Abstract
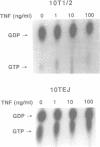
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) exerts cytotoxicity on many types of tumor cells but not on normal cells. The molecular events leading to cell death triggered by TNF are still poorly understood. Our previous studies have shown that enforced expression of an activated H-ras oncogene converted non-tumorigenic, TNF-resistant C3H 10T1/2 fibroblasts into tumorigenic cells that also became very sensitive to TNF-induced apoptosis. This finding suggested that Ras activation may play a role in TNF-induced apoptosis. In this study we investigated whether Ras activation is an obligatory step in TNF-induced apoptosis. Introduction of two different molecular antagonists of Ras, the rap1A tumor suppressor gene or the dominant-negative rasN17 gene, into H-ras-transformed 10TEJ cells inhibited TNF-induced apoptosis. Similar results were obtained with L929 cells, a fibroblast cell line sensitive to TNF-induced apoptosis, which does not have a ras mutation. While Ras is constitutively activated in TNF-sensitive 10TEJ cells, TNF treatment increased Ras-bound GTP in TNF-sensitive L929 cells but not in TNF-resistant 10T1/2 cells. Moreover, RasN17 expression blocked TNF-induced Ras-GTP formation in L929 cells. These results demonstrate that Ras activation is required for TNF-induced apoptosis in mouse fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., McGregor A. H., Toft N. J., Brown E. J., Wyllie A. H. Susceptibility to apoptosis is differentially regulated by c-myc and mutated Ha-ras oncogenes and is associated with endonuclease availability. Br J Cancer. 1993 Dec;68(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyaert R., Fiers W. Molecular mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity. What we do understand and what we do not. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Holskin B., Strickler J., Gorniak J., Clark M. A., Johnson P. J., Mitcho M., Shalloway D. Induction by E1A oncogene expression of cellular susceptibility to lysis by TNF. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):581–583. doi: 10.1038/330581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. M., Sun X. M., Fearnhead H., MacFarlane M., Brown D. G., Snowden R. T., Dinsdale D. Formation of large molecular weight fragments of DNA is a key committed step of apoptosis in thymocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Rubinfeld B., Albert I., McCormick F. RapV12 antagonizes Ras-dependent activation of ERK1 and ERK2 by LPA and EGF in Rat-1 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3475–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dbaibo G. S., Obeid L. M., Hannun Y. A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) signal transduction through ceramide. Dissociation of growth inhibitory effects of TNF-alpha from activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17762–17766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Chen P. W., Ananthaswamy H. N. ras-induced neoplastic transformation and sensitivity to tumor necrosis factor. Anticancer Res. 1994 Nov-Dec;14(6B):2649–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Fosdick L. J., Marin M. C., Diaz C., McDonnell T. J., Ananthaswamy H. N., McConkey D. J. Differential regulation of endogenous endonuclease activation in isolated murine fibroblast nuclei by ras and bcl-2. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):769–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Marin M. C., McDonnell T., Ananthaswamy H. N. Differential sensitivity of normal and Ha-ras-transformed C3H mouse embryo fibroblasts to tumor necrosis factor: induction of bcl-2, c-myc, and manganese superoxide dismutase in resistant cells. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):2009–2017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Leblanc J., Youdale T., Sikorska M., Walker P. R. Periodicity of DNA folding in higher order chromatin structures. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1319–1327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens V., Grooten J., De Vos K., Fiers W. Direct evidence for tumor necrosis factor-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen intermediates and their involvement in cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8115–8119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. M., Reade J. L., Ware C. F. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell viability: application to the quantitation of cytotoxic and growth inhibitory lymphokines. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 25;70(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Bissonnette R., Mahboubi A., Martin S., Nishioka W., Brunner T., Baier G., Baier-Bitterlich G., Byrd C., Lang F. FAS-induced apoptosis is mediated via a ceramide-initiated RAS signaling pathway. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):341–351. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Lewis G. D., Shalaby M. R., Eessalu T. E., Aggarwal B. B., Ullrich A., Shepard H. M. Amplified expression of the HER2/ERBB2 oncogene induces resistance to tumor necrosis factor alpha in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5102–5106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. Y., Linardic C., Obeid L., Hannun Y. Identification of sphingomyelin turnover as an effector mechanism for the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha and gamma-interferon. Specific role in cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):484–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. Genetic analysis of the Kirsten-ras-revertant 1 gene: potentiation of its tumor suppressor activity by specific point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4284–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama H., Sugimoto Y., Matsuzaki T., Ikawa Y., Noda M. A ras-related gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Jondal M., Orrenius S. Inhibition of DNA fragmentation in thymocytes and isolated thymocyte nuclei by agents that stimulate protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13399–13402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obeid L. M., Linardic C. M., Karolak L. A., Hannun Y. A. Programmed cell death induced by ceramide. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1769–1771. doi: 10.1126/science.8456305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizon V., Chardin P., Lerosey I., Olofsson B., Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam L. A., Der C. J., Clark R., O'Rourke E. C., Zhang K., McCormick F., Bokoch G. M. Biochemical characterization of baculovirus-expressed rap1A/Krev-1 and its regulation by GTPase-activating proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee P., Lee J. K., Leung C. C., Raffin T. A. TNF-alpha induces tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in adherent human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4785–4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S., Bollon A. P. Tumor necrosis factor activities and cancer therapy--a perspective. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Jan;57(1):79–128. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90037-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluss H. K., Barrett T., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor mediated by JNK protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8376–8384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Feig L. A., Gibbs J. B. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants selectively inhibit the activity of either cellular or oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4053–4064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Ishihara M., Kitagawa M., Harada H., Kimura T., Matsuyama T., Lamphier M. S., Aizawa S., Mak T. W., Taniguchi T. Cellular commitment to oncogene-induced transformation or apoptosis is dependent on the transcription factor IRF-1. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Ayres T. M., Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):845–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Weber R. F., Figari I. S., Reynolds C., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. The two different receptors for tumor necrosis factor mediate distinct cellular responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9292–9296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J., Agostinis P., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W., Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates multiple serine/threonine protein kinases in Swiss 3T3 and L929 cells. Implication of casein kinase-2 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases in the tumor necrosis factor signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25916–25921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vietor I., Schwenger P., Li W., Schlessinger J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation and increased tyrosine phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18994–18999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Rose K. A., Morris R. G., Steel C. M., Foster E., Spandidos D. A. Rodent fibroblast tumours expressing human myc and ras genes: growth, metastasis and endogenous oncogene expression. Br J Cancer. 1987 Sep;56(3):251–259. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao B., Zhang Y., Delikat S., Mathias S., Basu S., Kolesnick R. Phosphorylation of Raf by ceramide-activated protein kinase. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):307–310. doi: 10.1038/378307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]