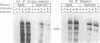Abstract
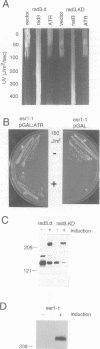
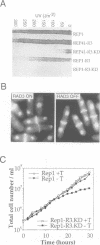
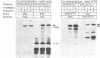
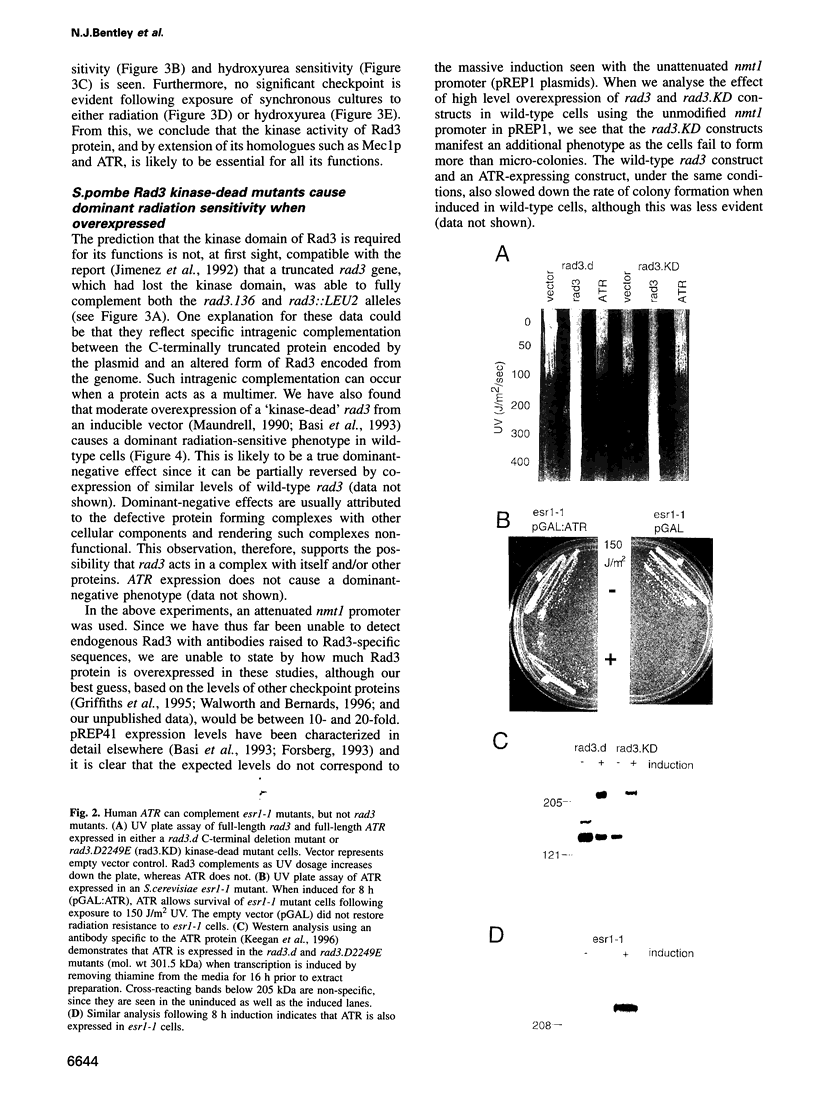
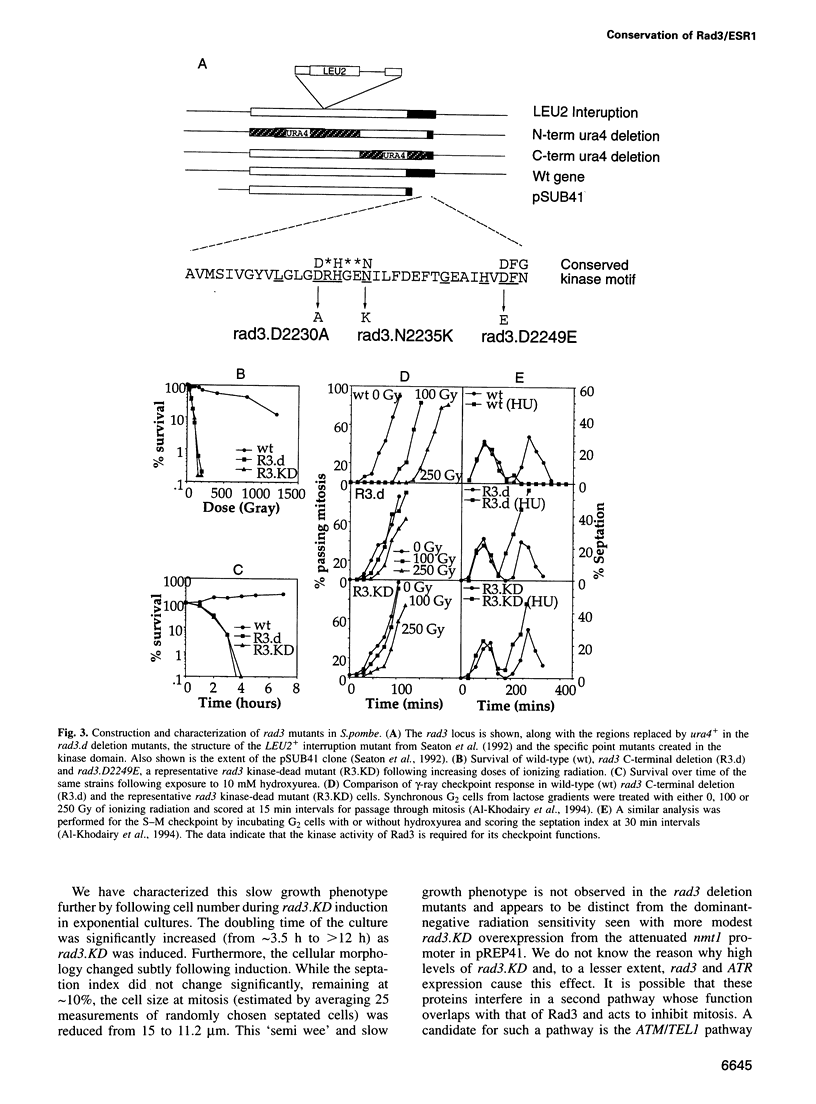
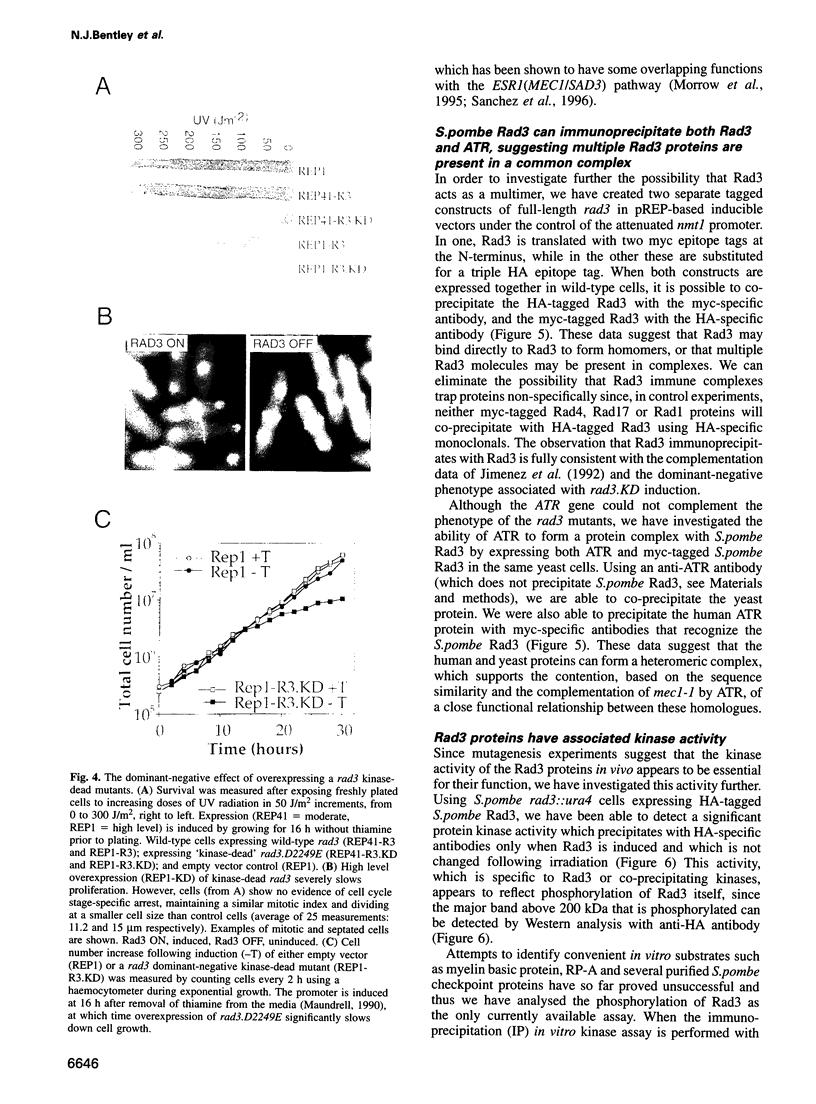
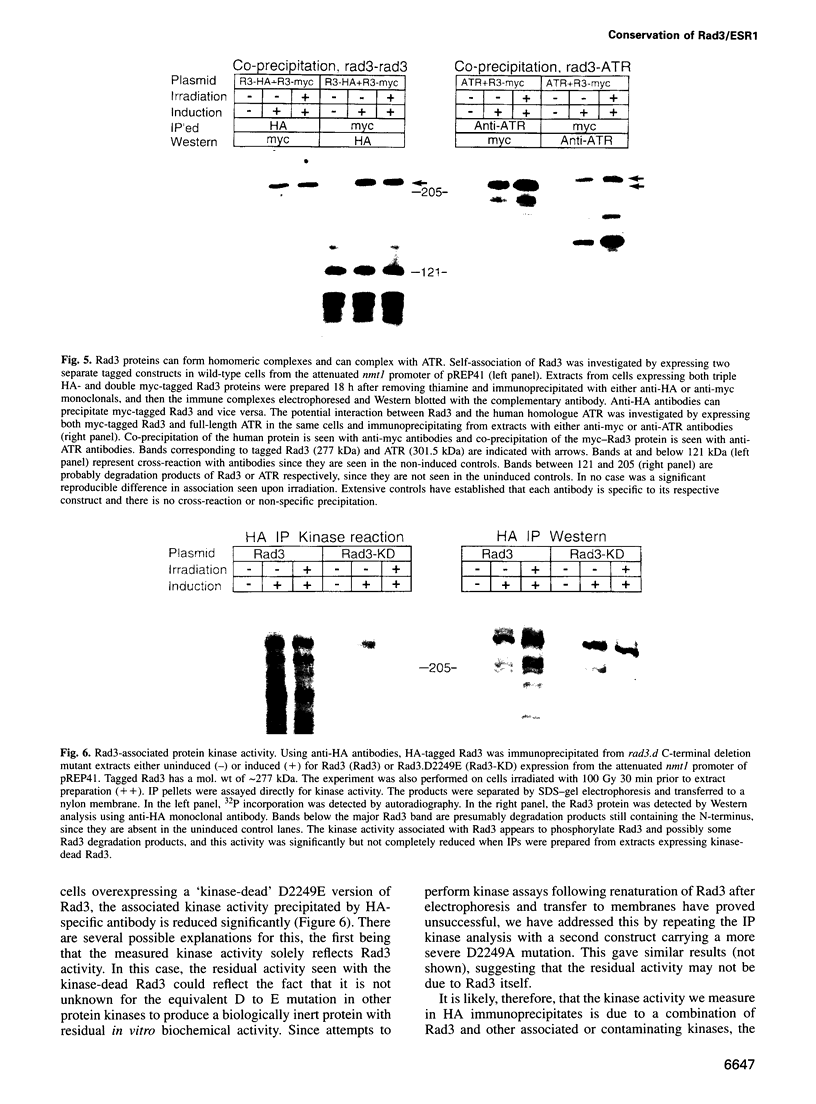
The rad3 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is required for checkpoint pathways that respond to DNA damage and replication blocks. We report the complete rad3 gene sequence and show that rad3 is the homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ESR1 (MEC1/SAD3) and Drosophila melanogaster mei-41 checkpoint genes. This establishes Rad3/Mec1 as the only conserved protein which is required for all the DNA structure checkpoints in both yeast model systems. Rad3 is an inessential member of the 'lipid kinase' subclass of kinases which includes the ATM protein defective in ataxia telangiectasia patients. Mutational analysis indicates that the kinase domain is required for Rad3 function, and immunoprecipitation of overexpressed Rad3 demonstrates an associated protein kinase activity. The previous observation that rad3 mutations can be rescued by a truncated clone lacking the kinase domain may be due to intragenic complementation. Consistent with this, biochemical data suggest that Rad3 exists in a complex containing multiple copies of Rad3. We have identified a novel human gene (ATR) whose product is closely related to Rad3/Esr1p/Mei-41. ATR can functionally complement esr1-1 radiation sensitivity in S. cerevisiae. Together, the structural conservation and functional complementation suggest strongly that the mechanisms underlying the DNA structure checkpoints are conserved throughout evolution.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. A., Kremenstova E., Luo L. Complete transposition requires four active monomers in the mu transposase tetramer. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 15;8(20):2416–2428. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.20.2416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet N. C., Carr A. M. Fission yeast wee1 protein kinase is not required for DNA damage-dependent mitotic arrest. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):824–827. doi: 10.1038/364824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet N., Muriel W. J., Carr A. M. Versatile shuttle vectors and genomic libraries for use with Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90707-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G., Schmid E., Maundrell K. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcription efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90552-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beamish H., Lavin M. F. Radiosensitivity in ataxia-telangiectasia: anomalies in radiation-induced cell cycle delay. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Feb;65(2):175–184. doi: 10.1080/09553009414550211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M. Checkpoints take the next step. Science. 1996 Jan 19;271(5247):314–315. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5247.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M., Hoekstra M. F. The cellular responses to DNA damage. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;5(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88934-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M., Moudjou M., Bentley N. J., Hagan I. M. The chk1 pathway is required to prevent mitosis following cell-cycle arrest at 'start'. Curr Biol. 1995 Oct 1;5(10):1179–1190. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M. Radiation checkpoints in model systems. Int J Radiat Biol. 1994 Dec;66(6 Suppl):S133–S139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M., Schmidt H., Kirchhoff S., Muriel W. J., Sheldrick K. S., Griffiths D. J., Basmacioglu C. N., Subramani S., Clegg M., Nasim A. The rad16 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a homolog of the RAD1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2029–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimprich K. A., Shin T. B., Keith C. T., Schreiber S. L. cDNA cloning and gene mapping of a candidate human cell cycle checkpoint protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):2850–2855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.7.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drwinga H. L., Toji L. H., Kim C. H., Greene A. E., Mulivor R. A. NIGMS human/rodent somatic cell hybrid mapping panels 1 and 2. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):311–314. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez Sarabia M. J., McInerny C., Harris P., Gordon C., Fantes P. The cell cycle genes cdc22+ and suc22+ of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe encode the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(1-2):241–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00279553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. C., al-Khodairy F., Fotou E., Sheldrick K. S., Griffiths D. J., Carr A. M. 14-3-3 protein homologs required for the DNA damage checkpoint in fission yeast. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):533–535. doi: 10.1126/science.8036497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L. Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces pombe expression systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2955–2956. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwell P. W., Kronmal S. L., Porter S. E., Gassenhuber J., Obermaier B., Petes T. D. TEL1, a gene involved in controlling telomere length in S. cerevisiae, is homologous to the human ataxia telangiectasia gene. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths D. J., Barbet N. C., McCready S., Lehmann A. R., Carr A. M. Fission yeast rad17: a homologue of budding yeast RAD24 that shares regions of sequence similarity with DNA polymerase accessory proteins. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 1;14(23):5812–5823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm C., Kohli J., Murray J., Maundrell K. Genetic engineering of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a system for gene disruption and replacement using the ura4 gene as a selectable marker. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00331307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari K. L., Santerre A., Sekelsky J. J., McKim K. S., Boyd J. B., Hawley R. S. The mei-41 gene of D. melanogaster is a structural and functional homolog of the human ataxia telangiectasia gene. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90478-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley K. O., Gell D., Smith G. C., Zhang H., Divecha N., Connelly M. A., Admon A., Lees-Miller S. P., Anderson C. W., Jackson S. P. DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit: a relative of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the ataxia telangiectasia gene product. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Kastan M. B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1821–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.7997877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helliwell S. B., Wagner P., Kunz J., Deuter-Reinhard M., Henriquez R., Hall M. N. TOR1 and TOR2 are structurally and functionally similar but not identical phosphatidylinositol kinase homologues in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jan;5(1):105–118. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez G., Yucel J., Rowley R., Subramani S. The rad3+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is involved in multiple checkpoint functions and in DNA repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4952–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Ogawa H. An essential gene, ESR1, is required for mitotic cell growth, DNA repair and meiotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3104–3112. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K. S., Holtzman D. A., Plug A. W., Christenson E. R., Brainerd E. E., Flaggs G., Bentley N. J., Taylor E. M., Meyn M. S., Moss S. B. The Atr and Atm protein kinases associate with different sites along meiotically pairing chromosomes. Genes Dev. 1996 Oct 1;10(19):2423–2437. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.19.2423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. J., Chinn R., Reus B. E., Hayes S., Schantz L., Dubois B., Overhauser J., Ballabio A., Drabkin H., Lewis T. B. Regional localization of 188 sequence tagged sites on a somatic cell hybrid mapping panel for human chromosome 3. Genomics. 1994 Dec;24(3):549–556. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long K. E., Sunnerhagen P., Subramani S. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad1 gene consists of three exons and the cDNA sequence is partially homologous to the Ustilago maydis REC1 cDNA. Gene. 1994 Oct 11;148(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydall D., Weinert T. Yeast checkpoint genes in DNA damage processing: implications for repair and arrest. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1488–1491. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Burkill H., Evans S., Cox B. S. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 gene complements a Schizosaccharomyces pombe repair mutation. Curr Genet. 1989 Jan;15(1):27–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00445748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow D. M., Tagle D. A., Shiloh Y., Collins F. S., Hieter P. TEL1, an S. cerevisiae homolog of the human gene mutated in ataxia telangiectasia, is functionally related to the yeast checkpoint gene MEC1. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami H., Okayama H. A kinase from fission yeast responsible for blocking mitosis in S phase. Nature. 1995 Apr 27;374(6525):817–819. doi: 10.1038/374817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Doe C. L., Schenk P., Carr A. M., Lehmann A. R., Watts F. Z. Cloning and characterisation of the S. pombe rad15 gene, a homologue to the S. cerevisiae RAD3 and human ERCC2 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2673–2678. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulovich A. G., Hartwell L. H. A checkpoint regulates the rate of progression through S phase in S. cerevisiae in response to DNA damage. Cell. 1995 Sep 8;82(5):841–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley R., Subramani S., Young P. G. Checkpoint controls in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: rad1. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabers C. J., Martin M. M., Brunn G. J., Williams J. M., Dumont F. J., Wiederrecht G., Abraham R. T. Isolation of a protein target of the FKBP12-rapamycin complex in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):815–822. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez Y., Desany B. A., Jones W. J., Liu Q., Wang B., Elledge S. J. Regulation of RAD53 by the ATM-like kinases MEC1 and TEL1 in yeast cell cycle checkpoint pathways. Science. 1996 Jan 19;271(5247):357–360. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5247.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitsky K., Bar-Shira A., Gilad S., Rotman G., Ziv Y., Vanagaite L., Tagle D. A., Smith S., Uziel T., Sfez S. A single ataxia telangiectasia gene with a product similar to PI-3 kinase. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1749–1753. doi: 10.1126/science.7792600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitsky K., Sfez S., Tagle D. A., Ziv Y., Sartiel A., Collins F. S., Shiloh Y., Rotman G. The complete sequence of the coding region of the ATM gene reveals similarity to cell cycle regulators in different species. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Nov;4(11):2025–2032. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.11.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schu P. V., Takegawa K., Fry M. J., Stack J. H., Waterfield M. D., Emr S. D. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.8385367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaton B. L., Yucel J., Sunnerhagen P., Subramani S. Isolation and characterization of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad3 gene, involved in the DNA damage and DNA synthesis checkpoints. Gene. 1992 Sep 21;119(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick K. S., Carr A. M. Feedback controls and G2 checkpoints: fission yeast as a model system. Bioessays. 1993 Dec;15(12):775–782. doi: 10.1002/bies.950151202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siede W., Friedberg A. S., Dianova I., Friedberg E. C. Characterization of G1 checkpoint control in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae following exposure to DNA-damaging agents. Genetics. 1994 Oct;138(2):271–281. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Z., Fay D. S., Marini F., Foiani M., Stern D. F. Spk1/Rad53 is regulated by Mec1-dependent protein phosphorylation in DNA replication and damage checkpoint pathways. Genes Dev. 1996 Feb 15;10(4):395–406. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Bernards R. rad-dependent response of the chk1-encoded protein kinase at the DNA damage checkpoint. Science. 1996 Jan 19;271(5247):353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5247.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N., Davey S., Beach D. Fission yeast chk1 protein kinase links the rad checkpoint pathway to cdc2. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):368–371. doi: 10.1038/363368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. Cell cycle arrest of cdc mutants and specificity of the RAD9 checkpoint. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):63–80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Kiser G. L., Hartwell L. H. Mitotic checkpoint genes in budding yeast and the dependence of mitosis on DNA replication and repair. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 15;8(6):652–665. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.6.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Khodairy F., Carr A. M. DNA repair mutants defining G2 checkpoint pathways in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1343–1350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Khodairy F., Fotou E., Sheldrick K. S., Griffiths D. J., Lehmann A. R., Carr A. M. Identification and characterization of new elements involved in checkpoint and feedback controls in fission yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):147–160. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]