Abstract
The complex of recA protein with single-stranded DNA in the presence of ATP is the active species in the three enzymatic activities of recA: the initiation of strand exchange, the hydrolysis of ATP and the cleavage of repressors. Here we find by cryo-electron microscopy of unstained and unfixed samples that the helical structure of the protein coat in this complex differs slightly but significantly from the structure in the complex with double-stranded DNA. We discuss how the larger pitch of the complex with single strands (100 +/- 2 A compared with 95 +/- 2 A with double strands) could contribute to its higher enzymatic activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L., Klug A. Arrangement of subunits in flagellar microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1974 May;14(3):523–549. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.3.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
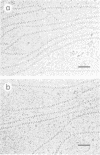
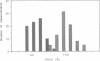
- Chang C. F., Rankert D. A., Jeng T. W., Morgan D. G., Schmid M. F., Chiu W. Cryo electron microscopy of unstained, unfixed RecA-cssDNA complexes. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Aug;100(2):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., West S. C. Homologous pairing and the formation of nascent synaptic intermediates between regions of duplex DNA by RecA protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):987–995. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Roberts J. W. E. coli recA protein-directed cleavage of phage lambda repressor requires polynucleotide. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):26–30. doi: 10.1038/283026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCapua E., Ruigrok R. W., Timmins P. A. Activation of recA protein: the salt-induced structural transition. J Struct Biol. 1990 Jul-Sep;104(1-3):91–96. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90062-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCapua E., Schnarr M., Ruigrok R. W., Lindner P., Timmins P. A. Complexes of RecA protein in solution. A study by small angle neutron scattering. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):557–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90198-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCapua E., Schnarr M., Timmins P. A. The location of DNA in complexes of recA protein with double-stranded DNA. A neutron scattering study. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3287–3292. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Stasiak A. Structure of helical RecA-DNA complexes. Complexes formed in the presence of ATP-gamma-S or ATP. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):677–697. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory J., Tsang S. S., Muniyappa K. Isolation and visualization of active presynaptic filaments of recA protein and single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7026–7030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D., Harris L. D. DNA strand exchanges. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23 (Suppl 1):S43–S86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Bear D. G., Kowalczykowski S. C. Stable DNA heteroduplex formation catalyzed by the Escherichia coli RecA protein in the absence of ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Koller T., Stasiak A. Characterization of the DNA binding activity of stable RecA-DNA complexes. Interaction between the two DNA binding sites within RecA helical filaments. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):97–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizicky E. M., Roberts J. W. Induction of SOS functions: regulation of proteolytic activity of E. coli RecA protein by interaction with DNA and nucleoside triphosphate. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Cox M. M. General mechanism for RecA protein binding to duplex DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Cox M. M. High salt activation of recA protein ATPase in the absence of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):76–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselli W., Stasiak A. Energetics of RecA-mediated recombination reactions. Without ATP hydrolysis RecA can mediate polar strand exchange but is unable to recycle. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):335–352. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Schnarr M. Investigation of RecA--polynucleotide interactions from the measurement of LexA repressor cleavage kinetics. Presence of different types of complex. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Chow S. A., Radding C. M. Networks of DNA and RecA protein are intermediates in homologous pairing. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3226–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C., Cassuto E., Howard-Flanders P. recA protein promotes homologous-pairing and strand-exchange reactions between duplex DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2100–2104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley N. G. The lattice spacing of crystalline catalase as an internal standard of length in electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Sep;24(5):454–464. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]