Abstract
We have shown that a transcriptional repressor protein can regulate promoter activity via DNA bending by using the pLS1 plasmid promoter PII (which has intrinsic curvature upstream of its -35 box) and the plasmid-encoded repressor protein RepA (which strongly bends DNA). Substitution of the curved region for a straight DNA fragment containing the RepA target resulted in increased (or decreased) gene expression when RepA was supplied in trans: enhanced gene expression was evident when the target of RepA and the promoter were on the same face of the DNA helix; repression was found when they were on opposite faces of the DNA. In vitro activation of transcription from PII was observed when supercoiled DNA was used as template, but not with linear molecules. We propose that promoter activity can be regulated by the proper positioning (in or out of phase) of an induced DNA bend with the RNA polymerase recognition sites.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. Multipartite genetic control elements: communication by DNA loop. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:227–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amouyal M., Buc H. Topological unwinding of strong and weak promoters by RNA polymerase. A comparison between the lac wild-type and the UV5 sites of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):795–808. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester S., Alonso J. C., López P., Espinosa M. Comparative expression of the pC194 cat gene in Streptococcus pneumoniae, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H. Mechanism of activation of transcription by the complex formed between cyclic AMP and its receptor in Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Apr;14(2):196–199. doi: 10.1042/bst0140196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Ptashne M. Turning lambda Cro into a transcriptional activator. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90551-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R., McCall M. J. The intrinsic curvature of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. M., Molloy P. L., Both G. W., Drew H. R. Influence of the sequence-dependent flexure of DNA on transcription in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9447–9468. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Fried M. Transmission of long-range effects in DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):263–269. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Hoar E. Upstream activation sites of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are active when inverted but not when placed downstream of the "TATA box". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Taylor A., Kedes L. DNA bending is induced by a transcription factor that interacts with the human c-FOS and alpha-actin promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W., Schleif R. F. Regulation of the Escherichia coli L-arabinose operon studied by gel electrophoresis DNA binding assay. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):611–628. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herendeen D. R., Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. An RNA polymerase-binding protein that is required for communication between an enhancer and a promoter. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):573–578. doi: 10.1126/science.2185541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Tsui P., Freundlich M. Integration host factor is a negative effector of in vivo and in vitro expression of ompC in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5293–5298. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5293-5298.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlarz D., Fritsch A., Buc H. Variations of intramolecular ligation rates allow the detection of protein-induced bends in DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):799–803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnke G., Theres C., Fritz H. J., Ehring R. RNA polymerase and gal repressor bind simultaneously and with DNA bending to the control region of the Escherichia coli galactose operon. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Baim S. B., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Conversion of the lac repressor into an allosterically regulated transcriptional activator for mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3343–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Lopez P., Greenberg B., Espinosa M. Identification and analysis of genes for tetracycline resistance and replication functions in the broad-host-range plasmid pLS1. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):753–765. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez P., Martinez S., Diaz A., Espinosa M., Lacks S. A. Characterization of the polA gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae and comparison of the DNA polymerase I it encodes to homologous enzymes from Escherichia coli and phage T7. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4255–4263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Rotational orientation of upstream curved DNA affects promoter function in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10451–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Patel I., Bastia D. Conformational changes in a replication origin induced by an initiator protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Bending and supercoiling of DNA at the attachment site of bacteriophage lambda. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Vanet A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. The role of FIS in trans activation of stable RNA operons of E. coli. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):727–734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Plasmid incompatibility. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):381–395. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.381-395.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaskon R. R., Wartell R. M. Sequence distributions associated with DNA curvature are found upstream of strong E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):785–796. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puyet A., del Solar G. H., Espinosa M. Identification of the origin and direction of replication of the broad-host-range plasmid pLS1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):115–133. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
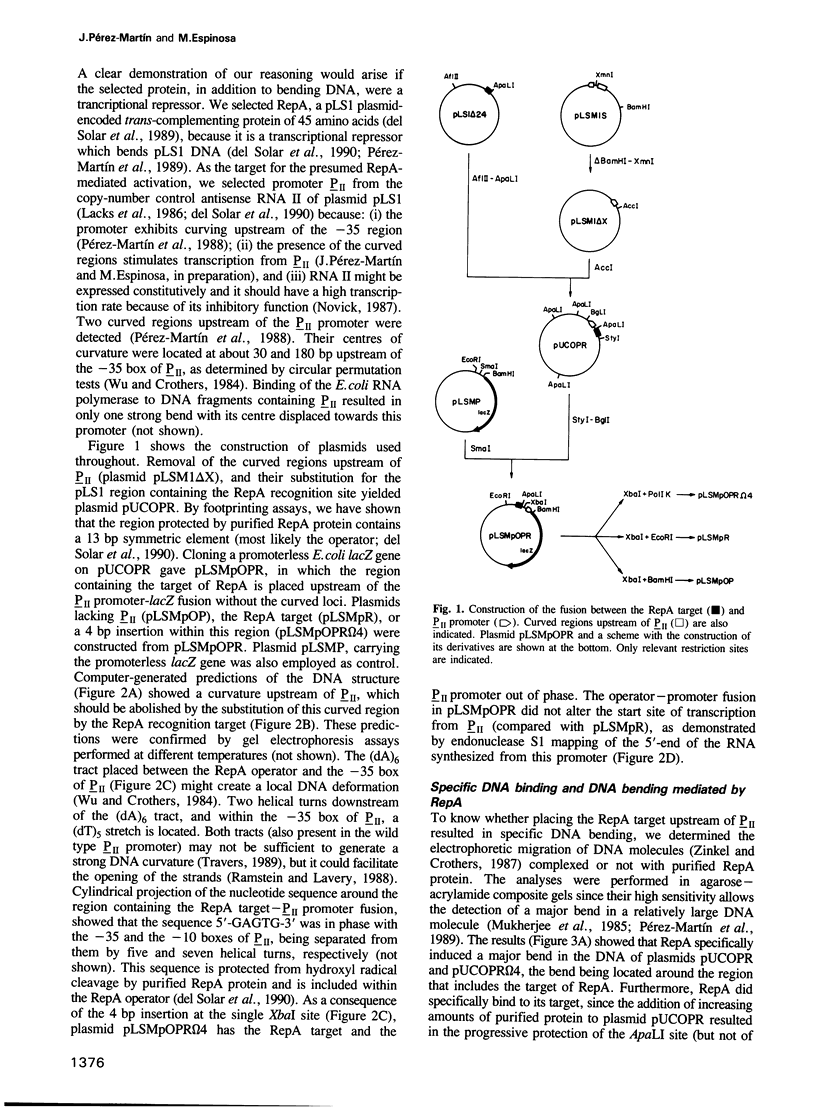
- Pérez-Martín J., del Solar G. H., Lurz R., de la Campa A. G., Dobrinski B., Espinosa M. Induced bending of plasmid pLS1 DNA by the plasmid-encoded protein RepA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21334–21339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., del Solar G. H., de la Campa A. G., Espinosa M. Three regions in the DNA of plasmid pLS1 show sequence-directed static bending. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9113–9126. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramstein J., Lavery R. Energetic coupling between DNA bending and base pair opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7231–7235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Zaballos A., Salas M. Bend induced by the phage phi 29 transcriptional activator in the viral late promoter is required for activation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90072-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase bends the res site into a recombinogenic complex. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3609–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Groot Koerkamp M. J., Teunissen A. W., Tabak H. F. RNA polymerase induces DNA bending at yeast mitochondrial promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9147–9163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Cook G. R., Bradbury E. M., Gottesfeld J. M. Transcription factor IIIA induced bending of the Xenopus somatic 5S gene promoter. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):487–488. doi: 10.1038/340487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. DNA conformation and protein binding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:427–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsung K., Brissette R. E., Inouye M. Enhancement of RNA polymerase binding to promoters by a transcriptional activator, OmpR, in Escherichia coli: its positive and negative effects on transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5940–5944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Sentenac A. Asymmetric DNA bending induced by the yeast multifunctional factor TUF. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Kim J., Adhya S. DNA bending by negative regulatory proteins: Gal and Lac repressors. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):606–611. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G. H., Pérez-Martín J., Espinosa M. Plasmid pLS1-encoded RepA protein regulates transcription from repAB promoter by binding to a DNA sequence containing a 13-base pair symmetric element. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12569–12575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G. H., de al Campa A. G., Pérez-Martín J., Choli T., Espinosa M. Purification and characterization of RepA, a protein involved in the copy number control of plasmid pLS1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2405–2420. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G., Diaz R., Espinosa M. Replication of the streptococcal plasmid pMV158 and derivatives in cell-free extracts of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Mar;206(3):428–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00428882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]