Abstract
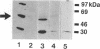
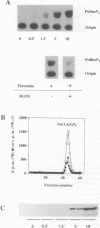
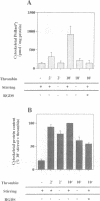
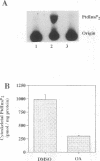
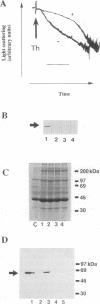
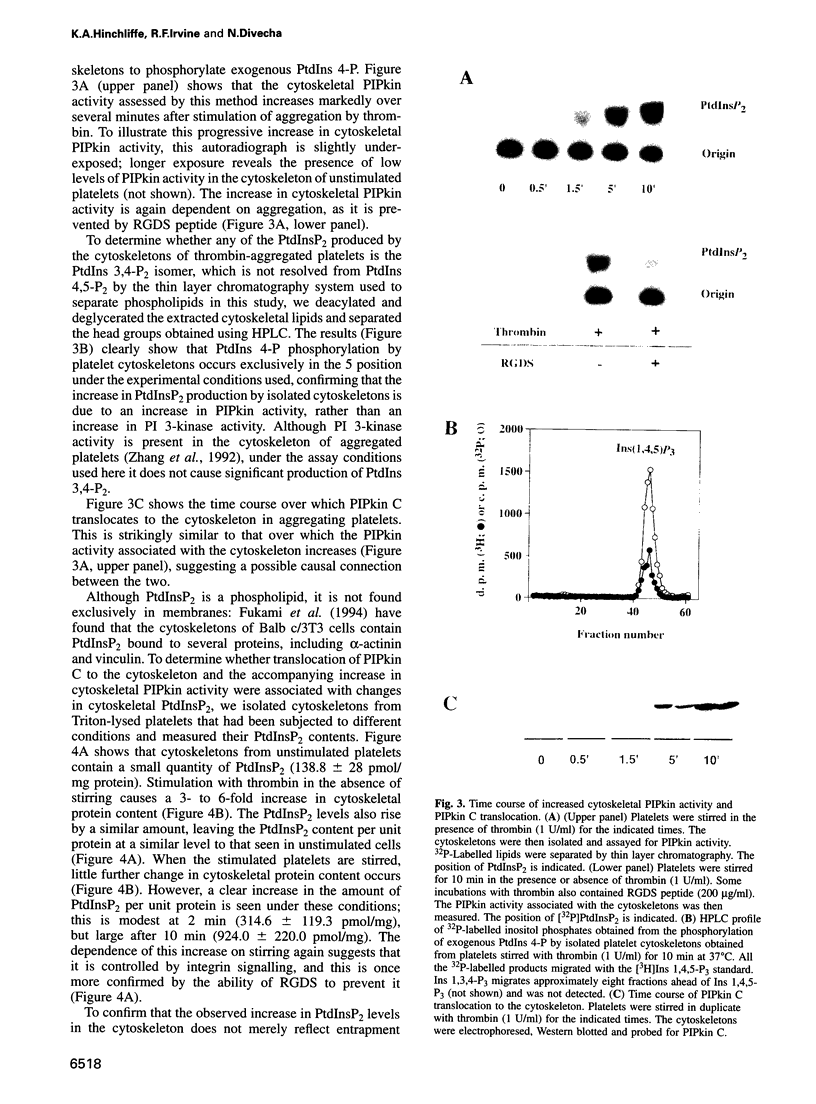
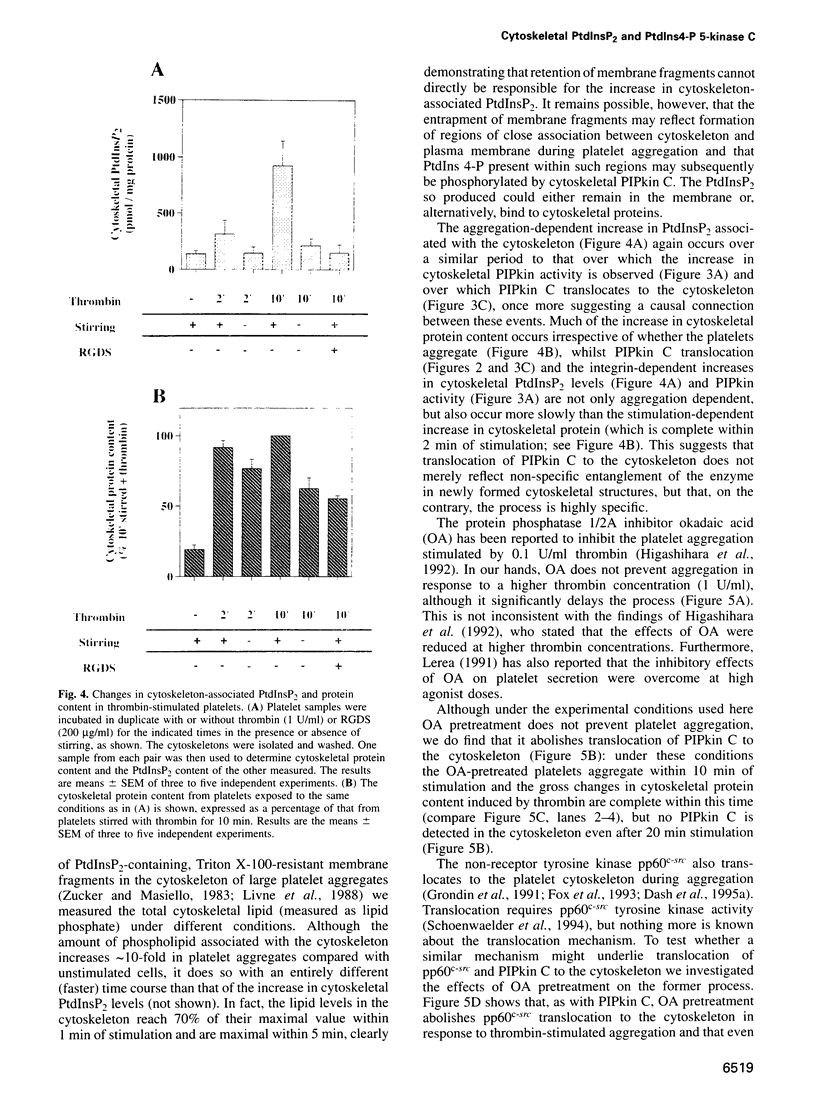
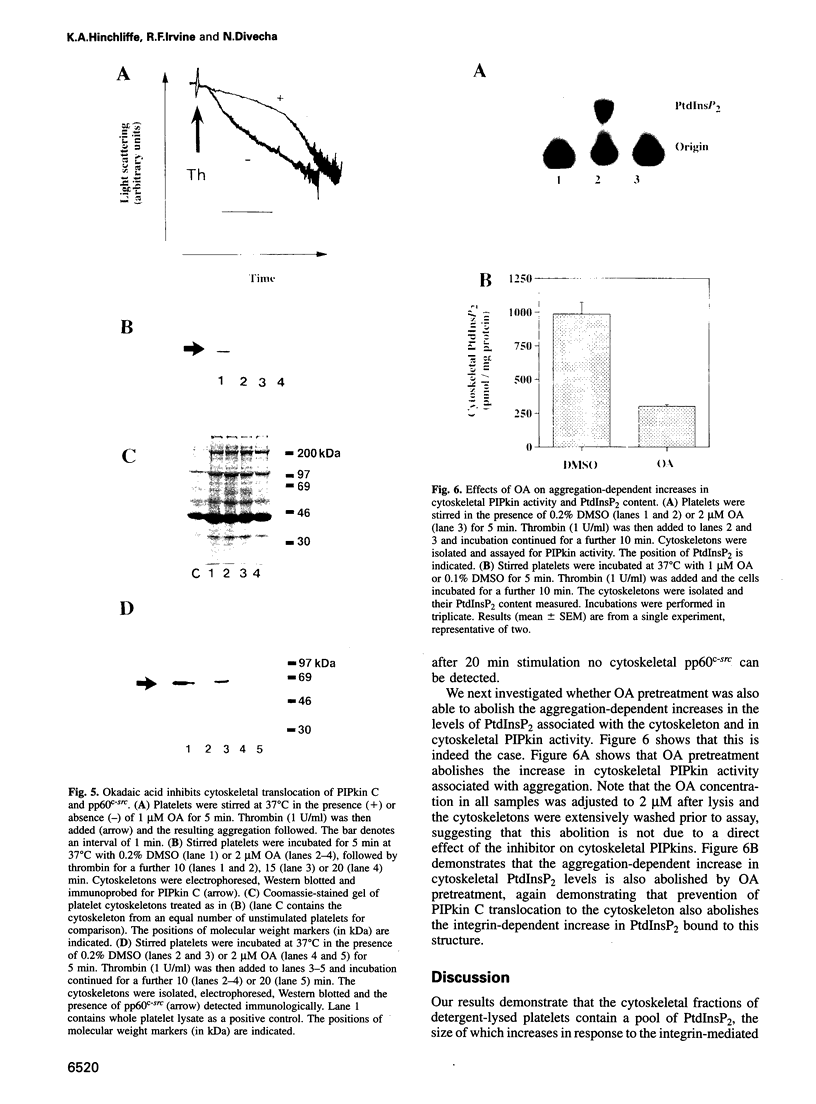
Thrombin-stimulated aggregation of human platelets promotes an increase in the phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns 4-P) 5-kinase (PIPkin) activity in the cytoskeleton. This phenomenon is associated with translocation of PIPkin isoform C to the cytoskeleton and with an increase in the amount of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PtdInsP2) bound to the cytoskeletal pellet. All three of these effects are prevented if the platelets are not stirred or if RGD-containing peptides are present, demonstrating that they require integrin activation. All three are also abolished by pretreatment with okadaic acid, which also prevents the aggregation-dependent translocation of pp60(c-src) to the cytoskeleton. The results point to the existence of a cytoskeletally associated PtdInsP2 pool under the control of integrin-mediated signals that act via PIPkin C and suggest that a common, okadaic acid-sensitive mechanism may underlie the aggregation-dependent translocation of certain signalling molecules to the platelet cytoskeleton.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asijee G. M., Sturk A., Bruin T., Wilkinson J. M., Ten Cate J. W. Vinculin is a permanent component of the membrane skeleton and is incorporated into the (re)organising cytoskeleton upon platelet activation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 20;189(1):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazenet C. E., Ruano A. R., Brockman J. L., Anderson R. A. The human erythrocyte contains two forms of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase which are differentially active toward membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18012–18022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boronenkov I. V., Anderson R. A. The sequence of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase defines a novel family of lipid kinases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):2881–2884. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.2881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooksbank C. E., Hutchings A., Butcher G. W., Irvine R. F., Divecha N. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase: distribution and intracellular localization of the C isoform. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):77–82. doi: 10.1042/bj2910077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Traynor-Kaplan A., Bokoch G. M., Schwartz M. A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H., Bolen J., Brugge J. S. Regulation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp72syk by platelet agonists and the integrin alpha IIb beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28859–28864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. G., Dawson R. M. Alkaline O leads to N-transacylation. A new method for the quantitative deacylation of phospholipids. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj1950301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Filhol O., Payrastre B., Hunter T., Gill G. N. Interaction between the epidermal growth factor receptor and phosphoinositide kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash D., Aepfelbacher M., Siess W. Integrin alpha IIb beta 3-mediated translocation of CDC42Hs to the cytoskeleton in stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17321–17326. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash D., Aepfelbacher M., Siess W. The association of pp125FAK, pp60Src, CDC42Hs and Rap1B with the cytoskeleton of aggregated platelets is a reversible process regulated by calcium. FEBS Lett. 1995 Apr 24;363(3):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Brooksbank C. E., Irvine R. F. Purification and characterization of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):637–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2880637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Hinchliffe K. A., Irvine R. F. The cloning and sequence of the C isoform of PtdIns4P 5-kinase. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 1;309(Pt 3):715–719. doi: 10.1042/bj3090715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Boyles J. K., Berndt M. C., Steffen P. K., Anderson L. K. Identification of a membrane skeleton in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1525–1538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Lipfert L., Clark E. A., Reynolds C. C., Austin C. D., Brugge J. S. On the role of the platelet membrane skeleton in mediating signal transduction. Association of GP IIb-IIIa, pp60c-src, pp62c-yes, and the p21ras GTPase-activating protein with the membrane skeleton. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25973–25984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami K., Endo T., Imamura M., Takenawa T. alpha-Actinin and vinculin are PIP2-binding proteins involved in signaling by tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1518–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondin P., Plantavid M., Sultan C., Breton M., Mauco G., Chap H. Interaction of pp60c-src, phospholipase C, inositol-lipid, and diacyglycerol kinases with the cytoskeletons of thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15705–15709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. D., Hoffman D. P., Fisette P. L., Baas P., Anderson R. A. A phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-sensitive casein kinase I alpha associates with synaptic vesicles and phosphorylates a subset of vesicle proteins. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(3):711–724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates formation of phosphatidyl inositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. E., Hajduk P. J., Yoon H. S., Fesik S. W. Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):168–170. doi: 10.1038/371168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Bokoch G. M., Carpenter C. L., Janmey P. A., Taylor L. A., Toker A., Stossel T. P. Thrombin receptor ligation and activated Rac uncap actin filament barbed ends through phosphoinositide synthesis in permeabilized human platelets. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Fisette P. L., Jenkins G. H., Fukami K., Takenawa T., Anderson R. A., Martin T. F. ATP-dependent inositide phosphorylation required for Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):173–177. doi: 10.1038/374173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara M., Takahata K., Kurokawa K., Ikebe M. The inhibitory effects of okadaic acid on platelet function. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80768-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A. Phosphoinositides and calcium as regulators of cellular actin assembly and disassembly. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:169–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins G. H., Fisette P. L., Anderson R. A. Type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase isoforms are specifically stimulated by phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11547–11554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Polyphosphoinositide synthesis in platelets stimulated with low concentrations of thrombin is enhanced before the activation of phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):231–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80197-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea K. M. Thrombin-induced effects are selectively inhibited following treatment of intact human platelets with okadaic acid. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6819–6824. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L. E., Schulz J. T., Cantley L. C. Characterization and purification of membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase from human red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5080–5088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Cantley L. C. Signal transduction and membrane traffic: the PITP/phosphoinositide connection. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):659–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90525-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Chalifa V., Pertile P., Chen C. S., Cantley L. C. Novel function of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate as a cofactor for brain membrane phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 26;269(34):21403–21406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livne A., Packham M. A., Guccione M. A., Mustard J. F. Aggregation-related association of lipid with the cytoskeleton of rabbit and human platelets prelabeled with [3H]palmitic acid. Similar effects of adenosine diphosphate- and thrombin-induced aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):288–299. doi: 10.1172/JCI113320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg G. A., Jergil B., Sundler R. Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase from rat brain. Activation by polyamines and inhibition by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee H. P., Ingber D. E., Schwartz M. A. Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates inositol lipid synthesis and enhances PDGF-induced inositol lipid breakdown. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):673–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A., De Graan P. N., Ekhart P. F., Gispen W. H., Wirtz K. W. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase from bovine brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):351–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. H., Dekker L. V., Woscholski R., Le Good J. A., Gigg R., Parker P. J. Activation of PRK1 by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. A comparison with protein kinase C isotypes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22412–22416. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., Plantavid M., Breton M., Chambaz E., Chap H. Relationship between phosphoinositide kinase activities and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plasma membranes from A431 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):665–670. doi: 10.1042/bj2720665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Arndt C. Characterization of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinases in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1967–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plopper G. E., McNamee H. P., Dike L. E., Bojanowski K., Ingber D. E. Convergence of integrin and growth factor receptor signaling pathways within the focal adhesion complex. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Oct;6(10):1349–1365. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.10.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaud-Sultan C., Mauco G., Guinebault C., Plantavid M., Payrastre B., Breton M., Chap H. Rapid and transient thrombin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis but not of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate independent of phospholipase C activation in platelets. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 20;330(3):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80902-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo P. A., Kahn R. A. GTP hydrolysis by ADP-ribosylation factor is dependent on both an ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein and acid phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10758–10763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenwaelder S. M., Jackson S. P., Yuan Y., Teasdale M. S., Salem H. H., Mitchell C. A. Tyrosine kinases regulate the cytoskeletal attachment of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa) and the cellular retraction of fibrin polymers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32479–32487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H., Brugge J. S. Adhesive signaling in platelets. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Chang K. J. Regulation of brain phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by GTP analogues. A potential role for guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3206–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hughes K. T., Irvine R. F. Pathway of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate synthesis in activated neutrophils. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):33–39. doi: 10.1038/351033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate supply by agonists and non-hydrolysable GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2960481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolias K. F., Cantley L. C., Carpenter C. L. Rho family GTPases bind to phosphoinositide kinases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17656–17659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti M., Ramaschi G., Sinigaglia F., Lapetina E. G., Balduini C. Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa and the translocation of Rap2B to the platelet cytoskeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4239–4243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urumow T., Wieland O. H. A small G-protein involved in phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase activation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):15–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80694-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen C. J., Zwiers H., Gispen W. H. Purification and partial characterization of the phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase from rat brain. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):197–203. doi: 10.1042/bj2230197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen L. A., Rossowska M., Bazan N. G. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase by its product phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90584-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Jaken S., Liao L., Fox J. E., Rittenhouse S. E. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase associates with membrane skeleton in thrombin-exposed platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., King W. G., Dillon S., Hall A., Feig L., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of platelet phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase requires the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22251–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Masiello N. C. The Triton X-100-insoluble residue ("cytoskeleton") of aggregated platelets contains increased lipid phosphorus as well as 125I-labeled glycoproteins. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):676–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]