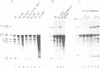Abstract
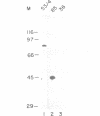
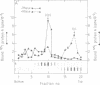
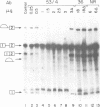
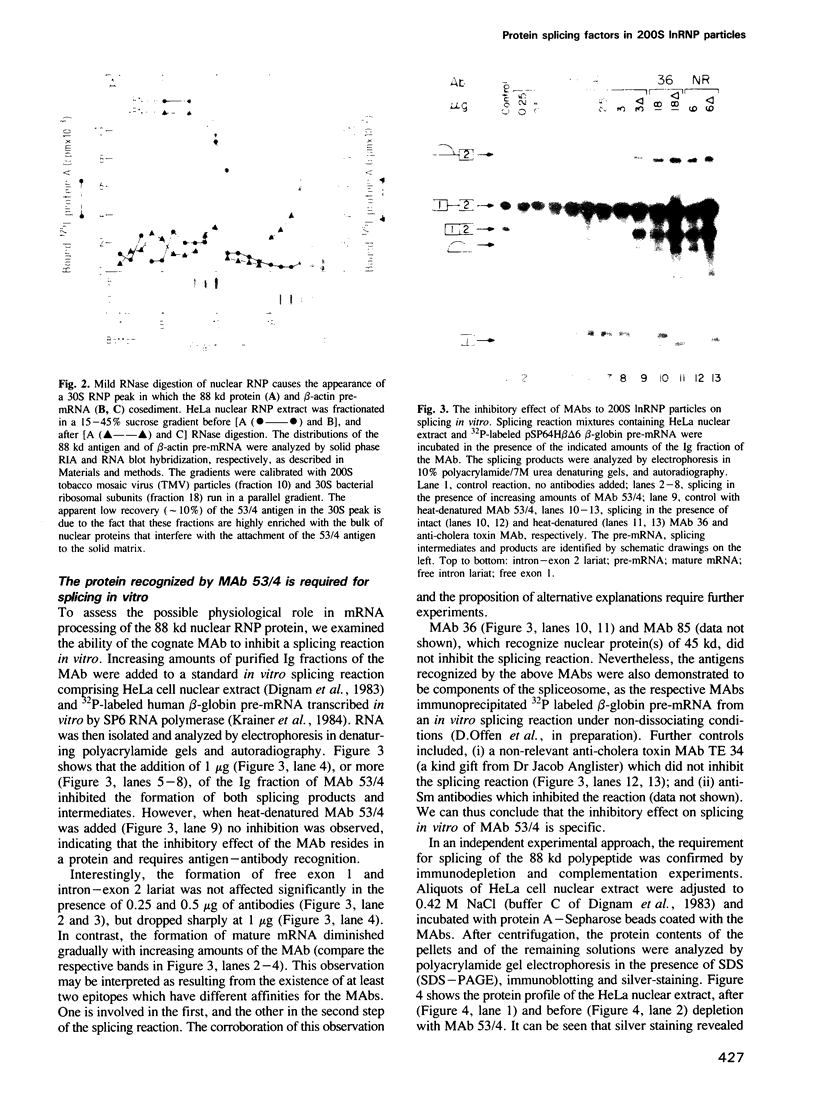
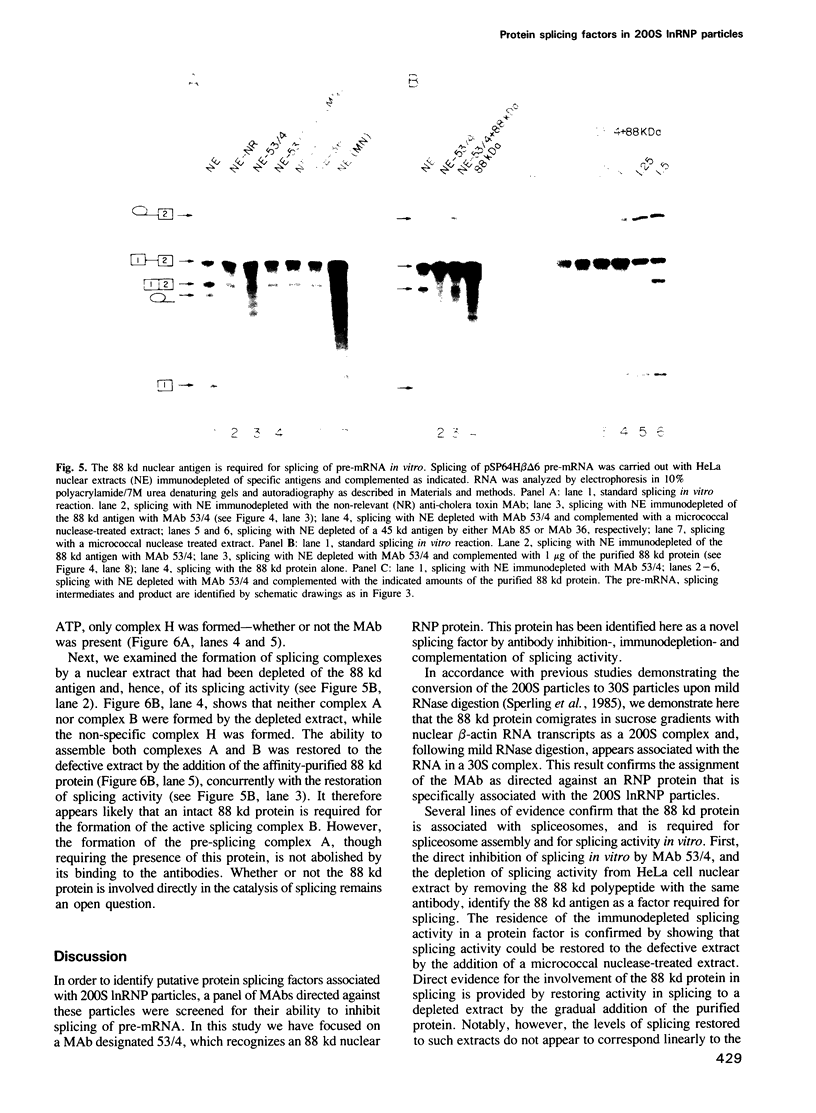
In previous studies we have shown that nuclear transcripts of several pre-mRNAs can be released from nuclei of mammalian cells in the form of large nuclear ribonucleoprotein (InRNP) particles. By electron microscopy, these particles appeared as compact composite structures, 50 nm in diameter, which invariably sedimented at the 200S region in sucrose gradients. In order to identify putative protein splicing factors associated with the 200S InRNP particles, a panel of monoclonal antibodies directed against these particles were screened for their ability to inhibit splicing of pre-mRNA in vitro. In this study we have focused on a nuclear protein of 88 kd in molecular weight, which is an integral component of the InRNP complex and is recognized by monoclonal antibodies from a specific clone. This protein has been identified here as a novel splicing factor by, (i) antibody inhibition of splicing in vitro and (ii) depletion of splicing activity from HeLa cell nuclear extract after removing the 88 kd polypeptide by immunoadsorption, and complementation of the depleted activity with an affinity-purified 88 kd antigen. This splicing factor has further been shown to be required for the assembly of an active splicing complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-ribonucleoprotein complex (hnRNP): a unique supramolecular assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7471–7475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Monoclonal antibody characterization of the C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1997–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Karpel R. L., Williams K. R., Notario V., Wilson S. H. Mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex protein A1. Large-scale overproduction in Escherichia coli and cooperative binding to single-stranded nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1063–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser D. F., Patchornik A., Merril C. R. Development of polyacrylamide gels that improve the separation of proteins and their detection by silver staining. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):412–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in formation of spliceosomes. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):763–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90614-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeStourgeon W. M., Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., Poupore S. M., Daniels L. P. The packaging proteins of core hnRNP particles and the maintenance of proliferative cell states. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):885–898. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leser G. P., Escara-Wilke J., Martin T. E. Monoclonal antibodies to heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes. The core proteins comprise a conserved group of related polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1827–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz Y., Jacob M., Fuchs J. P. The distribution of two hnRNP-associated proteins defined by a monoclonal antibody is altered in heat-shocked HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Mar;175(1):109–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm D. B., Sommerville J. The structure of chromosome-derived ribonucleoprotein in oocytes of Triturus cristatus carnifex (Laurenti). Chromosoma. 1974;48(2):137–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00283960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarina O. P., Lukanidin E. M., Molnar J., Georgiev G. P. Structural organization of nuclear complexes containing DNA-like RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Szer W., Furdon P. J., Kole R. Antibodies to hnRNP core proteins inhibit in vitro splicing of human beta-globin pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5241–5254. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spann P., Feinerman M., Sperling J., Sperling R. Isolation and visualization of large compact ribonucleoprotein particles of specific nuclear RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Spann P., Offen D., Sperling J. U1, U2, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are associated with large nuclear RNP particles containing transcripts of an amplified gene in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6721–6725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Sperling J., Levine A. D., Spann P., Stark G. R., Kornberg R. D. Abundant nuclear ribonucleoprotein form of CAD RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):569–575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]