Abstract
POU proteins constitute a family of ubiquitous as well as cell type-specific transcription factors that share the conserved POU DNA binding domain. This domain consists of two distinct subdomains, a POU-specific domain and a POU homeodomain, that are both required for high affinity sequence-specific DNA binding. In a circular permutation assay, several POU proteins, including Oct-1, Oct-2A, Oct-6 and Pit-1, demonstrated a position dependent mobility of the protein-DNA complexes, suggesting induction of DNA bending. This was confirmed by detection of relative bend direction, using pre-bent DNA, and by enhanced ligase mediated cyclization. Bending was caused by interaction with the POU domain. By contrast, binding of the POU homeodomain did not distort the DNA structure, indicating that the POU-specific domain confers DNA bending.
Full text
PDF

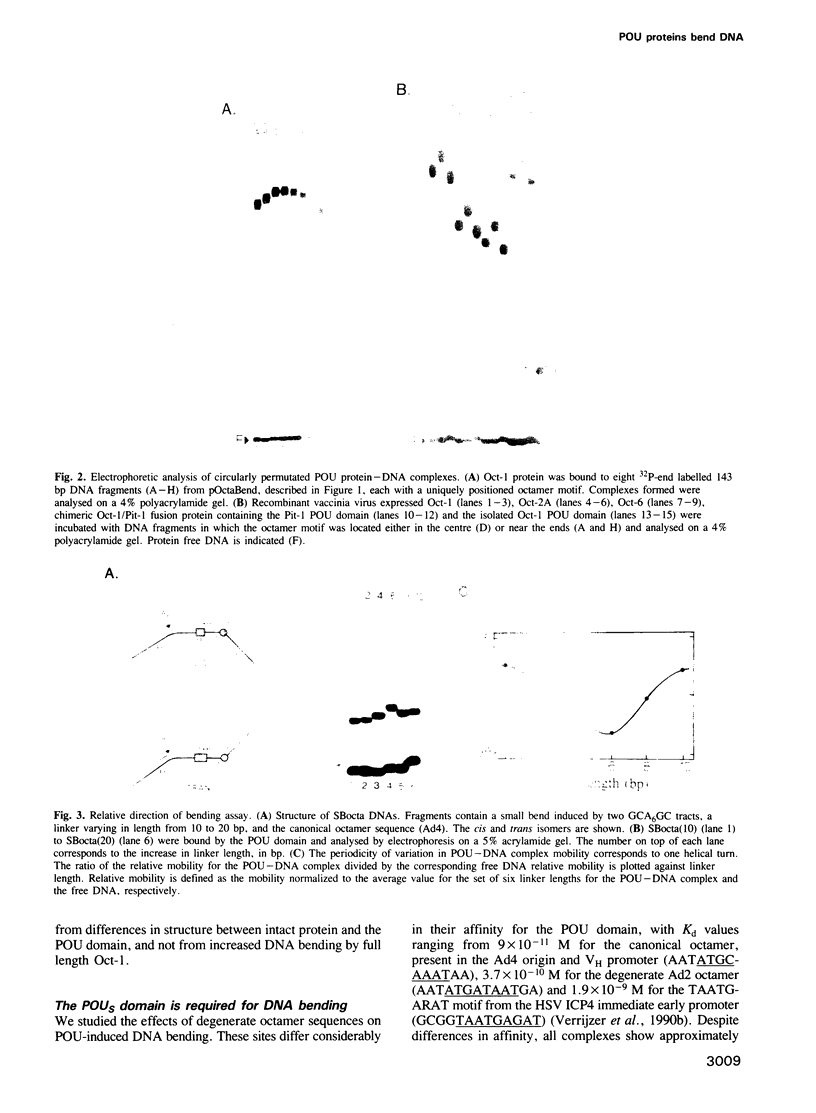

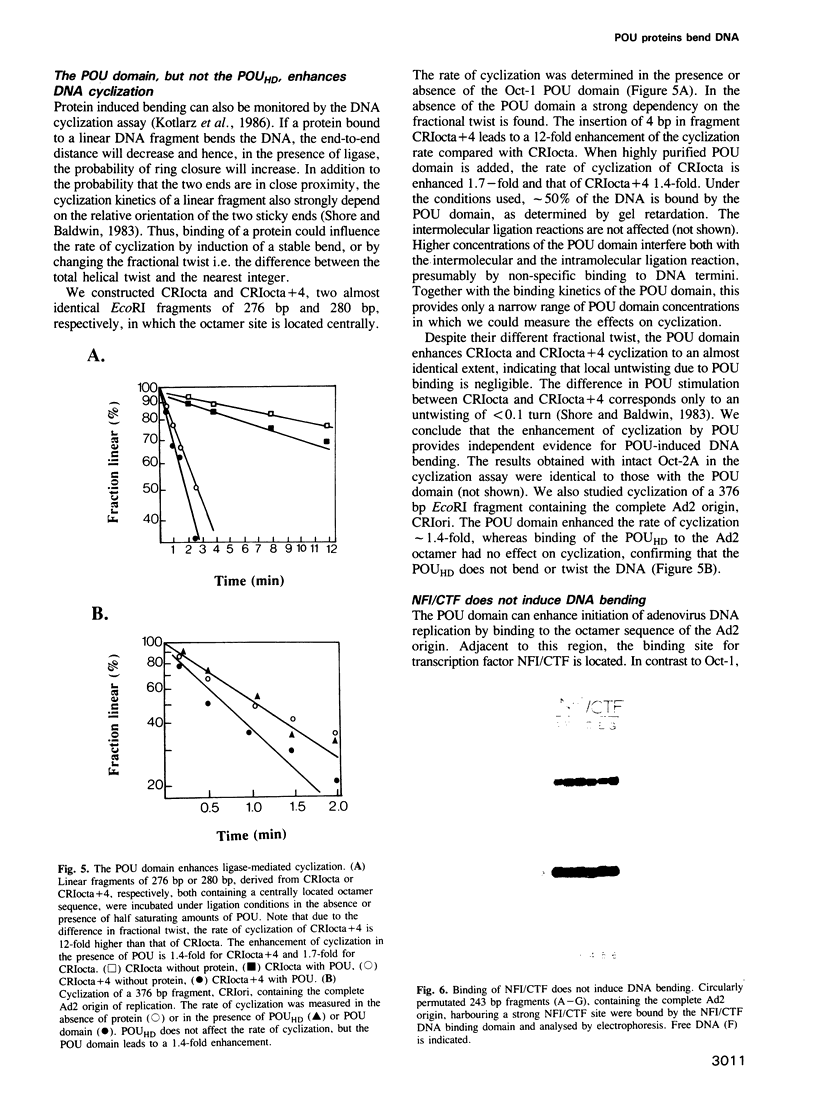



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Schier A., Gehring W. J. Homeodomain proteins and the regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Martin G., Giller T., Brunner L. DNA bending induced by specific interaction of decamer binding proteins with immunoglobulin gene control sequences. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Nov-Dec;101(2-3):145–158. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G., Roderick S. L., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Protein-DNA conformational changes in the crystal structure of a lambda Cro-operator complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8165–8169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Dailey L., Heintz N. H. RIP60, a mammalian origin-binding protein, enhances DNA bending near the dihydrofolate reductase origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6236–6243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drak J., Crothers D. M. Helical repeat and chirality effects on DNA gel electrophoretic mobility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3074–3078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding C. R., O'Hare P. Herpes simplex virus Vmw65-octamer binding protein interaction: a paradigm for combinatorial control of transcription. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):363–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounari F., De Francesco R., Schmitt J., van der Vliet P., Cortese R., Stunnenberg H. Amino-terminal domain of NF1 binds to DNA as a dimer and activates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):559–566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Johnson A. D. Homeo domain of the yeast repressor alpha 2 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain but is not sufficient for repression. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2887035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T. Origin of adenovirus DNA replication. Role of the nuclear factor I binding site in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90263-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Gerrero R., Simmons D. M., Park R. E., Lin C. J., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Tst-1, a member of the POU domain gene family, binds the promoter of the gene encoding the cell surface adhesion molecule P0. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1739–1744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann H., Ricchetti M., Werel W. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli induces bending or an increased flexibility of DNA by specific complex formation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4379–4381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E. Growth hormone gene regulation: a paradigm for cell-type-specific gene activation. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Haigh A., Verrijzer C. P., van der Vliet P. C., O'Hare P. Characterization of a cellular factor which interacts functionally with Oct-1 in the assembly of a multicomponent transcription complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6871–6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Hurwitz J. Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. II. Structural requirements using synthetic oligonucleotide adenovirus templates. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9809–9817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. A human protein specific for the immunoglobulin octamer DNA motif contains a functional homeobox domain. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlarz D., Fritsch A., Buc H. Variations of intramolecular ligation rates allow the detection of protein-induced bends in DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):799–803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A. Interactions of the Oct-1 POU subdomains with specific DNA sequences and with the HSV alpha-trans-activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2383–2396. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer D., Graus A., Kraay R., Langeveld A., Mulder M. P., Grosveld G. The octamer binding factor Oct6: cDNA cloning and expression in early embryonic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7357–7365. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara H., Kaiser E. T. A chemically synthesized Antennapedia homeo domain binds to a specific DNA sequence. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):925–927. doi: 10.1126/science.2903553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monuki E. S., Kuhn R., Weinmaster G., Trapp B. D., Lemke G. Expression and activity of the POU transcription factor SCIP. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1975954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S., Patel I., Bastia D. Conformational changes in a replication origin induced by an initiator protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., Verrijzer C. P., van der Vliet P. C. Transcription factors NFI and NFIII/oct-1 function independently, employing different mechanisms to enhance adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5510–5518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5510-5518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierani A., Heguy A., Fujii H., Roeder R. G. Activation of octamer-containing promoters by either octamer-binding transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) or OTF-2 and requirement of an additional B-cell-specific component for optimal transcription of immunoglobulin promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6204–6215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Chandler M., Galas D. J. Escherichia coli integration host factor bends the DNA at the ends of IS1 and in an insertion hotspot with multiple IHF binding sites. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2479–2487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Zaballos A., Salas M. Bend induced by the phage phi 29 transcriptional activator in the viral late promoter is required for activation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90072-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. H., Vigano M. A., Ozato K., Timmons P. M., Poirier F., Rigby P. W., Staudt L. M. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):686–692. doi: 10.1038/345686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G., Finney M. Regulation of transcription and cell identity by POU domain proteins. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90227-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Groot Koerkamp M. J., Teunissen A. W., Tabak H. F. RNA polymerase induces DNA bending at yeast mitochondrial promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9147–9163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Cook G. R., Bradbury E. M., Gottesfeld J. M. Transcription factor IIIA induced bending of the Xenopus somatic 5S gene promoter. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):487–488. doi: 10.1038/340487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Ruppert S., Suzuki N., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. New type of POU domain in germ line-specific protein Oct-4. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):435–439. doi: 10.1038/344435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. I. Relation between twist and cyclization probability. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):957–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder U. K., Thompson J. F., Landy A. Phasing of protein-induced DNA bends in a recombination complex. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):255–257. doi: 10.1038/341255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel T. T., Patel P., Bastia D. The integration host factor of Escherichia coli binds to bent DNA at the origin of replication of the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Herr W. The POU domain is a bipartite DNA-binding structure. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):601–604. doi: 10.1038/336601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Rohdewohld H., Neuman T., Gruss P., Schöler H. R. Oct-6: a POU transcription factor expressed in embryonal stem cells and in the developing brain. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3723–3732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., Van der Vliet P. C. The DNA binding domain (POU domain) of transcription factor oct-1 suffices for stimulation of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1883–1888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., van der Vliet P. C. The oct-1 homeo domain contacts only part of the octamer sequence and full oct-1 DNA-binding activity requires the POU-specific domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Binding and bending of the lambda replication origin by the phage O protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3605–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Direct evidence for DNA bending at the lambda replication origin. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):416–422. doi: 10.1126/science.2951850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorbas H., Rogge L., Meisterernst M., Winnacker E. L. Hydroxyl radical footprints reveal novel structural features around the NF I binding site in adenovirus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7735–7748. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Kim J., Adhya S. DNA bending by negative regulatory proteins: Gal and Lac repressors. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):606–611. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., van den Heuvel S. J., van der Vliet P. C. Contactpoint analysis of the HeLa nuclear factor I recognition site reveals symmetrical binding at one side of the DNA helix. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







