Abstract
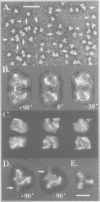
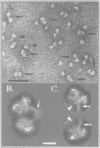
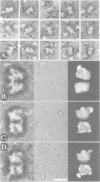
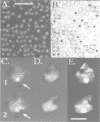
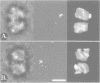
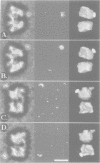
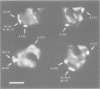
Immunoelectron microscopy was used to determine the spatial organization of the yeast RNA polymerase I core subunits on a three-dimensional model of the enzyme. Images of antibody-labeled enzymes were compared with the native enzyme to determine the localization of the antibody binding site on the surface of the model. Monoclonal antibodies were used as probes to identify the two largest subunits homologous to the bacterial beta and beta' subunits. The epitopes for the two monoclonal antibodies were mapped using subunit-specific phage display libraries, thus allowing a direct correlation of the structural data with functional information on conserved sequence elements. An epitope close to conserved region C of the beta-like subunit is located at the base of the finger-like domain, whereas a sequence between conserved regions C and D of the beta'-like subunit is located in the apical region of the enzyme. Polyclonal antibodies outlined the alpha-like subunit AC40 and subunit AC19 which were found co-localized also in the apical region of the enzyme. The spatial location of the subunits is correlated with their biological activity and the inhibitory effect of the antibodies.
Full text
PDF

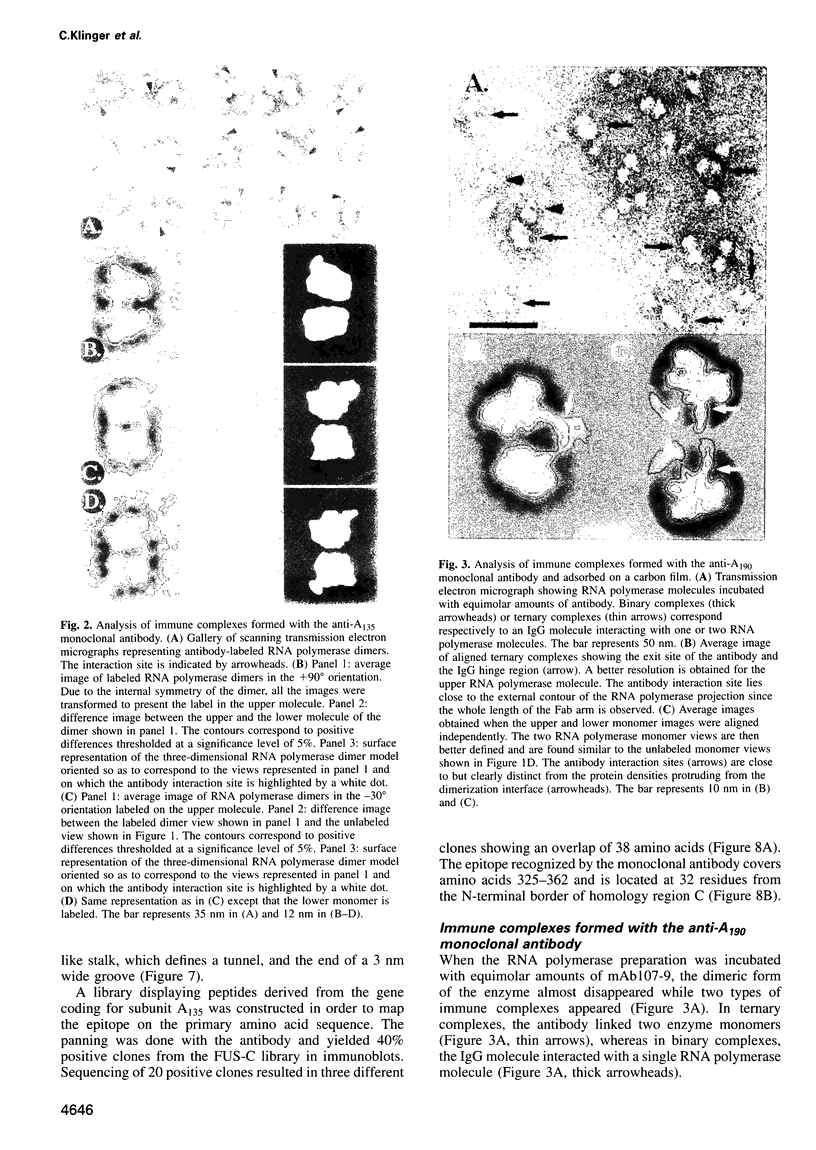

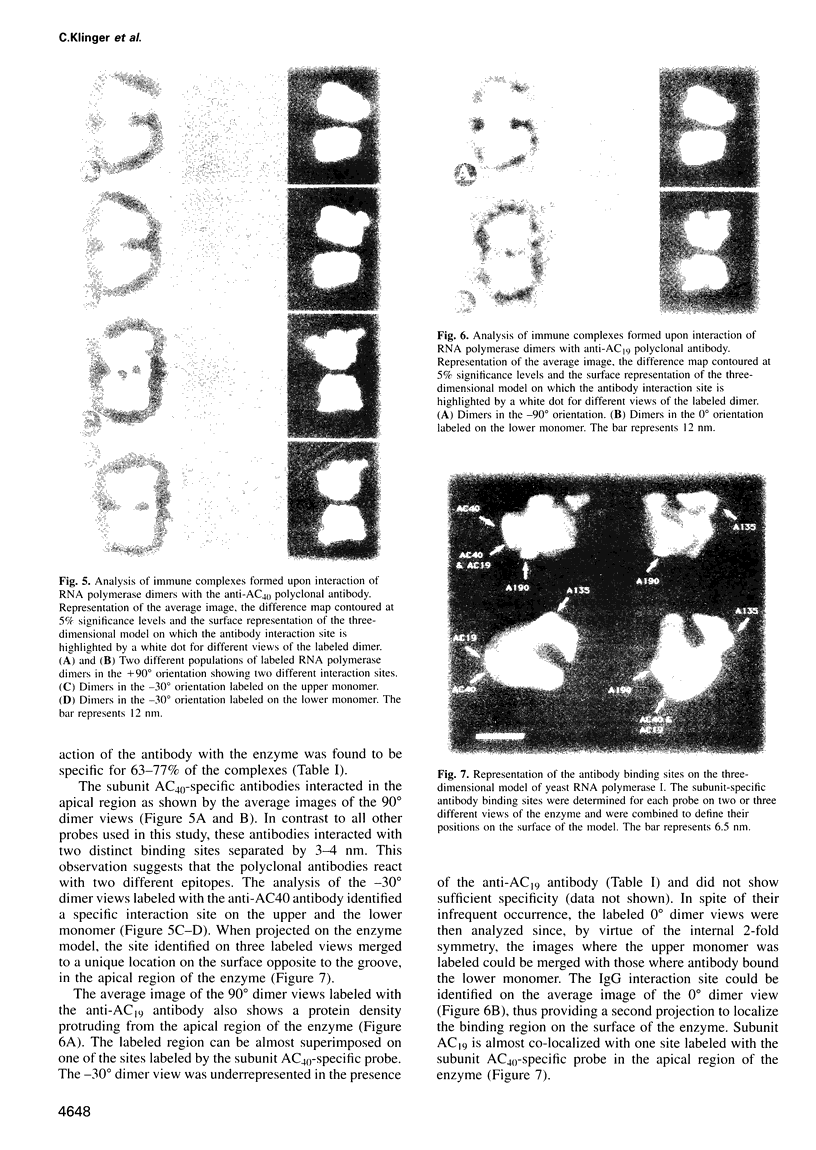





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Durkovich D., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Orientation and topography of RNA polymerase III in transcription complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):942–952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Corden J. L. Localization of an alpha-amanitin resistance mutation in the gene encoding the largest subunit of mouse RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):586–594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ross W., Tang H., Gourse R. L., Ebright R. H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase alpha subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boisset N., Radermacher M., Grassucci R., Taveau J. C., Liu W., Lamy J., Frank J., Lamy J. N. Three-dimensional immunoelectron microscopy of scorpion hemocyanin labeled with a monoclonal Fab fragment. J Struct Biol. 1993 Nov-Dec;111(3):234–244. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1993.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréant B., Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Analysis of yeast RNA polymerases with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler J. M., Huet J., Davies K. E., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Immunological studies of yeast nuclear RNA polymerases at the subunit level. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9949–9954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. A mutation in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II alters RNA chain elongation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13190–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Ahlers M., Meller P. H., Kubalek E. W., Blankenburg R., Ribi H. O., Ringsdorf H., Kornberg R. D. Two-dimensional crystals of streptavidin on biotinylated lipid layers and their interactions with biotinylated macromolecules. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):387–396. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82232-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Edwards A. M., Kubalek E. W., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of yeast RNA polymerase II at 16 A resolution. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90144-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Kubalek E. W., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme determined by electron crystallography. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):730–732. doi: 10.1038/340730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequard-Chablat M., Riva M., Carles C., Sentenac A. RPC19, the gene for a subunit common to yeast RNA polymerases A (I) and C (III). J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15300–15307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieci G., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Lukhtanov E., Thuriaux P., Werner M., Sentenac A. A universally conserved region of the largest subunit participates in the active site of RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3766–3776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Kolocheva T. I., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A. Studies on the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Highly selective affinity labelling by analogues of initiating substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):113–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F., Abdukayumov M. N., Rabinov I. V., Richter V. I., Skoblov Y. S., Chistyakov P. G. Studies of the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. A method for localization of the sites of affinity labelling. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundelfinger E. D. Interaction of nucleic acids with the DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of Drosophila. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekmatpanah D. S., Young R. A. Mutations in a conserved region of RNA polymerase II influence the accuracy of mRNA start site selection. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5781–5791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Conformational change of DNA binding subunit of RNA polymerase II on binding to DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Phalente L., Buttin G., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Probing yeast RNA polymerase A subunits with monospecific antibodies. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1193–1198. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Riva M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Yeast RNA polymerase C and its subunits. Specific antibodies as structural and functional probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15304–15310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Schnabel R., Sentenac A., Zillig W. Archaebacteria and eukaryotes possess DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of a common type. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1291–1294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Whelen S., Hall B. D. The RET1 gene of yeast encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase III. Structural analysis of the wild-type and ret1-1 mutant alleles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5616–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB3 is an essential component of the mRNA transcription apparatus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5387–5394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontermann R. E., Bautz E. K. Nucleic acid-binding regions of the second-largest subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II identified by southwestern blotting. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 16;344(2-3):166–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontermann R. E., Kobor M., Bautz E. K. Identification of a nucleic acid-binding region within the largest subunit of Drosophila melanogaster RNA polymerase II. Protein Sci. 1993 Feb;2(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalo D., Carles C., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Interactions between three common subunits of yeast RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Stewart J., Lee D. N. Amino acid changes in conserved regions of the beta-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alter transcription pausing and termination. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1623–1636. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K., Hanna M. M. NusA interferes with interactions between the nascent RNA and the C-terminal domain of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli transcription complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5012–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K., Zhang Y., Severinov K., Das A., Hanna M. M. Role of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit in modulation of pausing, termination and anti-termination by the transcription elongation factor NusA. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):150–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti M., Noah M., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Stöffler G. Localization of proteins L4, L5, L20 and L25 on the ribosomal surface by immuno-electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):245–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00334363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Buhler J. M., Treich I., Sentenac A. RPC40, a unique gene for a subunit shared between yeast RNA polymerases A and C. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W. A conjugation-specific gene (cnjC) from Tetrahymena encodes a protein homologous to yeast RNA polymerase subunits (RPB3, RPC40) and similar to a portion of the prokaryotic RNA polymerase alpha subunit (rpoA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2953–2960. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Heumann H. A cinematographic view of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2745–2754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Gouy M., Marck C., Sentenac A., Buhler J. M. RPA190, the gene coding for the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2830–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G., Song D., Hügle-Dörr B., Oldenburg I., Bautz E. K. Mapping of linear epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies with gene-fragment phage display libraries. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Dec 10;249(4):425–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00287104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov A., Severinova E., Darst S. A. Three-dimensional structure of E. coli core RNA polymerase: promoter binding and elongation conformations of the enzyme. Cell. 1995 Nov 3;83(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva M., Schäffner A. R., Sentenac A., Hartmann G. R., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F., Grachev M. A. Active site labeling of the RNA polymerases A, B, and C from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14377–14380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Maguire K. A., Wurpel J. N., Stetler D. A., Márquez E. D. Monoclonal antibodies directed against mammalian RNA polymerase I. Identification of the catalytic center. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12976–12981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J. Alpha: the Cinderella subunit of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14515–14518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Martin C., Nonet M., Podos S., Okamura S., Young R. A. Conditional mutations occur predominantly in highly conserved residues of RNA polymerase II subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1270–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P., Célia H., Riva M., Darst S. A., Colin P., Kornberg R. D., Sentenac A., Oudet P. Structural study of the yeast RNA polymerase A. Electron microscopy of lipid-bound molecules and two-dimensional crystals. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P., Célia H., Riva M., Sentenac A., Oudet P. Three-dimensional model of yeast RNA polymerase I determined by electron microscopy of two-dimensional crystals. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2601–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P., Nobelis P., Colin P., Louys M., Huet J., Sentenac A., Oudet P. Electron microscopic study of yeast RNA polymerase A: analysis of single molecular images. Chromosoma. 1990 Jul;99(3):196–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01731130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P., Scott J. K. Libraries of peptides and proteins displayed on filamentous phage. Methods Enzymol. 1993;217:228–257. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)17065-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sousa R., Chung Y. J., Rose J. P., Wang B. C. Crystal structure of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase at 3.3 A resolution. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):593–599. doi: 10.1038/364593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sousa R., Rose J., Wang B. C. The thumb's knuckle. Flexibility in the thumb subdomain of T7 RNA polymerase is revealed by the structure of a chimeric T7/T3 RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 18;244(1):6–12. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tichelaar W., Schutter W. G., Arnberg A. C., van Bruggen E. F., Stender W. The quaternary structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase studied with (scanning) transmission (immuno)electron microscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):263–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Carles C., Sentenac A., Riva M. Determination of lysine residues affinity labeled in the active site of yeast RNA polymerase II(B) by mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4721–4725. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Riva M., Sentenac A. Zinc-binding subunits of yeast RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21971–21976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weilbaecher R., Hebron C., Feng G., Landick R. Termination-altering amino acid substitutions in the beta' subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase identify regions involved in RNA chain elongation. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 1;8(23):2913–2927. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.23.2913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Kolb J. M., Dodd J., Yamagishi M., Mémet S., Buhler J. M., Nomura M. Conditional expression of RPA190, the gene encoding the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase I: effects of decreased rRNA synthesis on ribosomal protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2049–2059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., McKune K., Lane W. S., Young R. A. Yeast RNA polymerase II subunit RPB11 is related to a subunit shared by RNA polymerase I and III. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Nomura M. Suppressor analysis of temperature-sensitive mutations of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a suppressor gene encodes the second-largest subunit of RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):754–764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Ishihama A. Genetics of bacterial RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:59–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mercoyrol L., Job C., Job D. Studies on the inhibition by alpha-amanitin of single-step addition reactions and productive RNA synthesis catalysed by wheat-germ RNA polymerase II. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):165–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2580165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heel M., Frank J. Use of multivariate statistics in analysing the images of biological macromolecules. Ultramicroscopy. 1981;6(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(81)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]