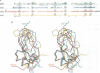Abstract
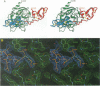
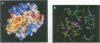
Ornithodorin, isolated from the blood sucking soft tick Ornithodoros moubata, is a potent (Ki = 10(-12) M) and highly selective thrombin inhibitor. Internal sequence homology indicates a two domain protein. Each domain resembles the Kunitz inhibitor basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) and also the tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP) isolated from the same organism. The 3.1 A crystal structure of the ornithodorin-thrombin complex confirms that both domains of ornithodorin exhibit a distorted BPTI-like fold. The N-terminal portion and the C-terminal helix of each domain are structurally very similar to BPTI, whereas the regions corresponding to the binding loop of BPTI adopt different conformations. Neither of the two 'reactive site loops' of ornithodorin contacts the protease in the ornithodorin-thrombin complex. Instead, the N-terminal residues of ornithodorin bind to the active site of thrombin, reminiscent of the thrombin-hirudin interaction. The C-terminal domain binds at the fibrinogen recognition exosite. Molecular recognition of its target protease by this double-headed Kunitz-type inhibitor diverges considerably from other members of this intensely studied superfamily. The complex structure provides a model to explain the perplexing results of mutagenesis studies on the TAP-factor Xa interaction.
Full text
PDF
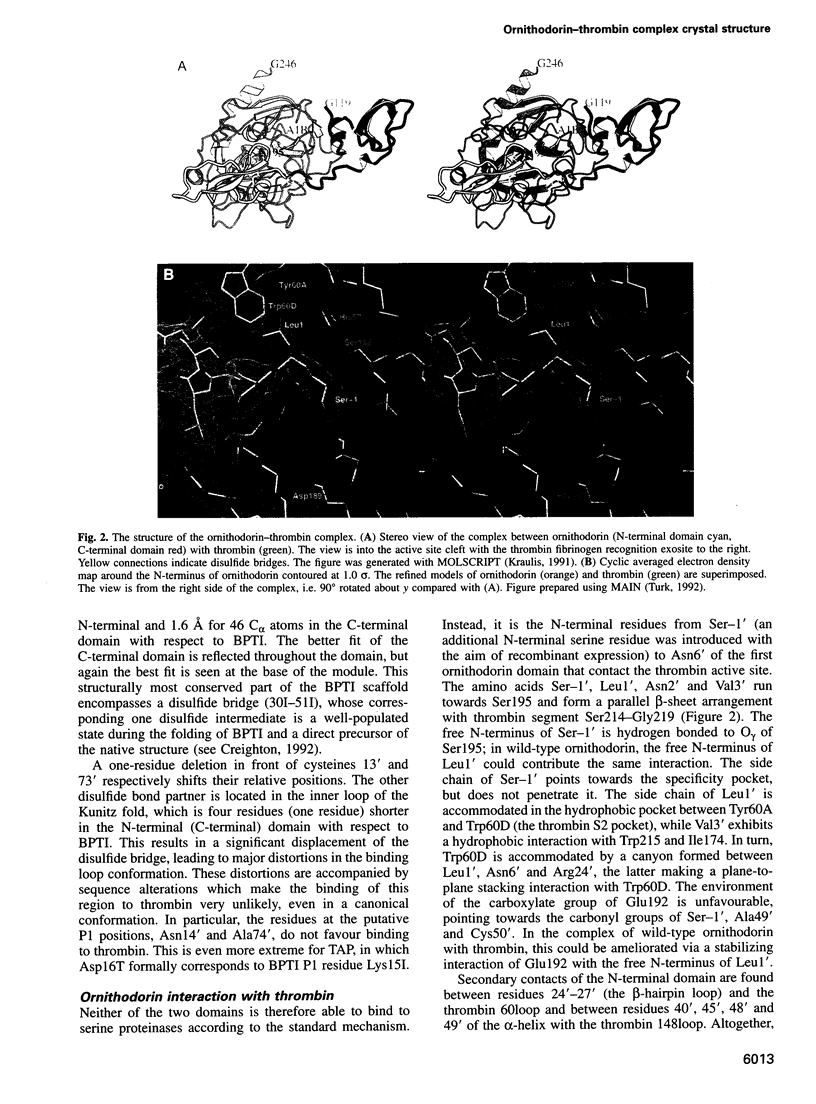
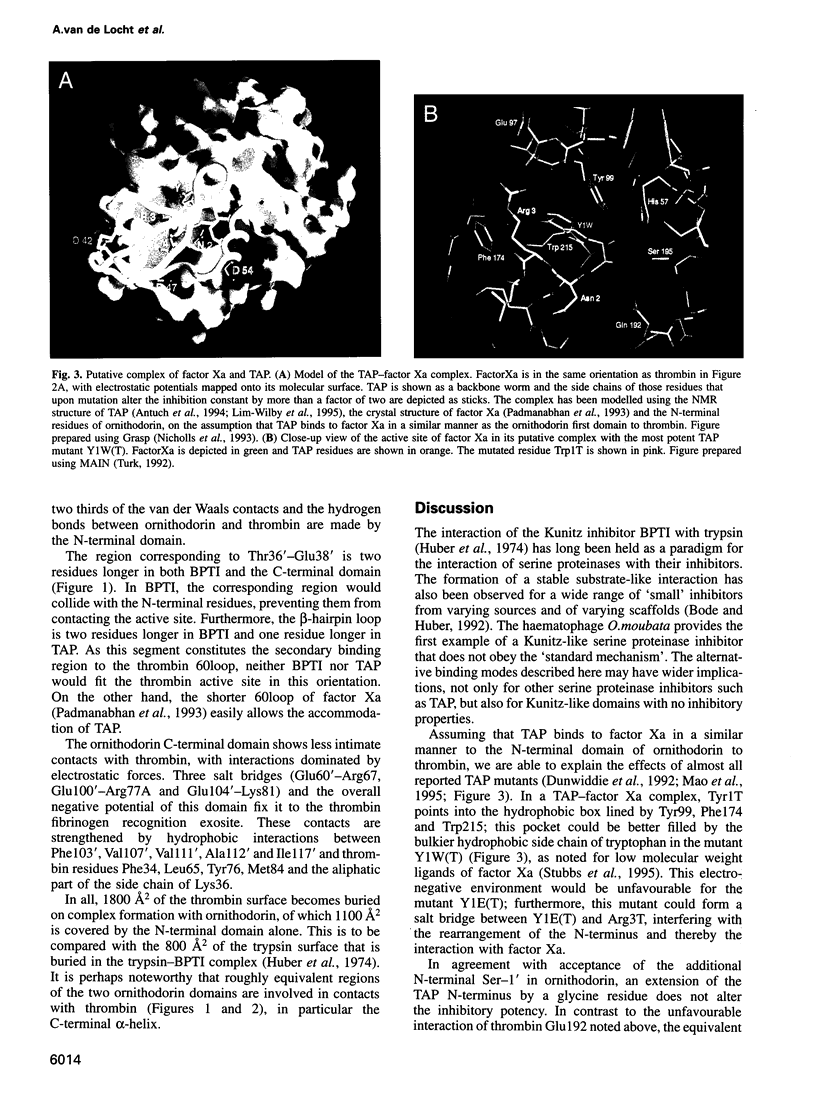



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antuch W., Berndt K. D., Chávez M. A., Delfín J., Wüthrich K. The NMR solution structure of a Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor from the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 15;212(3):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antuch W., Güntert P., Billeter M., Hawthorne T., Grossenbacher H., Wüthrich K. NMR solution structure of the recombinant tick anticoagulant protein (rTAP), a factor Xa inhibitor from the tick Ornithodoros moubata. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 26;352(2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00941-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascenzi P., Coletta M., Amiconi G., de Cristofaro R., Bolognesi M., Guarneri M., Menegatti E. Binding of the bovine basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz) to human alpha-, beta- and gamma-thrombin; a kinetic and thermodynamic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 21;956(2):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90262-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton G. J. ALSCRIPT: a tool to format multiple sequence alignments. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):37–40. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Huber R. Natural protein proteinase inhibitors and their interaction with proteinases. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 1;204(2):433–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Turk D., Karshikov A. The refined 1.9-A X-ray crystal structure of D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone-inhibited human alpha-thrombin: structure analysis, overall structure, electrostatic properties, detailed active-site geometry, and structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1992 Apr;1(4):426–471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandstetter H., Turk D., Hoeffken H. W., Grosse D., Stürzebecher J., Martin P. D., Edwards B. F., Bode W. Refined 2.3 A X-ray crystal structure of bovine thrombin complexes formed with the benzamidine and arginine-based thrombin inhibitors NAPAP, 4-TAPAP and MQPA. A starting point for improving antithrombotics. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1085–1099. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. The disulfide folding pathway of BPTI. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):111–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1373519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie C. T., Neeper M. P., Nutt E. M., Waxman L., Smith D. E., Hofmann K. J., Lumma P. K., Garsky V. M., Vlasuk G. P. Site-directed analysis of the functional domains in the factor Xa inhibitor tick anticoagulant peptide: identification of two distinct regions that constitute the enzyme recognition sites. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12126–12131. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie C. T., Smith D. E., Nutt E. M., Vlasuk G. P. Anticoagulant effects of the selective factor XA inhibitors tick anticoagulant peptide and antistasin in the APTT assay are determined by the relative rate of prothrombinase inhibition. Thromb Res. 1991 Dec 15;64(6):787–794. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Priestle J. P., Rahuel J., Grossenbacher H., Bode W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Crystal structure of the thrombin-hirudin complex: a novel mode of serine protease inhibition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2361–2365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Bode W., Schwager P., Bartels K., Deisenhofer J., Steigemann W. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Crystallographic refinement at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):73–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Rühlmann A., Epp O., Formanek H. The basic trypsin inhibitor of bovine pancreas. I. Structure analysis and conformation of the polypeptide chain. Naturwissenschaften. 1970 Aug;57(8):389–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00599976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. P., Mao S. S., Lewis S. D., Shafer J. A. Reaction pathway for inhibition of blood coagulation factor Xa by tick anticoagulant peptide. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 16;31(23):5374–5380. doi: 10.1021/bi00138a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Vlasuk G. P., Bergum P. W. Assembly of the prothrombinase complex enhances the inhibition of bovine factor Xa by tick anticoagulant peptide. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 28;33(25):7897–7907. doi: 10.1021/bi00191a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong P. D., McDonald N. Q., Sigler P. B., Hendrickson W. A. Structure of beta 2-bungarotoxin: potassium channel binding by Kunitz modules and targeted phospholipase action. Structure. 1995 Oct 15;3(10):1109–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelin J. M., Foray M. F., Poncin M., Hollecker M., Marion D. Proteinase inhibitor homologues as potassium channel blockers. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Apr;1(4):246–250. doi: 10.1038/nsb0494-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim-Wilby M. S., Hallenga K., de Maeyer M., Lasters I., Vlasuk G. P., Brunck T. K. NMR structure determination of tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP). Protein Sci. 1995 Feb;4(2):178–186. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Hall J. A., Blinder M., Binder E. P., Jackson C. M. The action of thrombin on peptide p-nitroanilide substrates. Substrate selectivity and examination of hydrolysis under different reaction conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):539–557. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao S. S., Huang J., Welebob C., Neeper M. P., Garsky V. M., Shafer J. A. Identification and characterization of variants of tick anticoagulant peptide with increased inhibitory potency toward human factor Xa. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 18;34(15):5098–5103. doi: 10.1021/bi00015a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwardt F. Coagulation inhibitors from blood-sucking animals. A new line of developing antithrombotic drugs. Pharmazie. 1994 May;49(5):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan K., Padmanabhan K. P., Tulinsky A., Park C. H., Bode W., Huber R., Blankenship D. T., Cardin A. D., Kisiel W. Structure of human des(1-45) factor Xa at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):947–966. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer L. W., Davidson J. T., Vlasuk G. P., Siegl P. K. Antithrombotic efficacy of recombinant tick anticoagulant peptide. A potent inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa in a primate model of arterial thrombosis. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1741–1748. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitko G. R., Ramjit D. R., Stabilito I. I., Lehman D., Lynch J. J., Vlasuk G. P. Conjunctive enhancement of enzymatic thrombolysis and prevention of thrombotic reocclusion with the selective factor Xa inhibitor, tick anticoagulant peptide. Comparison to hirudin and heparin in a canine model of acute coronary artery thrombosis. Circulation. 1992 Feb;85(2):805–815. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.2.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivasan U., Axelsen P. H. Buried water in homologous serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 29;31(51):12785–12791. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Bode W. A player of many parts: the spotlight falls on thrombin's structure. Thromb Res. 1993 Jan 1;69(1):1–58. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Bode W. The clot thickens: clues provided by thrombin structure. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jan;20(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Huber R., Bode W. Crystal structures of factor Xa specific inhibitors in complex with trypsin: structural grounds for inhibition of factor Xa and selectivity against thrombin. FEBS Lett. 1995 Nov 13;375(1-2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01190-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyperski T., Güntert P., Stone S. R., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Wüthrich K. Impact of protein-protein contacts on the conformation of thrombin-bound hirudin studied by comparison with the nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of hirudin(1-51). J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1206–1211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90326-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Ramjit D., Fujita T., Dunwiddie C. T., Nutt E. M., Smith D. E., Shebuski R. J. Comparison of the in vivo anticoagulant properties of standard heparin and the highly selective factor Xa inhibitors antistasin and tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP) in a rabbit model of venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Mar 4;65(3):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P. Structural and functional characterization of tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP): a potent and selective inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Connolly T. M. Isolation of an inhibitor selective for collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5445–5449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Smith D. E., Arcuri K. E., Vlasuk G. P. Tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP) is a novel inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):593–596. doi: 10.1126/science.2333510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Locht A., Lamba D., Bauer M., Huber R., Friedrich T., Kröger B., Höffken W., Bode W. Two heads are better than one: crystal structure of the insect derived double domain Kazal inhibitor rhodniin in complex with thrombin. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5149–5157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]