Abstract
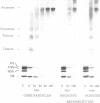
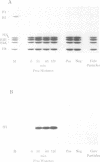
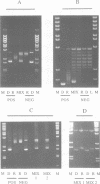
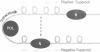
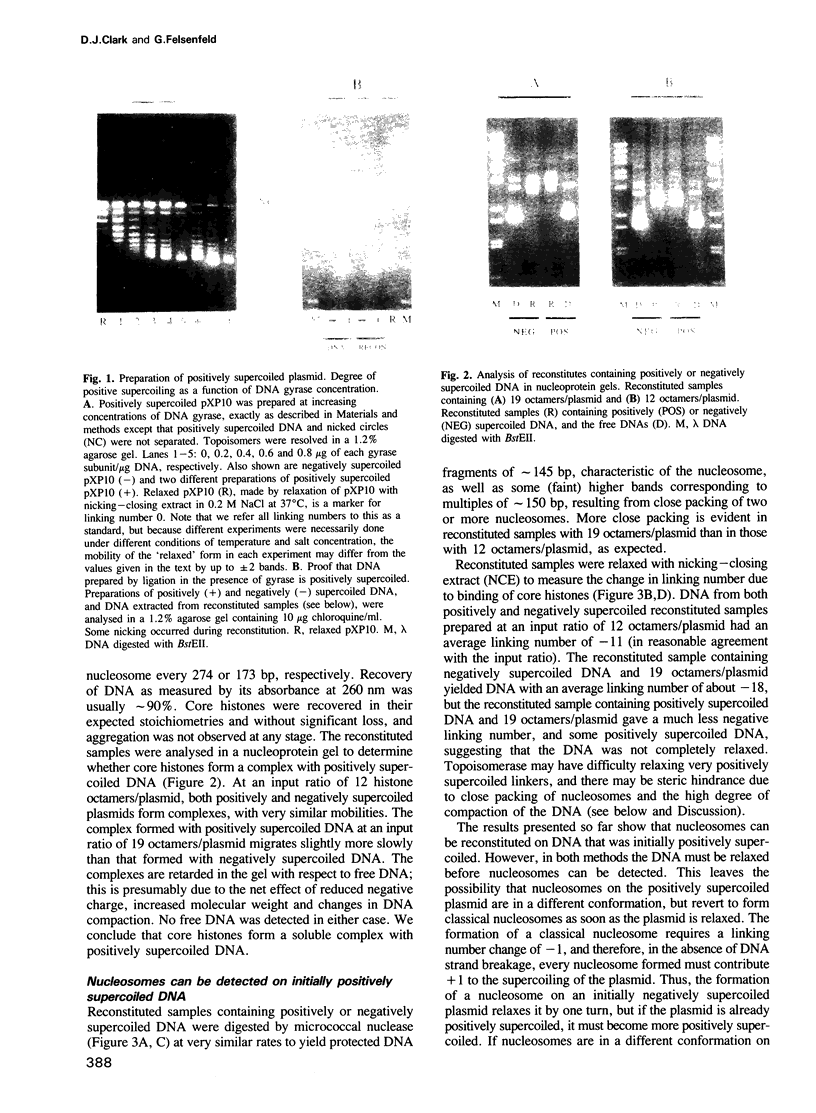
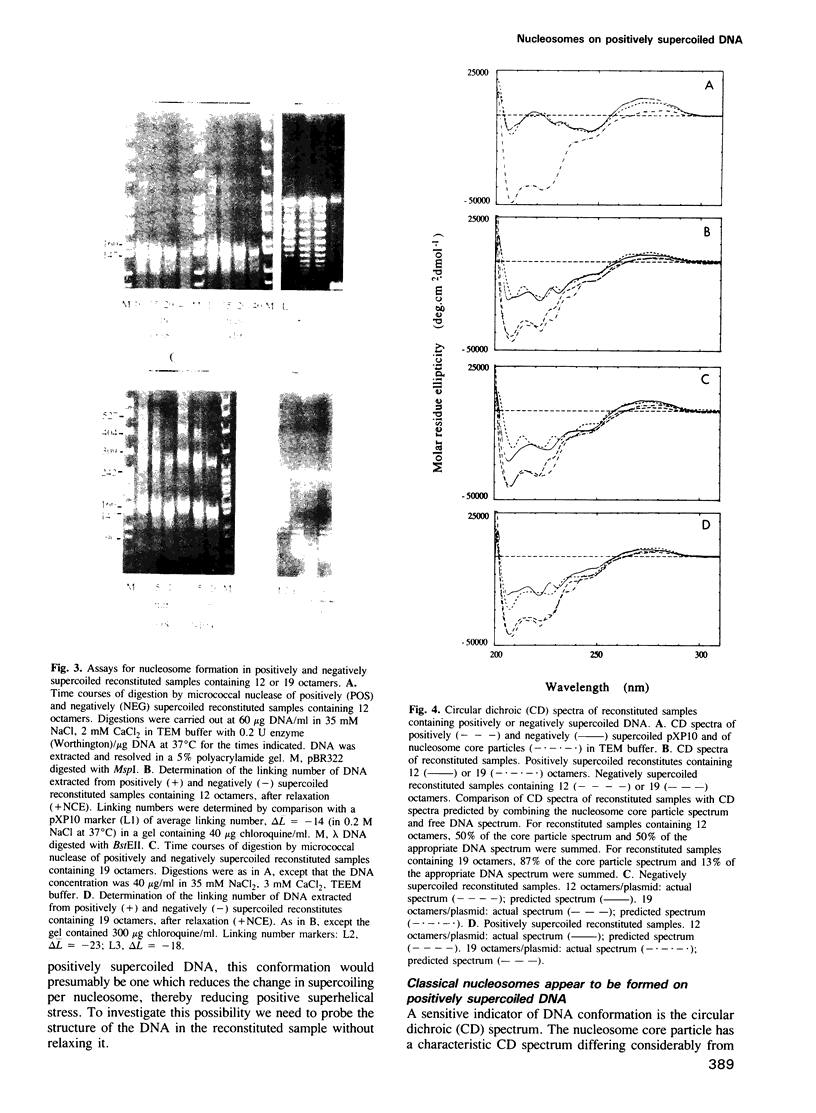
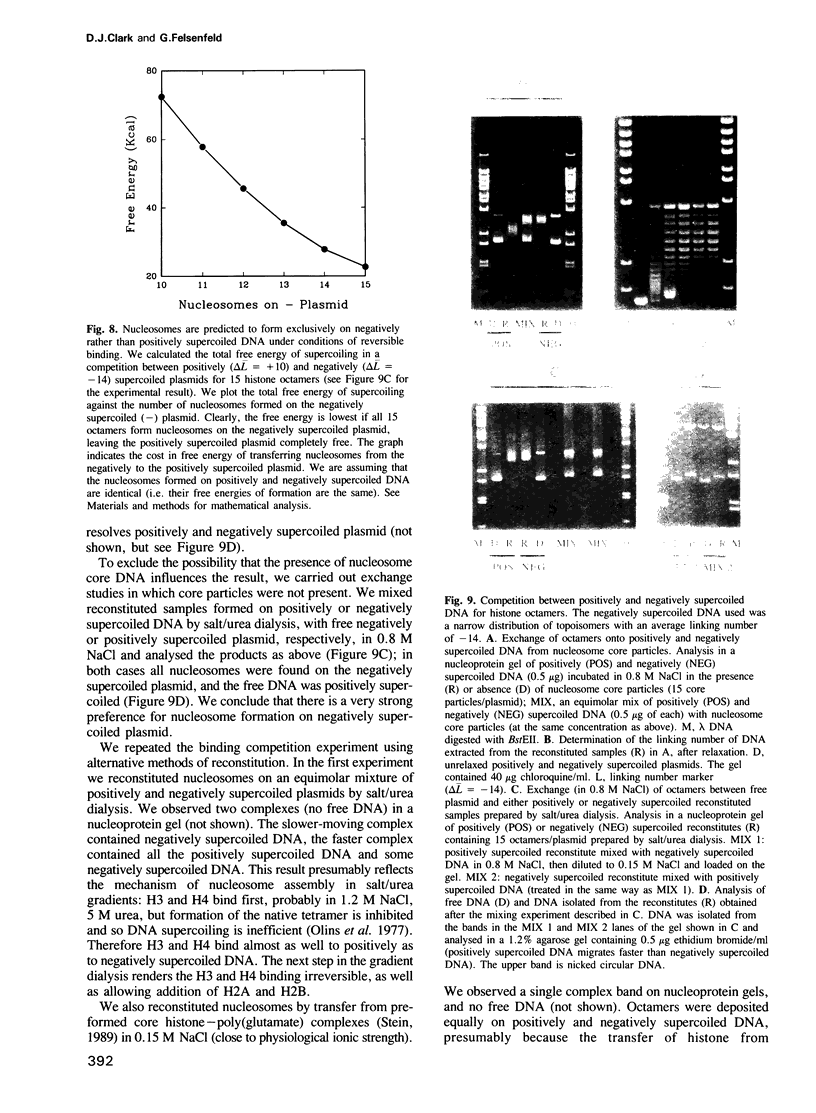
A transcribing RNA polymerase is thought to generate positive supercoils in front of the advancing transcription complex and negative supercoils behind. We have examined the possibility that positive supercoils might destabilize nucleosomes, facilitating transcription. We show that histone octamers bind to positively supercoiled DNA, and that after the complex is relaxed, 'classical' nucleosomes are present. We tested the possibility that nucleosomes on positively supercoiled DNA are in an altered (presumably more open) conformation, but revert to the classical structure only on release of this stress. However, circular dichroic spectra, and chemical cross-linking and modification of core histones, all suggest that the complexes initially formed on positively supercoiled DNA are classical nucleosomes. Although such structures are stable, their formation requires the plasmid to become more positively supercoiled, resulting in greater superhelical stress. In contrast, formation of nucleosomes on negatively supercoiled DNA relieves superhelical stress. In an exchange experiment in which equilibrium is achieved, nucleosomes transfer from positively to negatively supercoiled DNA, as predicted from the super-coiling free energies of the reactions. This suggests a mechanism for transcription of a gene assembled into chromatin, in which octamers are sequentially transferred from the region in front of the polymerase to the region behind.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegra P., Sterner R., Clayton D. F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatographic purification of nucleosomes containing transcriptionally active DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Dong F., van Holde K. E. Use of selectively trypsinized nucleosome core particles to analyze the role of the histone "tails" in the stabilization of the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates A. D., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase can supercoil DNA circles as small as 174 base pairs. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Cantor C. R., Axel R. Nucleosomes are phased along the mouse beta-major globin gene in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90835-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Butler M. J., Hyde J. E., Phillips D., Skidmore C. J., Walker I. O. The interaction of core histones with DNA: equilibrium binding studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3643–3663. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Histone H3 disulfide dimers and nucleosome structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5519–5523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Kimura T., Gould H., Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bernardin W., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Structure of in-vivo transcribing chromatin as studied in simian virus 40 minichromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):469–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Felsenfeld G. Hydrodynamic studies of the interaction between nucleosome core particles and core histones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):537–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. A., Felsenfeld G. Comparison of the folding of beta-globin and ovalbumin gene containing chromatin isolated from chicken oviduct and erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):8010–8016. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. Gene transcription. Waves of DNA supercoiling. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):206–206. doi: 10.1038/337206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Felsenfeld G., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Effects of DNA supercoiling on the topological properties of nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2620–2623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Jacob G. A., Luse D. S. Assembly of RNA polymerase II preinitiation complexes before assembly of nucleosomes allows efficient initiation of transcription on nucleosomal templates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3114–3121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Luse D. S. The presence of nucleosomes on a DNA template prevents initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libertini L. J., Ausió J., van Holde K. E., Small E. W. Histone hyperacetylation. Its effects on nucleosome core particle transitions. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):477–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83126-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. On the displacement of histones from DNA by transcription. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):743–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa R., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes in vitro through a nucleosome core without displacing it. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):801–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H. Nucleosomes inhibit both transcriptional initiation and elongation by RNA polymerase III in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2343–2351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins D. E., Bryan P. N., Harrington R. E., Hill W. E., Olins A. L. Conformational states of chromatin nu bodies induced by urea. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1911–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Morse R. H. Effect of transcription of yeast chromatin on DNA topology in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1873–1881. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Felsenfeld G. A new procedure for purifying histone pairs H2A + H2B and H3 + H4 from chromatin using hydroxylapatite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):689–696. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A. DNA folding by histones: the kinetics of chromatin core particle reassembly and the interaction of nucleosomes with histones. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 15;130(2):103–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A. Reconstitution of chromatin from purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:585–603. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O. Chemical cross-linking of histones. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:549–571. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. P., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Eisenberg H. Binding of additional histones to chromatin core particles. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):446–448. doi: 10.1038/273446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J., Chen T. A., Sterner R., Berger M., Winston F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatography of mammalian and yeast nucleosomes. Two modes of binding of transcriptionally active mammalian nucleosomes to organomercurial-agarose columns, and contrasting behavior of the active nucleosomes of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5736–5746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Shyy S. H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Transcription generates positively and negatively supercoiled domains in the template. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager T. D., McMurray C. T., van Holde K. E. Salt-induced release of DNA from nucleosome core particles. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2271–2281. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Jessee C. B., Lau K., Zhang H., Liu L. F. Template supercoiling during ATP-dependent DNA helix tracking: studies with simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]