Abstract
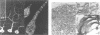
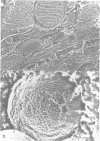
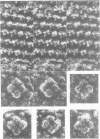
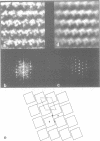
We used quick-freeze deep-etch replica electron microscopy to visualize the native structure of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) in the cell. In the dendrites of Purkinje neurons of bovine cerebellum there were many vesicular organelles whose surfaces were covered with a two-dimensional crystalline array of molecules. Detailed examination of the cytoplasmic true surface of such vesicles in replica revealed that the structural unit, identified as IP3R by immunocytochemistry and subsequent Fourier analysis, is a square-shaped assembly and is aligned so that the side of the square is inclined by approximately 20 degrees from the row-line of the lattice. Comparison with the ryanodine receptor (RyaR), another intracellular Ca2+ channel on the endoplasmic reticulum, suggested that IP3R, unlike RyaR, has a very compact structure, potentially reflecting the crucial difference in the function of the cytoplasmic portion of the molecule.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block B. A., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C. Structural evidence for direct interaction between the molecular components of the transverse tubule/sarcoplasmic reticulum junction in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2587–2600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Hardwicke P. M. Crystalline structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum from scallop. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Hardwicke P. M., Vibert P. Dimer ribbons in the three-dimensional structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):579–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick C. C., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation and characterization of the inositol trisphosphate receptor from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Two-dimensional arrays of proteins in sarcoplasmic reticulum and purified Ca2+-ATPase vesicles treated with vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2599–2603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Watras J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):583–586. doi: 10.1038/336583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Deerinck T. J., Ouyang Y., Beck C. F., Tanksley S. J., Walton P. D., Airey J. A., Sutko J. L. Identification and localization of ryanodine binding proteins in the avian central nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Aug;5(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Nunzi G. Junctional feet and particles in the triads of a fast-twitch muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1983 Apr;4(2):233–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00712033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Kohda K., Miyawaki A., Mikoshiba K. Intracellular channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERNDON R. M. LAMELLAR BODIES, AN UNUSUAL ARRANGEMENT OF THE GRANULAR ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:338–342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A. Lamellar bodies in Purkinje nerve cells experimentally induced by electric field. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E. Procedure for freeze-drying molecules adsorbed to mica flakes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):155–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Protocol for 3-D visualization of molecules on mica via the quick-freeze, deep-etch technique. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Nov;13(3):244–263. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060130310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota J., Michikawa T., Miyawaki A., Takahashi M., Tanzawa K., Okura I., Furuichi T., Mikoshiba K. Adenophostin-medicated quantal Ca2+ release in the purified and reconstituted inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 17;368(2):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00659-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama E., Nonomura Y. Electron microscopic analysis of tropomyosin paracrystals. J Biochem. 1979 Nov;86(5):1511–1522. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama E., Shiraishi T., Oosawa K., Baba N., Aizawa S. Geometry of the flagellar motor in the cytoplasmic membrane of Salmonella typhimurium as determined by stereo-photogrammetry of quick-freeze deep-etch replica images. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jan 26;255(3):458–475. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama E. The effects of various nucleotides on the structure of actin-attached myosin subfragment-1 studied by quick-freeze deep-etch electron microscopy. J Biochem. 1989 Nov;106(5):751–770. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G., Futatsugi A., Niinobe M., Nakanishi S., Mikoshiba K. Two types of ryanodine receptors in mouse brain: skeletal muscle type exclusively in Purkinje cells and cardiac muscle type in various neurons. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1133–1142. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90071-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesser K. E., Castellani L., Franzini-Armstrong C. Dispositions of junctional feet in muscles of invertebrates. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1992 Apr;13(2):161–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01874153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Kawasaki T., Nakade S., Yokota N., Taguchi T., Kasai M., Mikoshiba K. Structural and functional characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor channel from mouse cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1109–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Niinobe M., Mikoshiba K. A cerebellar Purkinje cell marker P400 protein is an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor protein. Purification and characterization of InsP3 receptor complex. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Darling E., Eveleth J. Kinetics of rapid Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and adenine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller K. Ultrastructural aspects of rapid-frozen, deep-etched and rotary-shadowed synaptosomes. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;231(2):347–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00222186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Südhof T. C. Structure and expression of the rat inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12679–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Furuichi T., Miyawaki A. Structure and function of IP3 receptors. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;5(4):273–281. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. P., Katayama E., Squire J. M. Evaluation of high-resolution shadowing applied to freeze-fractured, deep-etched particles: 3-D helical reconstruction of shadowed actin filaments. J Struct Biol. 1994 Jul-Aug;113(1):47–55. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1994.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakade S., Rhee S. K., Hamanaka H., Mikoshiba K. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of an immunoaffinity-purified homotetrameric inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (type I) increases Ca2+ flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6735–6742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu H., Yamamoto A., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K., Tashiro Y. Immunogold localization of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor in mouse cerebellar Purkinje cells using three monoclonal antibodies. Cell Struct Funct. 1990 Jun;15(3):163–173. doi: 10.1247/csf.15.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Rizzuto R., Volpe P., Meldolesi J. Molecular and cellular physiology of intracellular calcium stores. Physiol Rev. 1994 Jul;74(3):595–636. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher M., Rao V., Grassucci R., Frank J., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Wagenknecht T. Cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction of the calcium release channel/ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):411–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusakov D. A., Podini P., Villa A., Meldolesi J. Tridimensional organization of Purkinje neuron cisternal stacks, a specialized endoplasmic reticulum subcompartment rich in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. J Neurocytol. 1993 Apr;22(4):273–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01187126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Inui M., Radermacher M., Frank J., Fleischer S. Ultrastructure of the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Mignery G. A., Mugnaini E., Südhof T. C., De Camilli P. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor causes formation of ER cisternal stacks in transfected fibroblasts and in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei K., Stukenbrok H., Metcalf A., Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C., Volpe P., De Camilli P. Ca2+ stores in Purkinje neurons: endoplasmic reticulum subcompartments demonstrated by the heterogeneous distribution of the InsP3 receptor, Ca(2+)-ATPase, and calsequestrin. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):489–505. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00489.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Dux L., Martonosi A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of negatively stained crystals of the Ca2+-ATPase from muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Sasabe H., Stokes D. L. Three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy of the calcium ion pump in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):467–471. doi: 10.1038/362469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of membrane-bound ribosomes obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):118–122. doi: 10.1038/269118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa A., Podini P., Clegg D. O., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Intracellular Ca2+ stores in chicken Purkinje neurons: differential distribution of the low affinity-high capacity Ca2+ binding protein, calsequestrin, of Ca2+ ATPase and of the ER lumenal protein, Bip. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):779–791. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton P. D., Airey J. A., Sutko J. L., Beck C. F., Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H. Ryanodine and inositol trisphosphate receptors coexist in avian cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1145–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watras J., Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated channels in cerebellum: presence of multiple conductance states. J Neurosci. 1991 Oct;11(10):3239–3245. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-10-03239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Otsu H., Yoshimori T., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K., Tashiro Y. Stacks of flattened smooth endoplasmic reticulum highly enriched in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor in mouse cerebellar Purkinje cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1991 Oct;16(5):419–432. doi: 10.1247/csf.16.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]