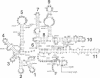Abstract
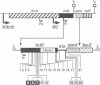
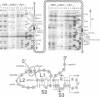
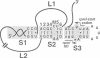
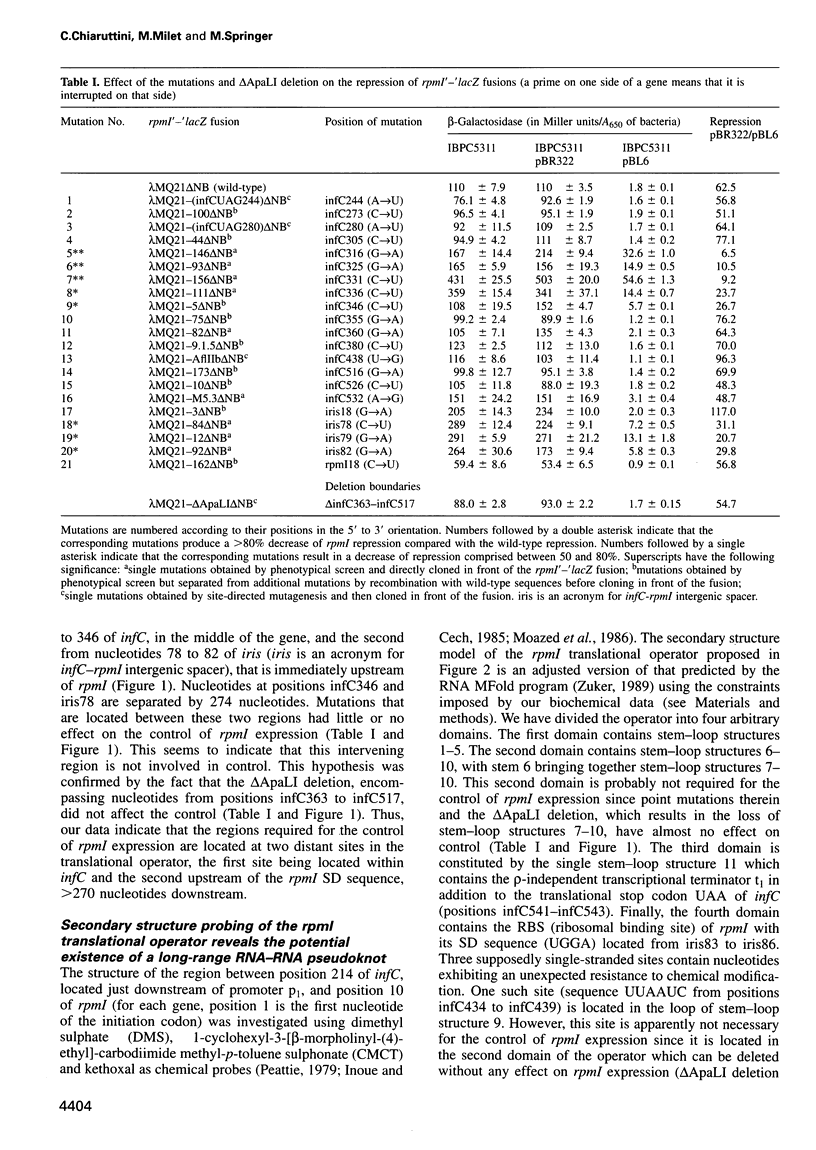
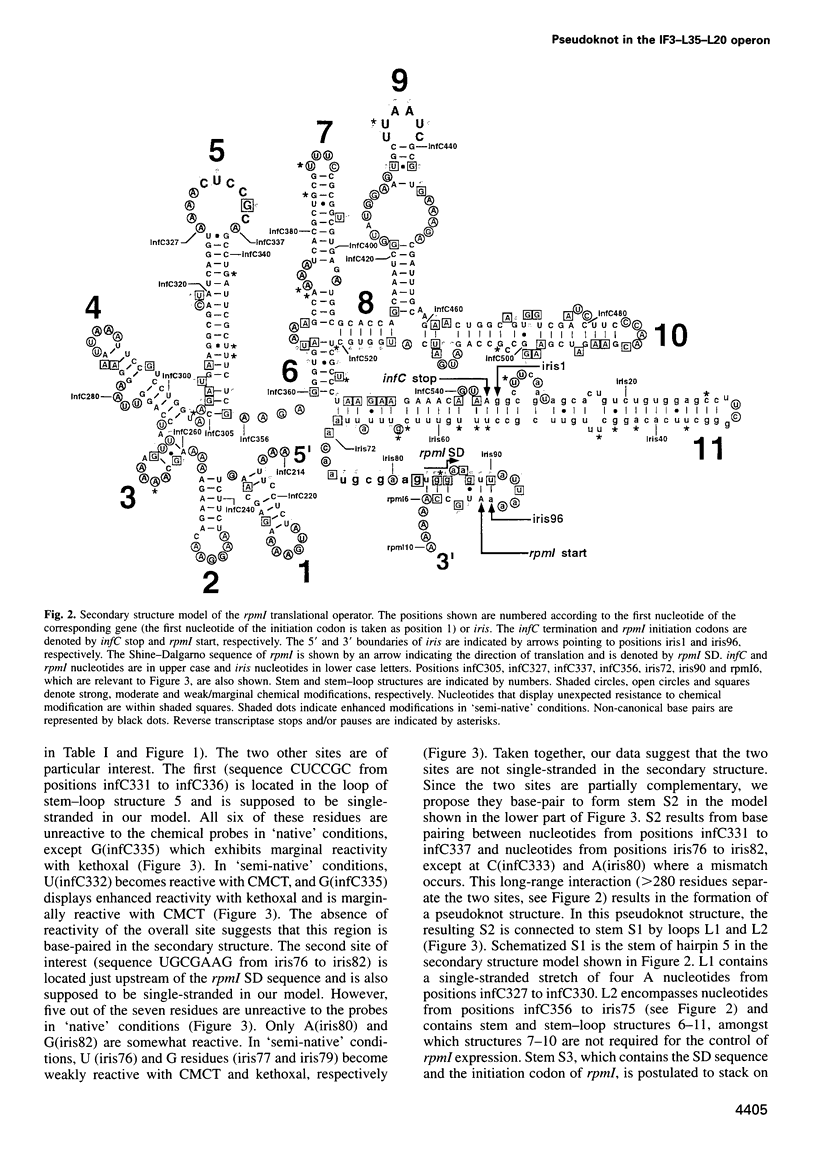
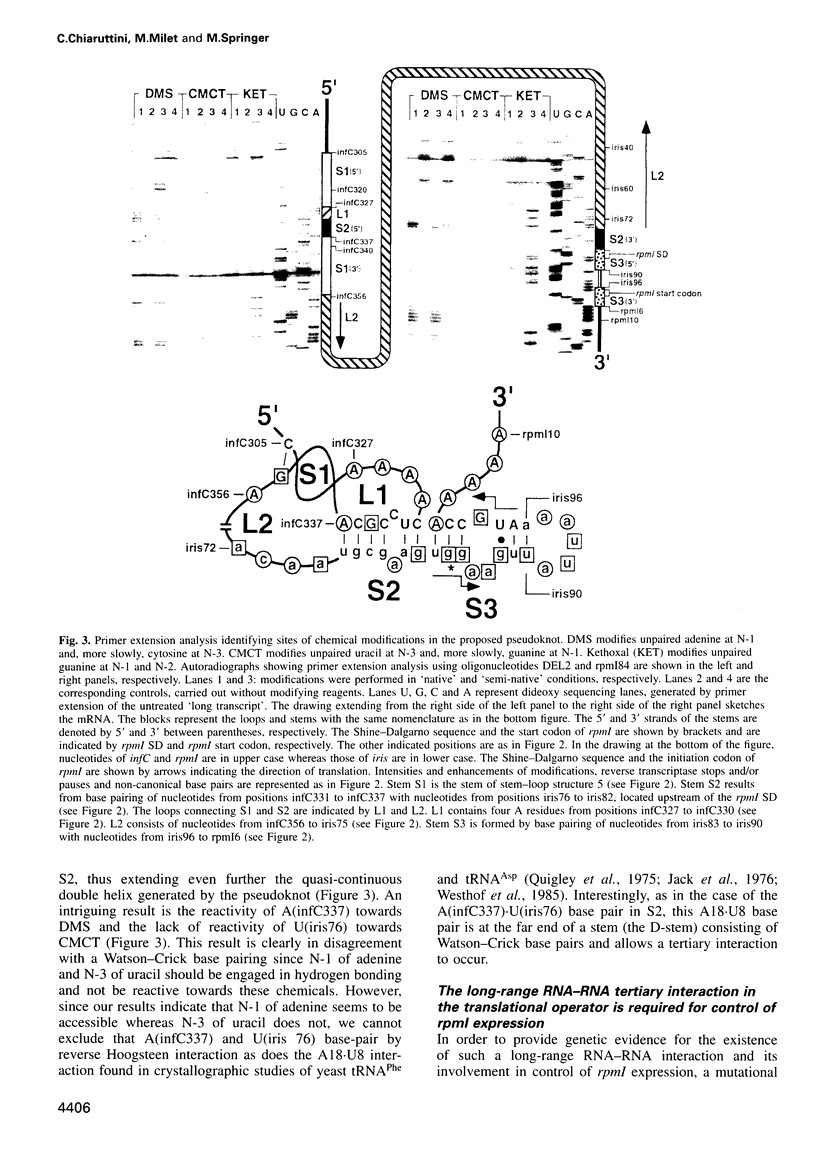
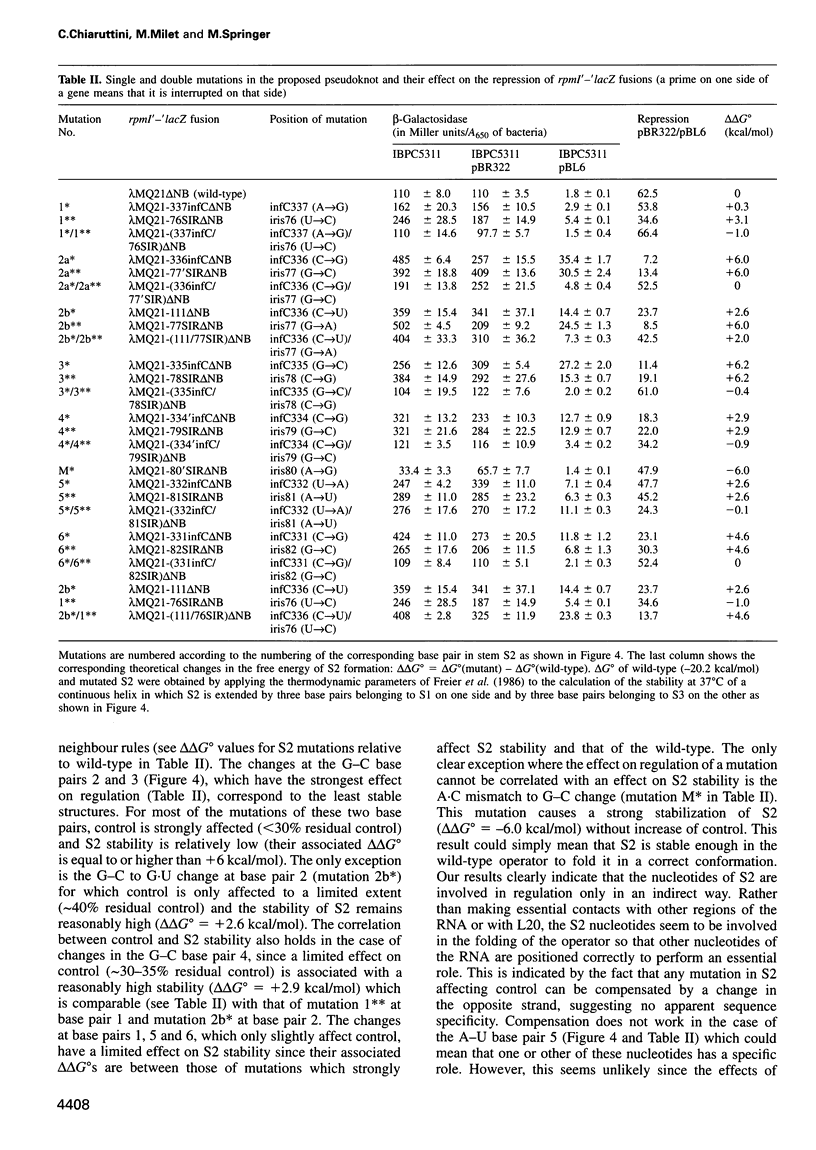
In the IF3-L35-L20 operon encoding translation initiation factor 3 (IF3) and the two ribosomal proteins L35 and L20, the expression of the genes that code for the two ribosomal proteins is negatively regulated at the translational level by the cellular concentration of L20. This translational repressor directly regulates the expression of the gene encoding L35 and, via translational coupling, that of its own gene. Mutations that affect the control of the L35 gene were found exclusively at two sites: the first is located approximately 300 nucleotides upstream, and the second immediately 5' of the translation initiation site of the L35 gene. Mutations that fall between these two sites have little or no effect on the control, and the lack of effect of a deletion in the intervening region confirms this finding. RNA structure mapping in vitro suggests that the first site pairs with the second. We show that this pairing is also likely to occur in vivo because single mutations in either of these sites affect control, but base pair compensatory mutations re-establish control. We propose that these two distant sites can base-pair to form a long-range pseudoknot which is required for the control of the expression of the L35 gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunel C., Caillet J., Lesage P., Graffe M., Dondon J., Moine H., Romby P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Grunberg-Manago M. Domains of the Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase translational operator and their relation to threonine tRNA isoacceptors. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):621–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Belfort M., Cech T. R., Davies R. W., Schweyen R. J., Shub D. A., Szostak J. W., Tabak H. F. Structural conventions for group I introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7217–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Springer M., Dondon J., Graffe M., Grunberg-Manago M. Escherichia coli protein synthesis initiation factor IF3 controls its own gene expression at the translational level in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):767–780. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Springer M., Grunberg-Manago M. AUU-to-AUG mutation in the initiator codon of the translation initiation factor IF3 abolishes translational autocontrol of its own gene (infC) in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4022–4025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen T., Johnsen M., Fiil N. P., Friesen J. D. RNA secondary structure and translation inhibition: analysis of mutants in the rplJ leader. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1609–1612. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee T., Herschlag D., Belfort M. Escherichia coli proteins, including ribosomal protein S12, facilitate in vitro splicing of phage T4 introns by acting as RNA chaperones. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1575–1588. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Control of transcription termination by RNA-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:893–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.004333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D., Tropak M., An G. Mutations in the rpIJ leader of Escherichia coli that abolish feedback regulation. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinaro H., Domenjoud L., Jacob M. Structural study of the 5' end of a synthetic premessenger RNA from adenovirus. Evidence for a long-range exon-intron interaction. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 15;240(3):205–225. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E. S., Morse D. P., Brown J. W., Schmidt F. J., Pace N. R. Long-range structure in ribonuclease P RNA. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):853–856. doi: 10.1126/science.1719634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Gold L. Selection of the initiator tRNA by Escherichia coli initiation factors. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1899–1912. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Klug A. Crystallographic refinement of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA at 2-5A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 25;108(4):619–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Multiple exon-binding sites in class II self-splicing introns. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage P., Chiaruttini C., Graffe M., Dondon J., Milet M., Springer M. Messenger RNA secondary structure and translational coupling in the Escherichia coli operon encoding translation initiation factor IF3 and the ribosomal proteins, L35 and L20. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):366–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90827-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage P., Truong H. N., Graffe M., Dondon J., Springer M. Translated translational operator in Escherichia coli. Auto-regulation in the infC-rpmI-rplT operon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Stern S., Noller H. F. Rapid chemical probing of conformation in 16 S ribosomal RNA and 30 S ribosomal subunits using primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moine H., Romby P., Springer M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNA(Thr) modulate the binding of the ribosome to the translational initiation site of the thrS mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Eyermann F., Bénard L., Portier C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Ribosomal protein S15 from Escherichia coli modulates its own translation by trapping the ribosome on the mRNA initiation loading site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Portier C., Mougel M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Target site of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S15 on its messenger RNA. Conformation and interaction with the protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90362-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Bosch L. RNA pseudoknots: structure, detection, and prediction. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:289–303. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Seeman N. C., Suddath F. L., Rich A., Sussman J. L., Kim S. H. Hydrogen bonding in yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4866–4870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding G., Gluick T. C., Draper D. E. Ribosome initiation complex formation with the pseudoknotted alpha operon messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 5;229(3):609–622. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M., Graffe M., Butler J. S., Grunberg-Manago M. Genetic definition of the translational operator of the threonine-tRNA ligase gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M., Plumbridge J. A., Butler J. S., Graffe M., Dondon J., Mayaux J. F., Fayat G., Lestienne P., Blanquet S., Grunberg-Manago M. Autogenous control of Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase expression in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. K., Draper D. E. Unusual mRNA pseudoknot structure is recognized by a protein translational repressor. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheimer S. J., Klotsky R. A., Schwartz I. Transcriptional patterns for the thrS-infC-rplT operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90534-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Dumas P., Moras D. Crystallographic refinement of yeast aspartic acid transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):119–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Morrissey L., Gauss P., Gold L., Hsu T., Karam J. Bacteriophage T4 regA protein binds to mRNAs and prevents translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7822–7826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witherell G. W., Gott J. M., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific interaction between RNA phage coat proteins and RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:185–220. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60842-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Diverse mechanisms for regulating ribosomal protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1994;47:331–370. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Himbergen J., van Geffen B., van Duin J. Translational control by a long range RNA-RNA interaction; a basepair substitution analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1713–1717. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]