Abstract
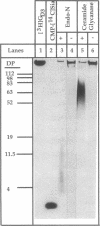
The CMP-sialic acid:poly alpha 2,8sialosyl sialyltransferase (polyST) in neurotropic Escherichia coli K1 inner membranes catalyzes synthesis of the alpha 2,8-linked polysialic acid capsule. The capsule is a neurovirulent determinant associated with neonatal meningitis in humans. A functionally similar polyST in human neuroblastomas polysialylates neural cell adhesion molecules. While bacteria do not synthesize glycosphingolipids (GSLs), we report here that the E. coli K1 polyST can selectively polysialylate several structurally related GSLs, when added as exogenous sialyl acceptors. A structural feature common to the preferred sialyl acceptors (GD3 > GT1a > GQ1b = GT1b > GD2 = GD1b = GD1a > GM1) was the disialyl glycotope, Sia alpha 2,8Sia, alpha 2,3-linked to galactose (Sia is sialic acid). A linear tetrasaccharide with a terminal Sia residue (e.g., GD3) was the minimum length oligosaccharide recognized by the polyST. Endo-N-acylneuraminidase was used to confirm the alpha 2,8-specific polysialylation of GSL. Ceramide glycanase was used to release the polysialyllactose chains from the ceramide moiety. Size analysis of these chains showed that 60-80 Sia residues were transferred to the disialyllactose moiety of GD3. The significance of these findings is two-fold. (i) The E. coli K1 polyST can be used as a synthetic reagent to enzymatically engineer the glycosyl moiety of GSL, thus creating oligo- or polysialylated GSLs. Such "designer" GSLs may have potentially important biological and pharmacological properties. (ii) The use of GSLs as exogenous sialyl acceptors increases the sensitivity of detecting polyST activity. The practical advantage of this finding is that polyST activity can be identified and studied in those eukaryotic cells that express low levels of this developmentally regulated enzyme and/or its acceptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Freire E., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Asymmetric incorporation of trisialoganglioside into dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2168–2172. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Leinonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Antigenic similarities between brain components and bacteria causing meningitis. Implications for vaccine development and pathogenesis. Lancet. 1983 Aug 13;2(8346):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freischütz B., Saito M., Rahmann H., Yu R. K. Activities of five different sialyltransferases in fish and rat brains. J Neurochem. 1994 May;62(5):1965–1973. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62051965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick M. C., Livingston B. D., Shaw G. W., Jacobs J. L., Troy F. A. Expression of polysialic acid on human neuroblastoma. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:267–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Bifunctional role of glycosphingolipids. Modulators for transmembrane signaling and mediators for cellular interactions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18713–18716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Vimr E. R., Yu F., Bassler B., Troy F. A. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage-induced endo-N-acetylneuraminidase specific for poly-alpha-2,8-sialosyl carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3553–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Li Y. T., Karlsson H. Characterization of glycosphingolipid mixtures with up to ten sugars by gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry as permethylated oligosaccharides and ceramides released by ceramide glycanase. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6672–6678. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg C. B., Snider M. D. Topography of glycosylation in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:63–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori A., Inoue S., Iwasaki M., Kitajima K., Kawai G., Yokoyama S., Inoue Y. Deaminated neuraminic acid-rich glycoprotein of rainbow trout egg vitelline envelope. Occurrence of a novel alpha-2,8-linked oligo(deaminated neuraminic acid) structure in O-linked glycan chains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21811–21819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Animal glycosphingolipids as membrane attachment sites for bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:309–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazume S., Kitajima K., Inoue S., Inoue Y., Troy F. A., 2nd Developmental expression of trout egg polysialoglycoproteins and the prerequisite alpha 2,6-, and alpha 2,8-sialyl and alpha 2,8-polysialyltransferase activities required for their synthesis during oogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10330–10340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazume S., Kitajima K., Inoue S., Troy F. A., 2nd, Cho J. W., Lennarz W. J., Inoue Y. Identification of polysialic acid-containing glycoprotein in the jelly coat of sea urchin eggs. Occurrence of a novel type of polysialic acid structure. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22712–22718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladisch S. Tumor cell gangliosides. Adv Pediatr. 1987;34:45–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J. Protein glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum: current topological issues. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7205–7210. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy R. D., Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. CMP-NeuNAc:poly-alpha-2,8-sialosyl sialyltransferase and the biosynthesis of polysialosyl units in neural cell adhesion molecules. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12695–12699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen S., Häyrinen J., Finne J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the capsular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli K1 and other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2646–2653. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2646-2653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. L., Nudelman E., Gaeta F. C., Perez M., Singhal A. K., Hakomori S., Paulson J. C. ELAM-1 mediates cell adhesion by recognition of a carbohydrate ligand, sialyl-Lex. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1701274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohr T. E., Troy F. A. Structure and biosynthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2332–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Blaha I., Bitter-Suermann D., Heitz P. U. Blastemal cells of nephroblastomatosis complex share an onco-developmental antigen with embryonic kidney and Wilms' tumor. An immunohistochemical study on polysialic acid distribution. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):596–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Zuber C., Wagner P., Blaha I., Bitter-Suermann D., Heitz P. U. Presence of the long chain form of polysialic acid of the neural cell adhesion molecule in Wilms' tumor. Identification of a cell adhesion molecule as an oncodevelopmental antigen and implications for tumor histogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):227–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Acheson A., Hall A. K., Mann D. M., Sunshine J. The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) as a regulator of cell-cell interactions. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):53–57. doi: 10.1126/science.3281256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Watanabe M., Silver J., Troy F. A., Vimr E. R. Specific alteration of NCAM-mediated cell adhesion by an endoneuraminidase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1842–1849. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato C., Kitajima K., Tazawa I., Inoue Y., Inoue S., Troy F. A., 2nd Structural diversity in the alpha 2-->8-linked polysialic acid chains in salmonid fish egg glycoproteins. Occurrence of poly(Neu5Ac), poly(Neu5Gc), poly(Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc), poly(KDN), and their partially acetylated forms. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23675–23684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg N., Ryd M., Lindberg A. A., Karlsson K. A. Studies on the binding of bacteria to glycolipids. Two species of Propionibacterium apparently recognize separate epitopes on lactose of lactosylceramide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd Polysialylation: from bacteria to brains. Glycobiology. 1992 Feb;2(1):5–23. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., McCloskey M. A. Role of a membranous sialyltransferase complex in the synthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. Temperature-induced alteration in the assembly process. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Vijay I. K., Tesche N. Role of undecaprenyl phosphate in synthesis of polymers containing sialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):156–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay I. K., Troy F. A. Properties of membrane-associated sialyltransferase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):164–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R. Map position and genomic organization of the kps cluster for polysialic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1335–1338. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1335-1338.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., McCoy R. D., Vollger H. F., Wilkison N. C., Troy F. A. Use of prokaryotic-derived probes to identify poly(sialic acid) in neonatal neuronal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Identification of an inducible catabolic system for sialic acids (nan) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):845–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.845-853.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz G., Aruffo A., Kolanus W., Bevilacqua M., Seed B. Recognition by ELAM-1 of the sialyl-Lex determinant on myeloid and tumor cells. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1132–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.1701275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgerber C., Hansen A., Frosch M. Complete nucleotide and deduced protein sequence of CMP-NeuAc: poly-alpha-2,8 sialosyl sialyltransferase of Escherichia coli K1. Glycobiology. 1991 Sep;1(4):357–365. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgerber C., Troy F. A. Biosynthesis of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. The endogenous acceptor of polysialic acid is a membrane protein of 20 kDa. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1578–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Adams D. A., Troy F. A. Biosynthesis and assembly of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. Role of a low-density vesicle fraction in activation of the endogenous synthesis of sialyl polymers. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12769–12775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Vimr E. R., Costerton J. W., Troy F. A. Membrane proteins correlated with expression of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):743–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.743-749.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou B., Li S. C., Laine R. A., Huang R. T., Li Y. T. Isolation and characterization of ceramide glycanase from the leech, Macrobdella decora. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12272–12277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber C., Lackie P. M., Catterall W. A., Roth J. Polysialic acid is associated with sodium channels and the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM in adult rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9965–9971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Echten G., Sandhoff K. Ganglioside metabolism. Enzymology, Topology, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5341–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]