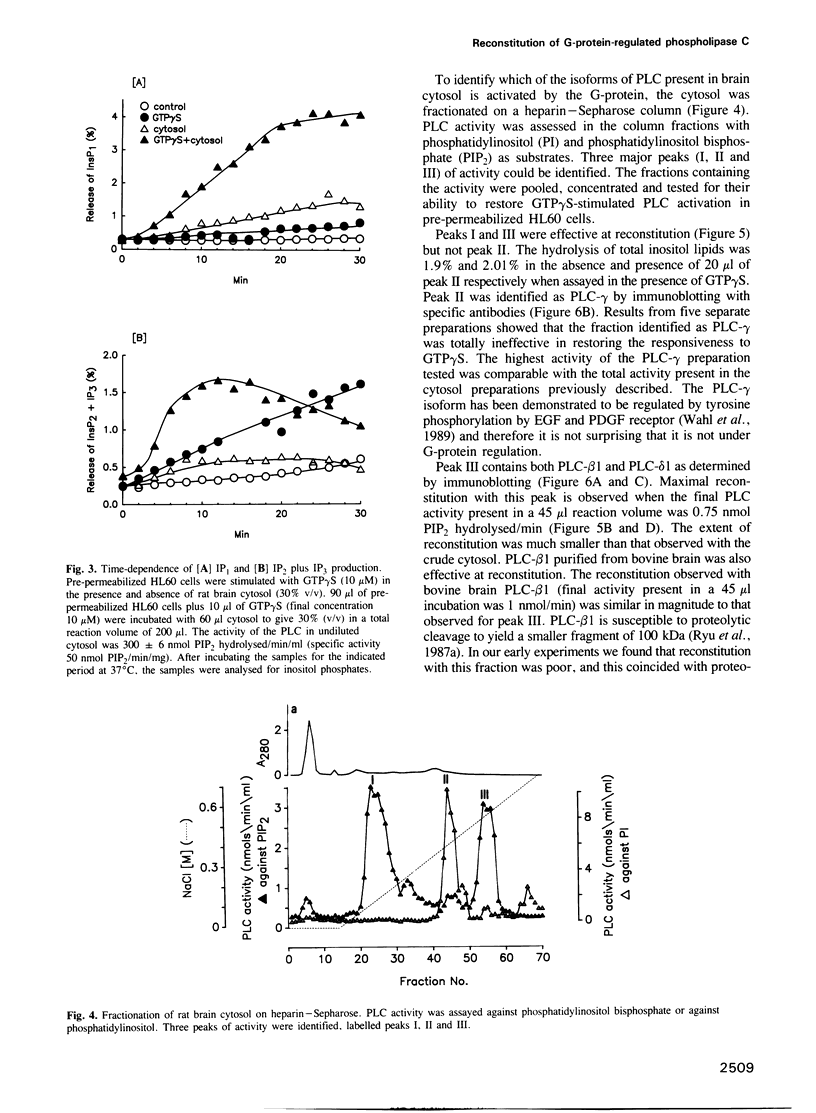
Abstract
Activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC) generates two intracellular signals which play major roles in many cellular processes including secretion, proliferation and contraction. PLC activation by many receptors occurs via a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein, Gp. PLCs are found predominantly in the cytosolic fraction though some activity is membrane-associated. At least four families of iso-enzymes of PLC (alpha, beta, gamma and delta) have been identified, but there is only scant evidence to indicate that any of the mammalian cytosolic activities are involved in G-protein-regulated signalling. In this study we demonstrate that the PLC activity from rat brain cytosol can be regulated in a G-protein-dependent manner in a reconstituted system using pre-permeabilized HL60 cells. We identify two enzymes, PLC-beta and a novel 86 kDa enzyme (designated PLC-epsilon) as the G-protein-regulated enzymes. PLC-epsilon was found to be the major G-protein-regulated enzyme.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldassare J. J., Knipp M. A., Henderson P. A., Fisher G. J. GTP gamma S-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate soluble phospholipase C from human platelets requires soluble GTP-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90692-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno Y., Nakashima S., Tohmatsu T., Nozawa Y., Lapetina E. G. GTP and GDP will stimulate platelet cytosolic phospholipase C independently of Ca2+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):728–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90792-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. R., Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Purification and characterization of PLC-beta m, a muscarinic cholinergic regulated phospholipase C from rabbit brain membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 13;1054(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90213-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. Effect of pertussis toxin and neomycin on G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. A comparison between HL60 membranes and permeabilized HL60 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):343–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2560343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckmyn H., Tu S. M., Majerus P. W. Guanine nucleotides stimulate soluble phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in the absence of membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16553–16558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. Heterogeneity of the calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in rat brain. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):437–442. doi: 10.1042/bj2050437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Imaki J., Nakanishi O., Takenawa T. Isolation and characterization of two different forms of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6592–6598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Simonds W. F., Merendino J. J., Jr, Brann M. R., Spiegel A. M. Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein alpha subunit is essential for its membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):568–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Kriz R. W., Totty N., Philp R., Meldrum E., Aldape R. A., Knopf J. L., Parker P. J. Determination of the primary structure of PLC-154 demonstrates diversity of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activities. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Parker P. J. Purification of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from a particulate fraction of bovine brain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriz R., Lin L. L., Sultzman L., Ellis C., Heldin C. H., Pawson T., Knopf J. Phospholipase C isozymes: structural and functional similarities. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;150:112–127. doi: 10.1002/9780470513927.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum E., Katan M., Parker P. A novel inositol-phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Rapid purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):673–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum E., Parker P. J., Carozzi A. The PtdIns-PLC superfamily and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 19;1092(1):49–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90177-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Waldo G. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. A receptor and G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from turkey erythrocytes. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13501–13507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Heukeroth R. O., Gordon J. I., Gilman A. G. G-protein alpha-subunit expression, myristoylation, and membrane association in COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):728–732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated phospholipase C in streptolysin-O-permeabilised cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):119–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Choi W. C., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Monoclonal antibodies to three phospholipase C isozymes from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Carpenter G. Growth factor signaling pathways: phosphoinositide metabolism and phosphorylation of phospholipase C. Cancer Cells. 1989 Dec;1(4):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



