Abstract
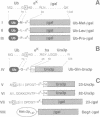
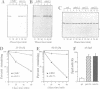
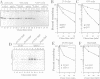
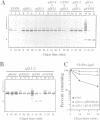
A library of random 10 residue peptides fused to the N-terminus of a reporter protein was screened in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae for sequences that can target the reporter for degradation by the N-end rule pathway, a ubiquitin (Ub)-dependent proteolytic system that recognizes potential substrates through binding to their destabilizing N-terminal residues. One of the N-terminal sequences identified by this screen was used in a second screen for mutants incapable of degrading the corresponding reporter fusion. A mutant thus identified had an abnormally low content of free Ub. This mutant was found to be allelic to a previously isolated mutant in a Ub-dependent proteolytic system distinct from the N-end rule pathway. We isolated the gene involved, termed UFD3, which encodes an 80 kDa protein containing tandem repeats of a motif that is present in many eukaryotic proteins and called the WD repeat. Both co-immunoprecipitation and two-hybrid assays demonstrated that Ufd3p is an in vivo ligand of Cdc48p, an essential ATPase required for the cell cycle progression and the fusion of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Further, we showed that, similarly to Ufd3p, Cdc48p is also required for the Ub-dependent proteolysis of test substrates. The discovery of the Ufd3p--Cdc48p complex and the finding that this complex is a part of the Ub system open up a new direction for studies of the function of Ub in the cell cycle and membrane dynamics.
Full text
PDF


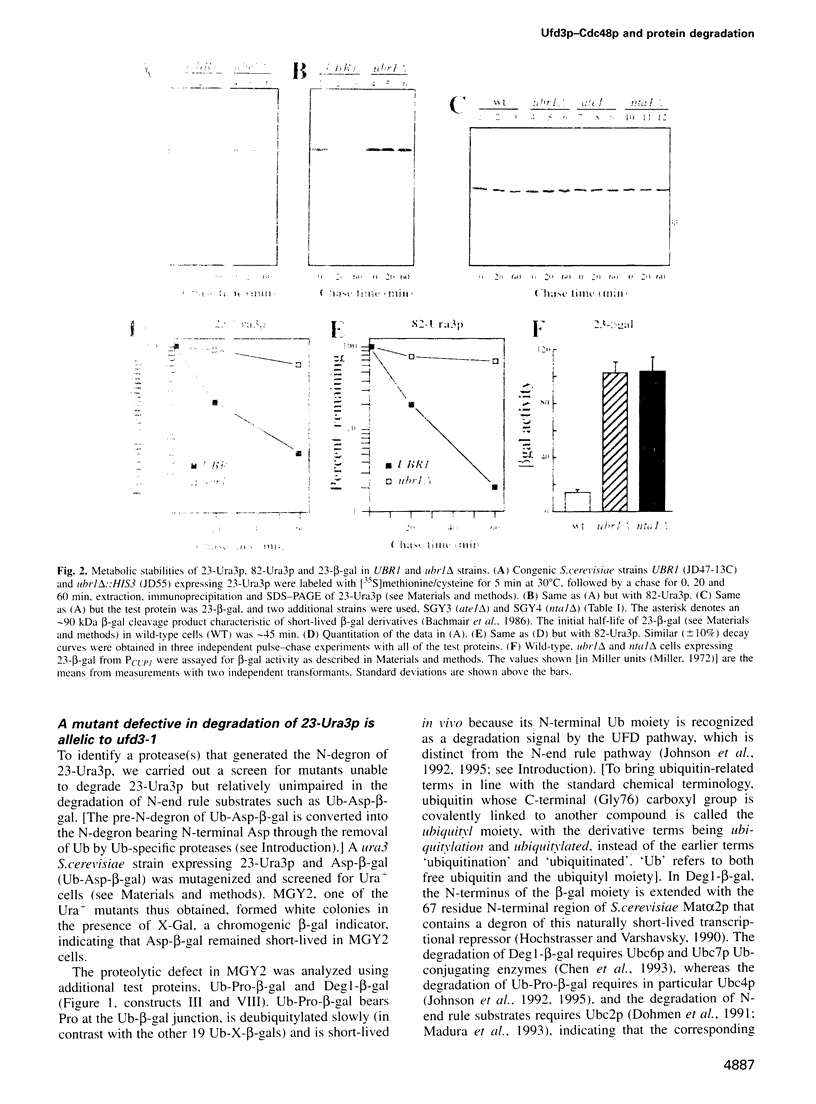












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmair A., Varshavsky A. The degradation signal in a short-lived protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1019–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Tobias J. W., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin-specific proteases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cloning of UBP2 and UBP3, and functional analysis of the UBP gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23364–23375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barral Y., Jentsch S., Mann C. G1 cyclin turnover and nutrient uptake are controlled by a common pathway in yeast. Genes Dev. 1995 Feb 15;9(4):399–409. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.4.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizzard B. L., Chubet R. G., Vizard D. L. Immunoaffinity purification of FLAG epitope-tagged bacterial alkaline phosphatase using a novel monoclonal antibody and peptide elution. Biotechniques. 1994 Apr;16(4):730–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Teichert U., Smith J. A. Molecular cloning, sequencing, deletion, and overexpression of a methionine aminopeptidase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8007–8011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1576–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2538923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Johnson P., Sommer T., Jentsch S., Hochstrasser M. Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90426-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Ozgür L. E., Conway T. M., Dispoto J., Crooke S. T., Bomalaski J. S. Cloning of a phospholipase A2-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5418–5422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. J., Jeffrey L. C., Kasperek E., Pickart C. M. Structure of tetraubiquitin shows how multiubiquitin chains can be formed. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 18;236(2):601–609. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J. Make it or break it: the role of ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis in cellular regulation. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;5(11):428–434. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Madura K., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule is mediated by the UBC2(RAD6) ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Stappen R., McGrath J. P., Forrová H., Kolarov J., Goffeau A., Varshavsky A. An essential yeast gene encoding a homolog of ubiquitin-activating enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):18099–18109. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.18099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohmen R. J., Wu P., Varshavsky A. Heat-inducible degron: a method for constructing temperature-sensitive mutants. Science. 1994 Mar 4;263(5151):1273–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.8122109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubiel W., Ferrell K., Rechsteiner M. Peptide sequencing identifies MSS1, a modulator of HIV Tat-mediated transactivation, as subunit 7 of the 26 S protease. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 1;323(3):276–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Alexandraki D., André B., Ansorge W., Baladron V., Ballesta J. P., Banrevi A., Bolle P. A., Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Bossier P. Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome XI. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):371–378. doi: 10.1038/369371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann R., Wiebel F. F., Flessau A., Rytka J., Beyer A., Fröhlich K. U., Kunau W. H. PAS1, a yeast gene required for peroxisome biogenesis, encodes a member of a novel family of putative ATPases. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90234-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler H. S., Desprez T., Santoni V., Kronenberger J., Caboche M., Traas J. The higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a functional CDC48 homologue which is highly expressed in dividing and expanding cells. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5626–5637. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilotter H. E., Hannon G. J., Ruddell C. J., Beach D. Construction of an improved host strain for two hybrid screening. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1502–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Hurley J. B., Hopkins R. S., Miake-Lye R., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F., Simon M. I. Repetitive segmental structure of the transducin beta subunit: homology with the CDC4 gene and identification of related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich K. U., Fries H. W., Rüdiger M., Erdmann R., Botstein D., Mecke D. Yeast cell cycle protein CDC48p shows full-length homology to the mammalian protein VCP and is a member of a protein family involved in secretion, peroxisome formation, and gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):443–453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghislain M., Udvardy A., Mann C. S. cerevisiae 26S protease mutants arrest cell division in G2/metaphase. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):358–362. doi: 10.1038/366358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Bachmair A., Wünning I., Tobias J. W., Lane W. S., Varshavsky A. Universality and structure of the N-end rule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16700–16712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Adachi H., Tsujimoto M., Arai H., Inoue K. Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene encodes a subunit of brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase [corrected]. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):216–218. doi: 10.1038/370216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. P., Johnston N. L., Cohen R. E. Crystal structure of a ubiquitin-dependent degradation substrate: a three-disulfide form of lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4136–4140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilt W., Wolf D. H. Proteasomes: destruction as a programme. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Mar;21(3):96–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M., Varshavsky A. In vivo degradation of a transcriptional regulator: the yeast alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90481-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Purification of his-tagged proteins in non-denaturing conditions suggests a convenient method for protein interaction studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6337–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovland P., Flick J., Johnston M., Sclafani R. A. Galactose as a gratuitous inducer of GAL gene expression in yeasts growing on glucose. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y., Baker R. T., Fischer-Vize J. A. Control of cell fate by a deubiquitinating enzyme encoded by the fat facets gene. Science. 1995 Dec 15;270(5243):1828–1831. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5243.1828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Schlenker S. Selective protein degradation: a journey's end within the proteasome. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):881–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Bartel B., Seufert W., Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin as a degradation signal. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):497–505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. cis-trans recognition and subunit-specific degradation of short-lived proteins. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):287–291. doi: 10.1038/346287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Ma P. C., Ota I. M., Varshavsky A. A proteolytic pathway that recognizes ubiquitin as a degradation signal. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17442–17456. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J. Use of a cDNA clone to identify a supposed precursor protein containing valosin. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):542–545. doi: 10.1038/325542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latterich M., Fröhlich K. U., Schekman R. Membrane fusion and the cell cycle: Cdc48p participates in the fusion of ER membranes. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W. Classical mutagenesis techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:273–281. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Fields S. Identification of mutations in p53 that affect its binding to SV40 large T antigen by using the yeast two-hybrid system. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):957–963. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Chang Y. H. Amino-terminal protein processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an essential function that requires two distinct methionine aminopeptidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 19;92(26):12357–12361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy F., Johnsson N., Rümenapf T., Varshavsky A. Using ubiquitin to follow the metabolic fate of a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4907–4912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Dohmen R. J., Varshavsky A. N-recognin/Ubc2 interactions in the N-end rule pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12046–12054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Varshavsky A. Degradation of G alpha by the N-end rule pathway. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1454–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.8073290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. Enigma variations: protein mediators of membrane fusion. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):869–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerschell R. P., Hosokawa Y., Tsunasawa S., Sherman F. The specificities of yeast methionine aminopeptidase and acetylation of amino-terminal methionine in vivo. Processing of altered iso-1-cytochromes c created by oligonucleotide transformation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19638–19643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Schmidt C. J., Nambudripad R., Smith T. F. The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):297–300. doi: 10.1038/371297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelbock P., Dillon P. J., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. A cDNA for a protein that interacts with the human immunodeficiency virus Tat transactivator. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1650–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.2194290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Lemmon S. K. Suppressors of clathrin deficiency: overexpression of ubiquitin rescues lethal strains of clathrin-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):521–532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Nussbaum A. L., Struhl K. Cloning of random-sequence oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. M., Walsh M. J., Franke W. W. An abundant and ubiquitous homo-oligomeric ring-shaped ATPase particle related to the putative vesicle fusion proteins Sec18p and NSF. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1757–1767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizicky E. M., Fields S. Protein-protein interactions: methods for detection and analysis. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Mar;59(1):94–123. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.1.94-123.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleasure I. T., Black M. M., Keen J. H. Valosin-containing protein, VCP, is a ubiquitous clathrin-binding protein. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):459–462. doi: 10.1038/365459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Hoffman L., Dubiel W. The multicatalytic and 26 S proteases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6065–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Broach J. R. Cloning genes by complementation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:195–230. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. M., Coux O., Wefes I., Hengartner C., Young R. A., Goldberg A. L., Finley D. Identification of the gal4 suppressor Sug1 as a subunit of the yeast 26S proteasome. Nature. 1996 Feb 15;379(6566):655–657. doi: 10.1038/379655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadis S., Atienza C., Jr, Finley D. Synthetic signals for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4086–4094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnall R., Mannhaupt G., Stucka R., Tauer R., Ehnle S., Schwarzlose C., Vetter I., Feldmann H. Identification of a set of yeast genes coding for a novel family of putative ATPases with high similarity to constituents of the 26S protease complex. Yeast. 1994 Sep;10(9):1141–1155. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Shrader T. E., Rocap G., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in bacteria. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1962196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzermia M., Horaitis O., Alexandraki D. The complete sequencing of a 24.6 kb segment of yeast chromosome XI identified the known loci URA1, SAC1 and TRP3, and revealed 6 new open reading frames including homologues to the threonine dehydratases, membrane transporters, hydantoinases and the phospholipase A2-activating protein. Yeast. 1994 May;10(5):663–679. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Naming a targeting signal. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):13–15. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90202-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:461–478. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1995.060.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90285-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Wilcox C. A., Flynn G. C., Chen E., Kuang W. J., Henzel W. J., Block M. R., Ullrich A., Rothman J. E. A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):355–359. doi: 10.1038/339355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Rümenapf T., Kuhn R. J., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sindbis virus RNA polymerase is degraded by the N-end rule pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]