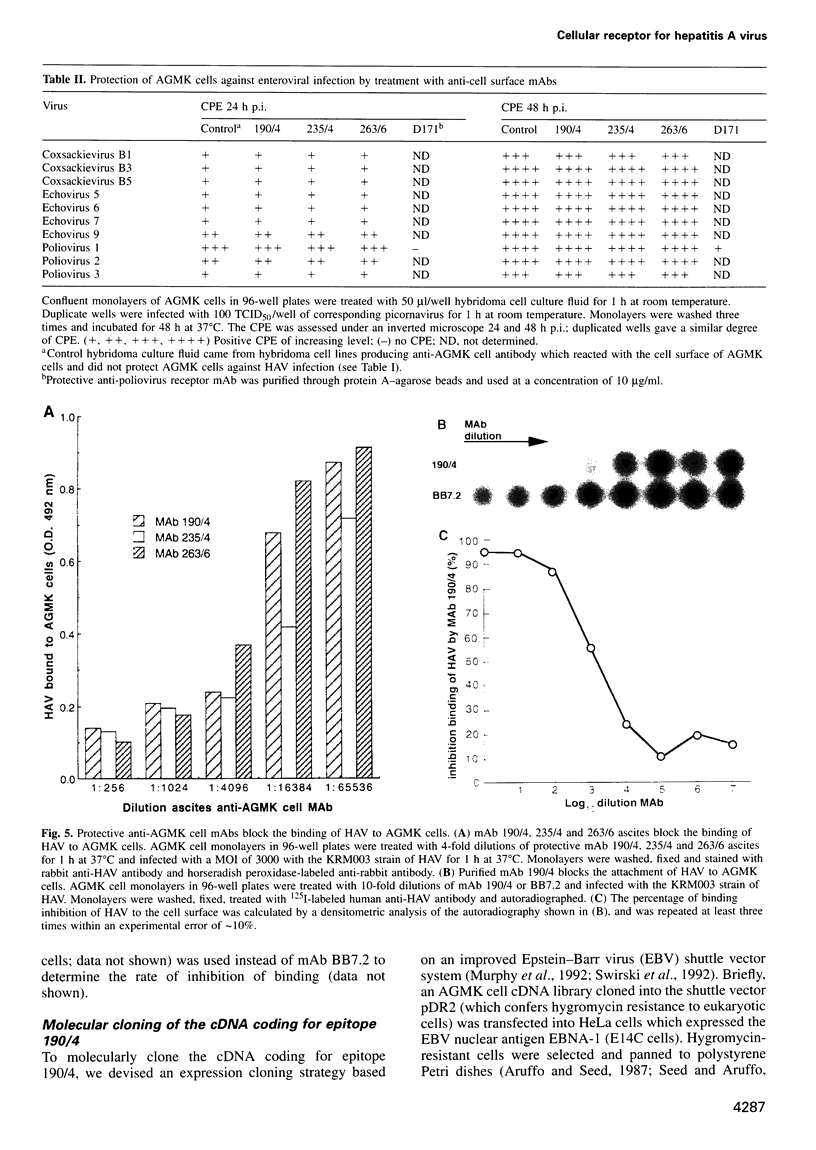
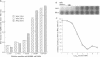Abstract
Very little is known about the mechanism of cell entry of hepatitis A virus (HAV), and the identification of cellular receptors for this picornavirus has been elusive. Here we describe the molecular cloning of a cellular receptor for HAV using protective monoclonal antibodies raised against susceptible African green monkey kidney (AGMK) cells as probes. Monoclonal antibodies 190/4, 235/4 and 263/6, which reacted against similar epitopes, specifically protected AGMK cells against HAV infection by blocking the binding of HAV. Expression cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the cDNA coding for epitope 190/4 revealed a novel mucin-like class I integral membrane glycoprotein of 451 amino acids, the HAV cellular receptor 1 (HAVcr-1). Immunofluorescence analysis indicated that mouse Ltk- cells transfected with HAVcr-1 cDNA gained limited susceptibility to HAV infection, which was blocked by treatment with monoclonal antibody 190/4. Our results demonstrate that the HAVcr-1 polypeptide is an attachment receptor for HAV and strongly suggest that it is also a functional receptor which mediates HAV infection. This report constitutes the first identification of a cellular receptor for HAV.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Luo G., Wu R. Expression of MUC2 gene is down-regulated by vitamin A at the transcriptional level in vitro in tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 May;10(5):546–551. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.10.5.8179918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. A., Ross B. C., Locarnini S. A. Restricted replication of hepatitis A virus in cell culture: encapsidation of viral RNA depletes the pool of RNA available for replication. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4201–4206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4201-4206.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Rosenblum B., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis A virus cDNA and its RNA transcripts are infectious in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3035-3039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crevat D., Crance J. M., Chevrinais A. M., Passagot J., Biziagos E., Somme G., Deloince R. Monoclonal antibodies against an immunodominant and neutralizing epitope on hepatitis A virus antigen. Arch Virol. 1990;113(1-2):95–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01318357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggfeldt A., Bengtén E., Pilström L. A cluster type organization of the loci of the immunoglobulin light chain in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) indicated by nucleotide sequences of cDNAs and hybridization analysis. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(3):199–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00211520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine P. L., McKenzie I. F. Mucins: structure, function, and associations with malignancy. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):619–625. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotzauer A., Feinstone S. M., Kaplan G. Susceptibility of nonprimate cell lines to hepatitis A virus infection. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):6064–6068. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.6064-6068.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel M. D., Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. DNA sequences, gene regulation and modular protein evolution in the Drosophila 68C glue gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):765–789. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Eddy R. L., Jr, Shows T. B. The core polypeptide of cystic fibrosis tracheal mucin contains a tandem repeat structure. Evidence for a common mucin in airway and gastrointestinal tissue. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1921–1927. doi: 10.1172/JCI114925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Hoffmann W. P-domains as shuffled cysteine-rich modules in integumentary mucin C.1 (FIM-C.1) from Xenopus laevis. Polydispersity and genetic polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24620–24624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W. A new repetitive protein from Xenopus laevis skin highly homologous to pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7686–7690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft N. Why are proteins O-glycosylated? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Levy A., Racaniello V. R. Isolation and characterization of HeLa cell lines blocked at different steps in the poliovirus life cycle. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):43–51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.43-51.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Sato Y., Yonekawa H., Gotoh O., Nomoto A. A second gene for the African green monkey poliovirus receptor that has no putative N-glycosylation site in the functional N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7059–7066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7059-7066.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Incomplete neutralization of hepatitis A virus in vitro due to lipid-associated virions. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2501–2505. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. The use of sodium dodecyl sulfate in studies on the interaction of poliovirus and HeLa cells. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:288–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Gutierrez L., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Targeting of oncoproteins to membranes by fatty acylation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:149–160. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Nainan O. V. Identification of virus components in circulating immune complexes isolated during hepatitis A virus infection. Hepatology. 1990 Jan;11(1):31–37. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Nainan O. V., Krawczynski K., Bradley D. W., Ebert J. W., Spelbring J., Fields H. A., Maynard J. E. Appearance of immune complexes during experimental hepatitis A infection in chimpanzees. J Med Virol. 1988 Nov;26(3):315–326. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meezaman D., Charles P., Daskal E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Martin B. M., Rose M. C. Cloning and analysis of cDNA encoding a major airway glycoprotein, human tracheobronchial mucin (MUC5). J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12932–12939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. J., Spithill T. W. Variants of a Leishmania surface antigen derived from a multigenic family. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24477–24484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Brodsky F. M. Partial purification and some properties of BB7.2. A cytotoxic monoclonal antibody with specificity for HLA-A2 and a variant of HLA-A28. Hum Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(4):277–299. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Giesa P. A., McAleer W. J., Hilleman M. R. Isolation of hepatitis A virus in vitro in cell culture directly from human specimens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Jun;167(2):201–206. doi: 10.3181/00379727-167-41149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M. B., Pollevick G. D., Frasch A. C. An unusually small gene encoding a putative mucin-like glycoprotein in Trypanosoma cruzi. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90745-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Jansen R. W., Khanna B., Totsuka A., Nainan O. V., Siegl G., Widell A., Margolis H. S., Isomura S., Ito K. Genetic relatedness of hepatitis A virus strains recovered from different geographical regions. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jun;73(Pt 6):1365–1377. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-6-1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Lu C. F., Marykwas D. L., Lipke P. N., Kurjan J. The AGA1 product is involved in cell surface attachment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell adhesion glycoprotein a-agglutinin. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4196–4206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig R., Pott G., Seelig H. P., Liehr H., Metzger P., Waldherr R. Virus-binding activity of fibronectin: masking of hepatitis A virus. J Virol Methods. 1984 Jul;8(4):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seganti L., Superti F., Orsi N., Gabrieli R., Divizia M., Panà A. Study of the chemical nature of Frp/3 cell recognition units for hepatitis A virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(1):21–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00189405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton J. T., Frederick J., Meyer B. Hepatitis A virus attachment to cultured cell lines. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1098–1103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Dekker J. Mucin-type glycoproteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(1-2):57–92. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swida U., Lucka L., Kress H. Glue protein genes in Drosophila virilis: their organization, developmental control of transcription and specific mRNA degradation. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):269–280. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toribara N. W., Gum J. R., Jr, Culhane P. J., Lagace R. E., Hicks J. W., Petersen G. M., Kim Y. S. MUC-2 human small intestinal mucin gene structure. Repeated arrays and polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):1005–1013. doi: 10.1172/JCI115360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsarev S. A., Emerson S. U., Balayan M. S., Ticehurst J., Purcell R. H. Simian hepatitis A virus (HAV) strain AGM-27: comparison of genome structure and growth in cell culture with other HAV strains. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1677–1683. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. S., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Ou S., Strauss J. H. High-affinity laminin receptor is a receptor for Sindbis virus in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4992–5001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4992-5001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward T., Pipkin P. A., Clarkson N. A., Stone D. M., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. Decay-accelerating factor CD55 is identified as the receptor for echovirus 7 using CELICS, a rapid immuno-focal cloning method. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5070–5074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Watanabe K., Shimonaka M., Yamaguchi Y. Molecular cloning of brevican, a novel brain proteoglycan of the aggrecan/versican family. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10119–10126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac A. J., Amphlett E. M., Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V. Parameters influencing the attachment of hepatitis A virus to a variety of continuous cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1667–1675. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]