Abstract
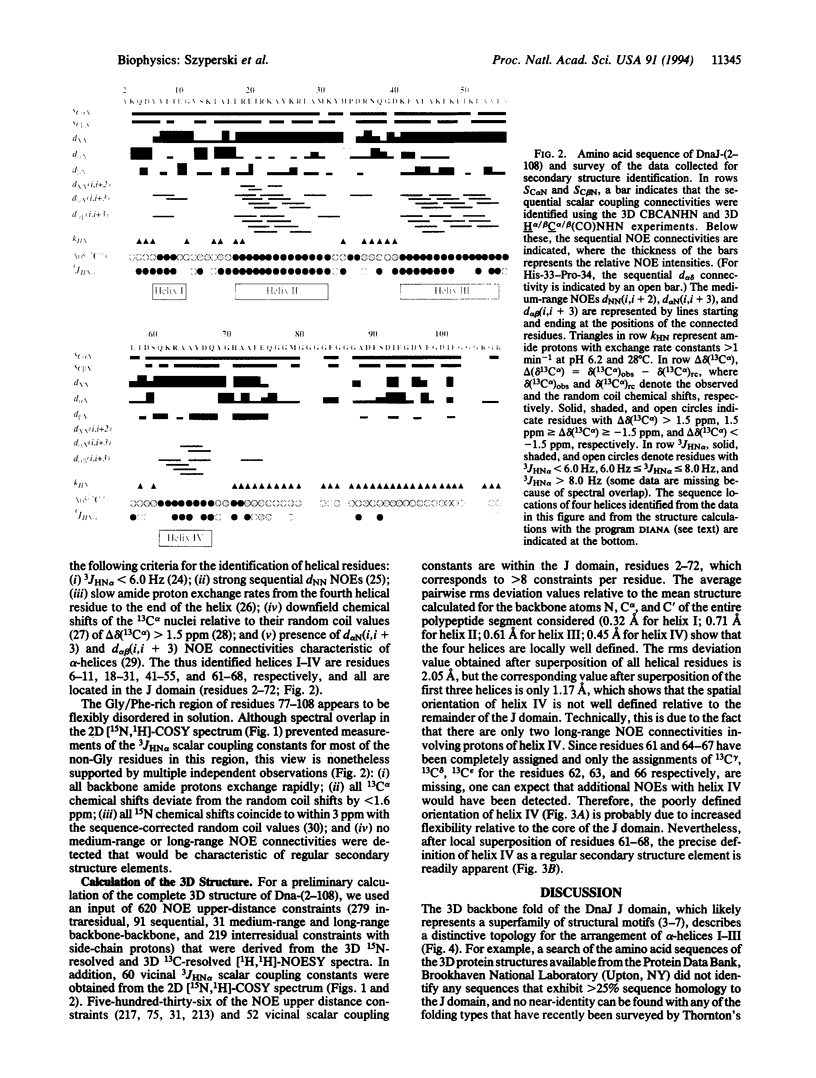
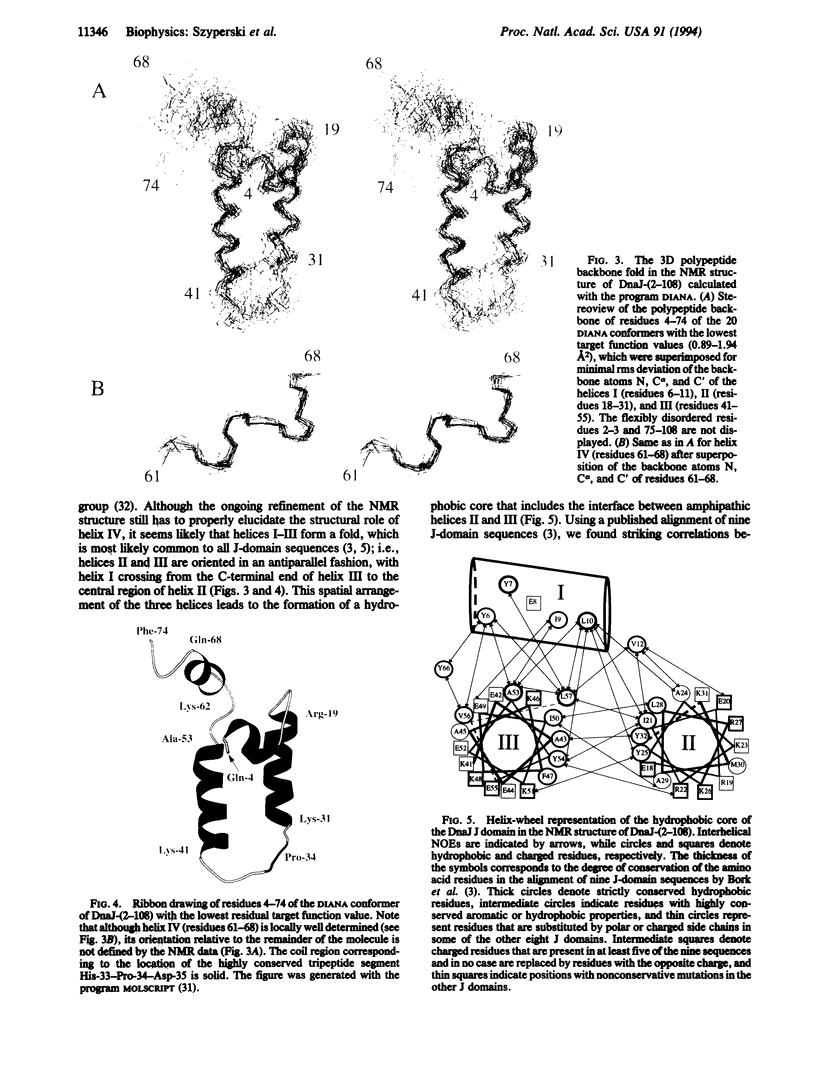
DnaJ from Escherichia coli is a 376-amino acid protein that functions in conjunction with DnaK and GrpE as a chaperone machine. The N-terminal fragment of residues 2-108, DnaJ-(2-108), retains many of the activities of the full-length protein and contains a structural motif, the J domain of residues 2-72, which is highly conserved in a superfamily of proteins. In this paper, NMR spectroscopy was used to determine the secondary structure and the three-dimensional polypeptide backbone fold of DnaJ-(2-108). By using 13C/15N doubly labeled DnaJ-(2-108), nearly complete sequence-specific assignments were obtained for 1H, 15N, 13C alpha, and 13C beta, and about 40% of the peripheral aliphatic carbon resonances were also assigned. Four alpha-helices in polypeptide segments of residues 6-11, 18-31, 41-55, and 61-68 in the J domain were identified by sequential and medium-range nuclear Overhauser effects. For the J domain, the three-dimensional structure was calculated with the program DIANA from an input of 536 nuclear Overhauser effect upper-distance constraints and 52 spin-spin coupling constants. The polypeptide backbone fold is characterized by the formation of an antiparallel bundle of two long helices, residues 18-31 and 41-55, which is stabilized by a hydrophobic core of side chains that are highly conserved in homologous J domain sequences. The Gly/Phe-rich region from residues 77 to 108 is flexibly disordered in solution.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billeter M., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Computation of sterically allowed proton-proton distances and statistical analysis of proton-proton distances in single crystal protein conformations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):321–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolliger L., Deloche O., Glick B. S., Georgopoulos C., Jenö P., Kronidou N., Horst M., Morishima N., Schatz G. A mitochondrial homolog of bacterial GrpE interacts with mitochondrial hsp70 and is essential for viability. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1998–2006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Sander C., Valencia A., Bukau B. A module of the DnaJ heat shock proteins found in malaria parasites. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):129–129. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90319-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldheim D., Rothblatt J., Schekman R. Topology and functional domains of Sec63p, an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein required for secretory protein translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3288–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., Welch W. J. Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:601–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güntert P., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Efficient computation of three-dimensional protein structures in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data using the program DIANA and the supporting programs CALIBA, HABAS and GLOMSA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):517–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90754-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. L., Landry S. J. Chaperone power in a virus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):277–278. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. K., Kurihara T., Silver P. A. Extragenic suppressors of mutations in the cytoplasmic C terminus of SEC63 define five genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):159–173. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orengo C. A., Flores T. P., Taylor W. R., Thornton J. M. Identification and classification of protein fold families. Protein Eng. 1993 Jul;6(5):485–500. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.5.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Wüthrich K. Heteronuclear filters in two-dimensional [1H,1H]-NMR spectroscopy: combined use with isotope labelling for studies of macromolecular conformation and intermolecular interactions. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Feb;23(1):39–96. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Calibration of the angular dependence of the amide proton-C alpha proton coupling constants, 3JHN alpha, in a globular protein. Use of 3JHN alpha for identification of helical secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarz R., Wüthrich K. High-field 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies at 90.5 MHz of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2263–2269. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Way J. C. Eukaryotic DnaJ homologs and the specificity of Hsp70 activity. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90287-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The NH2-terminal 108 amino acids of the Escherichia coli DnaJ protein stimulate the ATPase activity of DnaK and are sufficient for lambda replication. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5446–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylicz M., Yamamoto T., McKittrick N., Sell S., Georgopoulos C. Purification and properties of the dnaJ replication protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7591–7598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]