Abstract
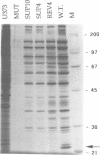
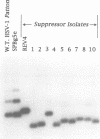
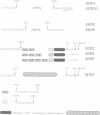
Novel suppressor variants of conditionally lethal HSV-1 gamma34.5 deletion mutants have been isolated which exhibit restored ability to grow on neoplastic neuronal cells. Deletion of the viral gamma34.5 genes, whose products share functional similarity with the cellular GADD34 gene, renders the virus non-neurovirulent and imposes a block to viral replication in neuronal cells. Protein synthesis ceases at late times post-infection and the translation initiation factor eIF2alpha is phosphorylated by the cellular PKR kinase [Chou et al. (1990) Science, 252, 1262-1266; (1995) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 10516-10520]. The suppressor mutants have overcome the translational block imposed by PKR. Multiple, independent isolates all contain rearrangements within a 595 bp element in the HSV-1 genome where the unique short component joins the terminal repeats. This alteration, which affects the production of the viral mRNA and protein from the Us11 and Us12 genes, is both necessary and sufficient to confer the suppressor phenotype on gamma34.5 mutant viruses. HSV-1 thus encodes a specific element which inhibits ongoing protein synthesis in the absence of the viral GADD34-like function. Since this inhibition involves the accumulation of phosphorylated eIF2alpha, the element identified by the suppressor mutations may be a discrete PKR activator. Activation of the PKR kinase thus does not proceed through a general, cellular 'antiviral' sensing mechanism. Instead, the virus deliberately activates PKR and encodes a separate function which selectively prevents the phosphorylation of at least one PKR target, eIF2alpha. The nature of this potential activator element, and how analogous cellular elements could affect PKR pathways which affect growth arrest and differentiation are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie E., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus-encoded eIF-2 alpha homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus can functionally substitute for the virus-associated RNAs in the lytic growth of adenovirus 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4789–4793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Barber G. N., Katze M. G. Degradation of the interferon-induced 68,000-M(r) protein kinase by poliovirus requires RNA. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.791-800.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolovan C. A., Sawtell N. M., Thompson R. L. ICP34.5 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 strain 17syn+ are attenuated for neurovirulence in mice and for replication in confluent primary mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.48-55.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Harland J. Three mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: one lacking the genes US10, US11 and US12 and two in which Rs has been extended by 6 kb to 0.91 map units with loss of Us sequences between 0.94 and the Us/TRs junction. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Watson J. C., Jacobs B. L. The E3L gene of vaccinia virus encodes an inhibitor of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4825–4829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Chen J. J., Gross M., Roizman B. Association of a M(r) 90,000 phosphoprotein with protein kinase PKR in cells exhibiting enhanced phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 alpha and premature shutoff of protein synthesis after infection with gamma 134.5- mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10516–10520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Kern E. R., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2173860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 gamma(1)34.5 gene function, which blocks the host response to infection, maps in the homologous domain of the genes expressed during growth arrest and DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5247–5251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The gamma 1(34.5) gene of herpes simplex virus 1 precludes neuroblastoma cells from triggering total shutoff of protein synthesis characteristic of programed cell death in neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3266–3270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Chang H. W., Jacobs B. L., Kaufman R. J. The E3L and K3L vaccinia virus gene products stimulate translation through inhibition of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1688–1692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1688-1692.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donzé O., Jagus R., Koromilas A. E., Hershey J. W., Sonenberg N. Abrogation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 phosphorylation causes malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3828–3834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr Mammalian genes induced by radiation; activation of genes associated with growth control. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:507–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 stimulates protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro: relationship between structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11557–11561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Chou J., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Roizman B. The carboxyl terminus of the murine MyD116 gene substitutes for the corresponding domain of the gamma(1)34.5 gene of herpes simplex virus to preclude the premature shutoff of total protein synthesis in infected human cells. J Virol. 1996 Jan;70(1):84–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.1.84-90.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Jugovic P., York I., Russ G., Bennink J., Yewdell J., Ploegh H., Johnson D. Herpes simplex virus turns off the TAP to evade host immunity. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):411–415. doi: 10.1038/375411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A. Molecular controls of apoptosis: differentiation/growth arrest primary response genes, proto-oncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes as positive & negative modulators. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):1807–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., MacLean C., Marsden H. S., Dalziel R. G., Everett R. D. The product of gene US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 is expressed as a true late gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):871–883. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G. Regulation of the interferon-induced PKR: can viruses cope? Trends Microbiol. 1995 Feb;3(2):75–78. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(00)88880-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Tumor-suppressor genes: news about the interferon connection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5893–5895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. M., Shatkin A. J. Translational stimulation by reovirus polypeptide sigma 3: substitution for VAI RNA and inhibition of phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6878–6884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6878-6884.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean A. R., ul-Fareed M., Robertson L., Harland J., Brown S. M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 deletion variants 1714 and 1716 pinpoint neurovirulence-related sequences in Glasgow strain 17+ between immediate early gene 1 and the 'a' sequence. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):631–639. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra R. K., McMillan N. A., Desai S., McSwiggen J., Hovanessian A. G., Sen G., Williams B. R., Silverman R. H. HIV-1 TAR RNA has an intrinsic ability to activate interferon-inducible enzymes. Virology. 1994 Nov 1;204(2):823–827. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Barnett B. C. Neurovirulence factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):609–609. doi: 10.1038/353609b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Galabru J., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Hovanessian A. G. Tumor suppressor function of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama Y., Kurachi R., Daikoku T., Umene K. The US 9, 10, 11, and 12 genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 are of no importance for its neurovirulence and latency in mice. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):419–423. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H., Davies M. V., Langland J. O., Chang H. W., Nam Y. S., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E., Jacobs B. L., Kaufman R. J., Venkatesan S. TAR RNA-binding protein is an inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase PKR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Detection of activated double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3-F442A cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 RNA-binding protein US11 negatively regulates the accumulation of a truncated viral mRNA. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5873–5879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5873-5879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 RNA binding protein US11 is a virion component and associates with ribosomal 60S subunits. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3624-3632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus Us11 open reading frame encodes a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3463–3470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3463-3470.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T. V., Schwemmle M., Jeffrey I., Laing K., Mellor H., Proud C. G., Hilse K., Clemens M. J. Comparative analysis of the regulation of the interferon-inducible protein kinase PKR by Epstein-Barr virus RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 and adenovirus VAI RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4483–4490. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. D., Lu Z., Kutish G., Afonso C. L., Roberts P., Rock D. L. Identification of an African swine fever virus gene with similarity to a myeloid differentiation primary response gene and a neurovirulence-associated gene of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5586–5589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5586-5589.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Conversion of a fraction of the unique sequence to part of the inverted repeats in the S component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Lord K. A., Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C., Carrier F., Ron D., Kohn K. W., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A., Fornace A. J., Jr The gadd and MyD genes define a novel set of mammalian genes encoding acidic proteins that synergistically suppress cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2361–2371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]