Abstract
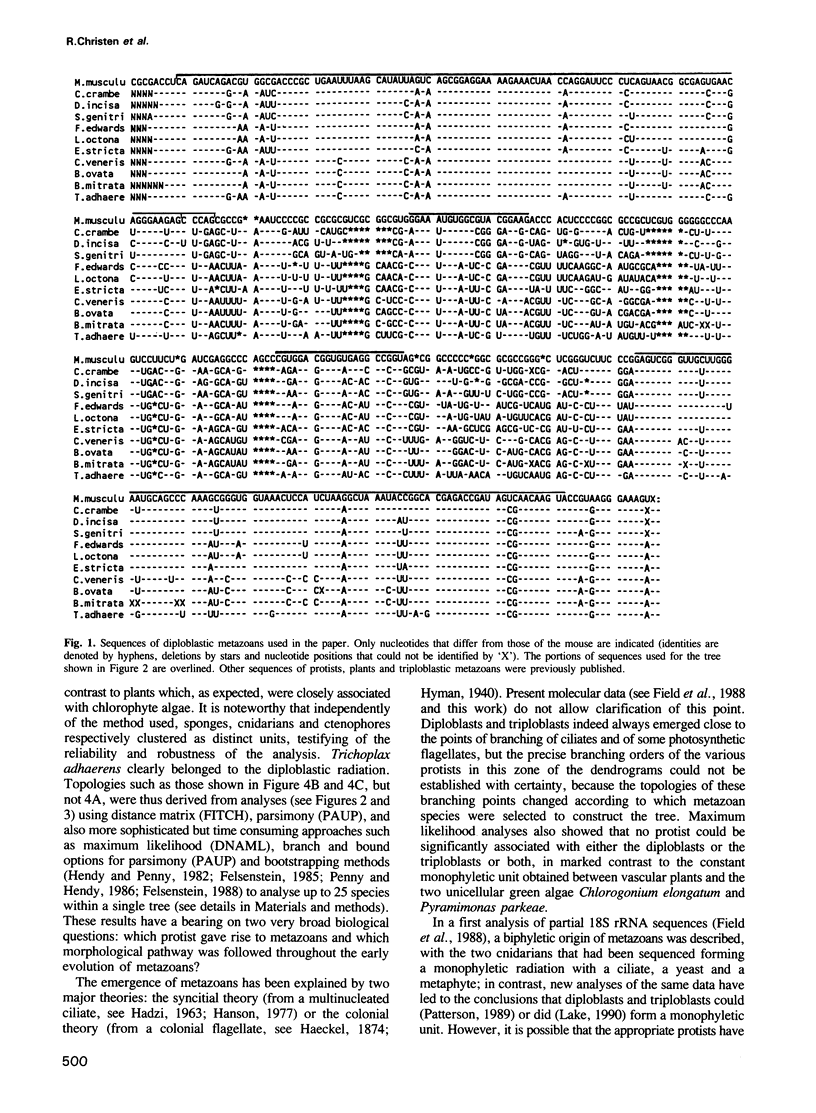
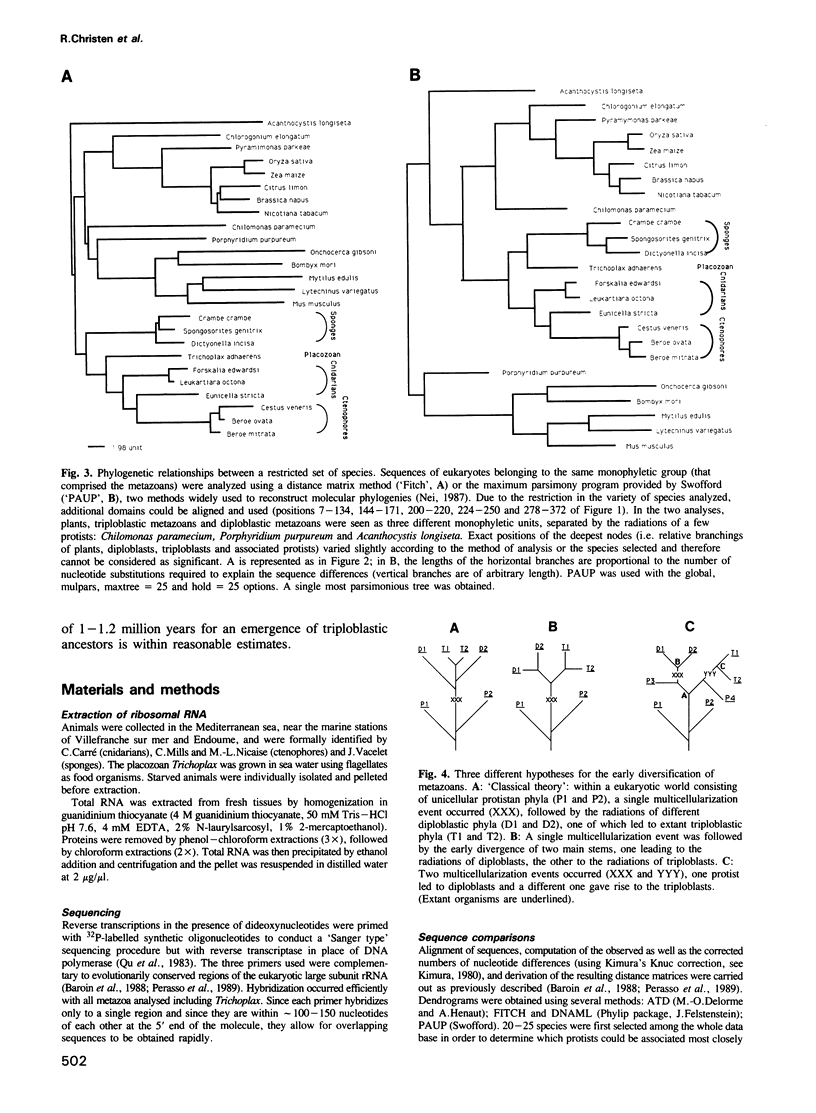
In order to study the origin of metazoans, we have compared sequences from the 5' end of the large subunit ribosomal RNA of a number of protists, fungi, plants and metazoans, including all diploblastic phyla (sequences of 10 new species have been determined, including that of the placozoan, Trichoplax adhaerens). These sequences were analyzed using distance matrix, maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood methods, and the validity of the results was ascertained with bootstrapping and species removal or addition. Triploblasts and diploblasts formed two clearly separated monophyletic units; this divergence, which apparently preceded the diversification of diploblastic animals (i.e. the successive sponge, ctenophore, cnidarian radiations), showed a much more ancient origin of triploblasts with respect to diploblasts than classically assumed. These results do not exclude the possibility that triploblasts and diploblasts arose independently from different protists.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroin A., Perasso R., Qu L. H., Brugerolle G., Bachellerie J. P., Adoutte A. Partial phylogeny of the unicellular eukaryotes based on rapid sequencing of a portion of 28S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloud P., Glaessner M. F. The ediacarian period and syste: metazoa inherit the Earth. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):783–792. doi: 10.1126/science.217.4562.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:521–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field K. G., Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Ghiselin M. T., Raff E. C., Pace N. R., Raff R. A. Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):748–753. doi: 10.1126/science.3277277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Li W. H. Molecular phylogeny of the kingdoms Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Mar;6(2):109–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Origin of the Metazoa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):763–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. C. Burgess shale faunas and the cambrian explosion. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):339–346. doi: 10.1126/science.246.4928.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny D., Hendy M. Estimating the reliability of evolutionary trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):403–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perasso R., Baroin A., Qu L. H., Bachellerie J. P., Adoutte A. Origin of the algae. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):142–144. doi: 10.1038/339142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu H. L., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Improved methods for structure probing in large RNAs: a rapid 'heterologous' sequencing approach is coupled to the direct mapping of nuclease accessible sites. Application to the 5' terminal domain of eukaryotic 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5903–5920. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu L. H., Nicoloso M., Bachellerie J. P. Phylogenetic calibration of the 5' terminal domain of large rRNA achieved by determining twenty eucaryotic sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02143502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J., Gunderson J. H. Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker R. H., Margulis L. Protist classification and the kingdoms of organisms. Biosystems. 1978 Apr;10(1-2):3–18. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


