Abstract
The type III connecting segment of fibronectin contains two cell binding sites, represented by the peptides CS1 and CS5, that are recognized by the integrin receptor alpha 4 beta 1. Using assays measuring the spreading of A375-SM human melanoma cells, we now report that the adhesion promoting activity of a 29 kDa protease fragment of fibronectin containing the COOH-terminal heparin-binding domain (HepII), but lacking CS1 and CS5, is completely sensitive to anti-alpha 4 and anti-beta 1 antibodies, suggesting that HepII contains a third alpha 4 beta 1-binding sequence. Examination of the primary structure of HepII revealed a sequence with homology to CS1. A 19mer peptide spanning this region (designated H1) was found to support cell spreading to the same level as the 29 kDa fragment. H1-dependent adhesion was completely sensitive to anti-alpha 4 and anti-beta 1 antibodies. When soluble peptides were tested for their ability to block cell spreading on the 29 kDa fragment, a 13mer peptide comprising the central core of H1 was found to be completely inhibitory. The active region of H1 was localized to the pentapeptide IDAPS, which is homologous to LDVPS from the active site of CS1. Taken together, these results identify a novel peptide sequence in the HepII region of fibronectin that supports alpha 4 beta 1-dependent cell adhesion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Nagata K., Yamada K. M. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1031(1):91–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota S., Nagai T., Yamada K. M. Characterization of regions of fibronectin besides the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid sequence required for adhesive function of the cell-binding domain using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15938–15943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W. A monoclonal antibody to VLA-4 alpha-chain (CDw49d) induces homotypic lymphocyte aggregation. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):777–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi P., Patel V. P., Lodish H. F. Lymphoid precursor cells adhere to two different sites on fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):489–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernfield M., Sanderson R. D. Syndecan, a developmentally regulated cell surface proteoglycan that binds extracellular matrix and growth factors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Mar 12;327(1239):171–186. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanero M. R., Pulido R., Ursa M. A., Rodríguez-Moya M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. An alternative leukocyte homotypic adhesion mechanism, LFA-1/ICAM-1-independent, triggered through the human VLA-4 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2157–2165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., McIntyre B. W., Koller T. D., Parham P., Brodsky F., Linn D. J., Evans E. L. Identification and characterization of two novel lymphocyte function-associated antigens, L24 and L25. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1510–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbi A. L., Miller L. J., O'Connor K., Larson R. S., Springer T. A. cDNA cloning and complete primary structure of the alpha subunit of a leukocyte adhesion glycoprotein, p150,95. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4023–4028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Matsueda G. R., Plow E. F. A discrete sequence in a platelet integrin is involved in ligand recognition. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):66–68. doi: 10.1038/350066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. G., Hameed H., Campbell G. Induction of fibroblast spreading by Mn2+: a possible role for unusual binding sites for divalent cations in receptors for proteins containing Arg-Gly-Asp. J Cell Sci. 1988 Apr;89(Pt 4):507–513. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.4.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogerty F. J., Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M., Mosher D. F. Inhibition of binding of fibronectin to matrix assembly sites by anti-integrin (alpha 5 beta 1) antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):699–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Cohen I., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Roberts J., Lam S. C., Ginsberg M. H. Selective inhibition of integrin function by antibodies specific for ligand-occupied receptor conformers. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6346–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T. The extended family of proteoglycans: social residents of the pericellular zone. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1201–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Ferreira O. C. Adhesion of human T-lymphoid cells to fibronectin is mediated by two different fibronectin domains. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):121–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Rostagno A., Frangione B. Primary structure of human plasma fibronectin. Characterization of a 38 kDa domain containing the C-terminal heparin-binding site (Hep III site) and a region of molecular heterogeneity. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):923–928. doi: 10.1042/bj2410923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Ferreira O. C., Jr Human B lymphocytes define an alternative mechanism of adhesion to fibronectin. The interaction of the alpha 4 beta 1 integrin with the LHGPEILDVPST sequence of the type III connecting segment is sufficient to promote cell attachment. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3361–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Loftus J. C., Plow E. F. Cytoadhesins, integrins, and platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Feb 25;59(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Hynes R. O. Lymphoid cells recognize an alternatively spliced segment of fibronectin via the integrin receptor alpha 4 beta 1. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90715-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen P. K., McCarthy J. B., Skubitz A. P., Furcht L. T., Letourneau P. C. Recognition of the A chain carboxy-terminal heparin binding region of fibronectin involves multiple sites: two contiguous sequences act independently to promote neural cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2733–2745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Timmons S., Kloczewiak M., Strong D. D., Doolittle R. F. gamma and alpha chains of human fibrinogen possess sites reactive with human platelet receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2068–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of an alternatively spliced site in human plasma fibronectin that mediates cell type-specific adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2637–2647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Komoriya A., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of two distinct regions of the type III connecting segment of human plasma fibronectin that promote cell type-specific adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J. The molecular basis and specificity of integrin-ligand interactions. J Cell Sci. 1990 Dec;97(Pt 4):585–592. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.4.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. Molecular biology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:67–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzard C. S., Radinsky R., Culp L. A. Substratum contacts and cytoskeletal reorganization of BALB/c 3T3 cells on a cell-binding fragment and heparin-binding fragments of plasma fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Aug;165(2):320–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhofer D., Grzesiak J., Pierschbacher M. D. Calcium as a potential physiological regulator of integrin-mediated cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4471–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
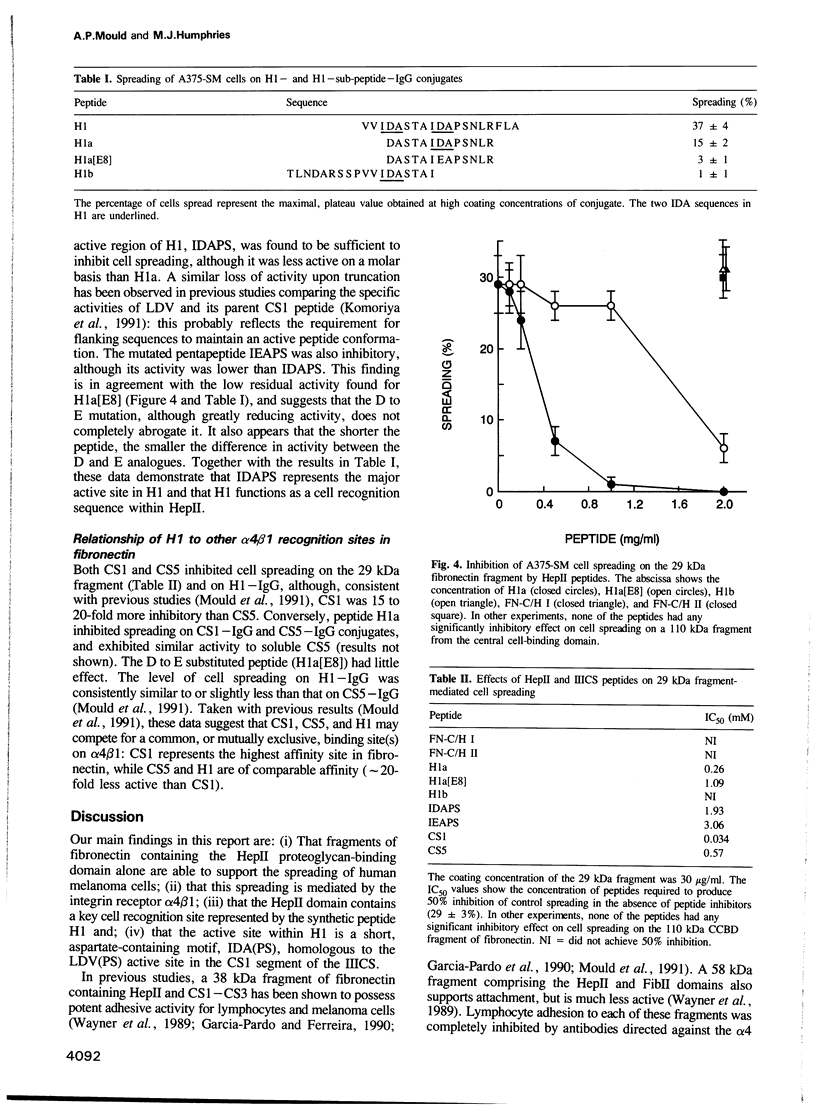
- Komoriya A., Green L. J., Mervic M., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M., Humphries M. J. The minimal essential sequence for a major cell type-specific adhesion site (CS1) within the alternatively spliced type III connecting segment domain of fibronectin is leucine-aspartic acid-valine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15075–15079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Umezawa K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1755–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski J. M., Hart I. R., Fidler I. J., Hanna N. A human melanoma line heterogeneous with respect to metastatic capacity in athymic nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Apr;72(4):913–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao N. S., ST John J., McCarthy J. B., Furcht L. T., Cheung H. T. Adhesion of lymphoid cells to the carboxyl-terminal heparin-binding domains of fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):348–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., O'Toole T. E., Plow E. F., Glass A., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Ginsberg M. H. A beta 3 integrin mutation abolishes ligand binding and alters divalent cation-dependent conformation. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.2392682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Chelberg M. K., Mickelson D. J., Furcht L. T. Localization and chemical synthesis of fibronectin peptides with melanoma adhesion and heparin binding activities. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1380–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Hagen S. T., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin contains distinct adhesion- and motility-promoting domains for metastatic melanoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):179–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Skubitz A. P., Qi Z., Yi X. Y., Mickelson D. J., Klein D. J., Furcht L. T. RGD-independent cell adhesion to the carboxy-terminal heparin-binding fragment of fibronectin involves heparin-dependent and -independent activities. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Quade B. J., Broekelmann T. J., LaChance R., Forsman K., Hasegawa E., Akiyama S. Fibronectin's cell-adhesive domain and an amino-terminal matrix assembly domain participate in its assembly into fibroblast pericellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2957–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Komoriya A., Yamada K. M., Humphries M. J. The CS5 peptide is a second site in the IIICS region of fibronectin recognized by the integrin alpha 4 beta 1. Inhibition of alpha 4 beta 1 function by RGD peptide homologues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3579–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Wheldon L. A., Komoriya A., Wayner E. A., Yamada K. M., Humphries M. J. Affinity chromatographic isolation of the melanoma adhesion receptor for the IIICS region of fibronectin and its identification as the integrin alpha 4 beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4020–4024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugnai G., Lewandowska K., Carnemolla B., Zardi L., Culp L. A. Modulation of matrix adhesive responses of human neuroblastoma cells by neighboring sequences in the fibronectins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):931–943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Yamakawa N., Aota S., Yamada S. S., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Monoclonal antibody characterization of two distant sites required for function of the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin in cell adhesion, cell migration, and matrix assembly. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1295–1305. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Hynes R. O. Alternative splicing of chicken fibronectin in embryos and in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4297–4307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande H., Calaycay J., Lee T. D., Legesse K., Shively J. E., Siri A., Borsi L., Zardi L. Demonstration of structural differences between the two subunits of human-plasma fibronectin in the carboxy-terminal heparin-binding domain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 15;162(2):403–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. I., Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Cell-type-specific fibronectin subunits generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12258–12265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido R., Elices M. J., Campanero M. R., Osborn L., Schiffer S., García-Pardo A., Lobb R., Hemler M. E., Sánchez-Madrid F. Functional evidence for three distinct and independently inhibitable adhesion activities mediated by the human integrin VLA-4. Correlation with distinct alpha 4 epitopes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10241–10245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., Letourneau P. C., Peterson B. A., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B. Selective interaction of peripheral and central nervous system cells with two distinct cell-binding domains of fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1435–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., McCarthy J. B., Palm S. L., Furcht L. T., Letourneau P. C. Neuron-specific interactions with two neurite-promoting fragments of fibronectin. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):369–378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00369.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorstengaard K., Jensen M. S., Sahl P., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Complete primary structure of bovine plasma fibronectin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):441–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada Y., Elices M. J., Crouse C., Hemler M. E. The primary structure of the alpha 4 subunit of VLA-4: homology to other integrins and a possible cell-cell adhesion function. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1361–1368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R., Johansson S., Hök M. Adhesion and cytoskeletal organisation of fibroblasts in response to fibronectin fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):665–670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Dualistic nature of adhesive protein function: fibronectin and its biologically active peptide fragments can autoinhibit fibronectin function. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):29–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zardi L., Carnemolla B., Balza E., Borsi L., Castellani P., Rocco M., Siri A. Elution of fibronectin proteolytic fragments from a hydroxyapatite chromatography column. A simple procedure for the purification of fibronectin domains. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):571–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]