Abstract
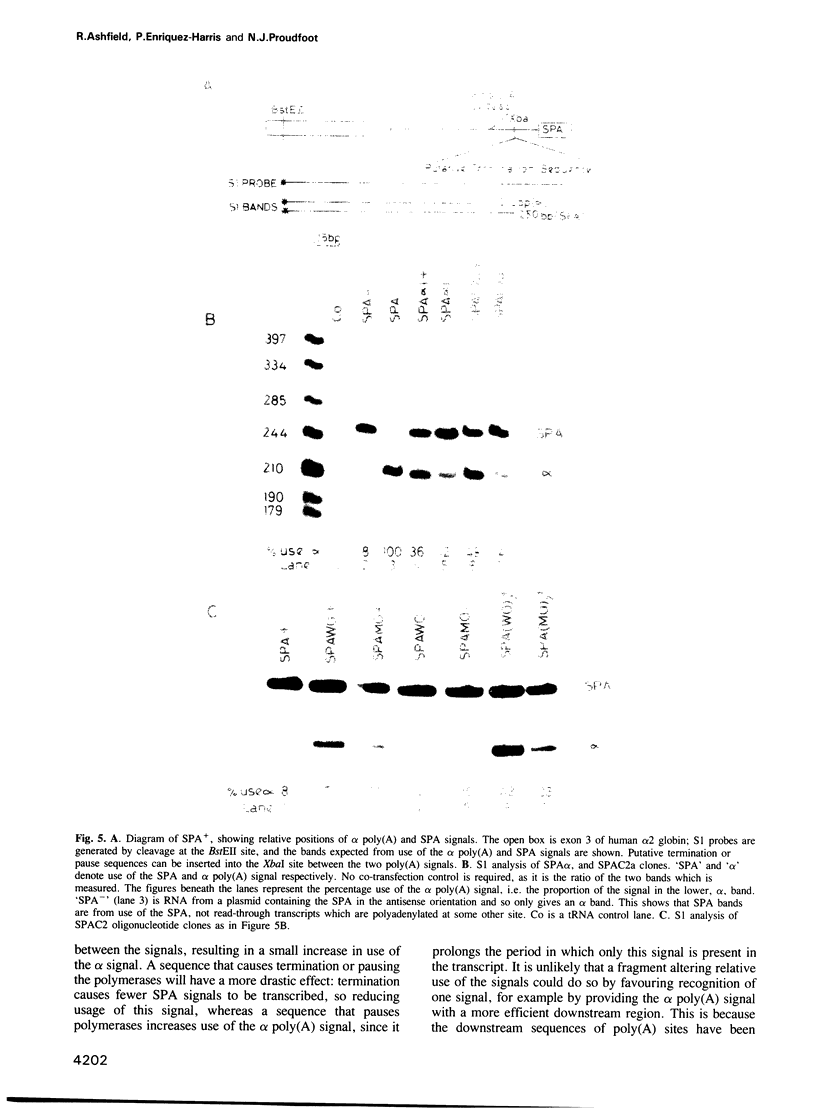
We have demonstrated, using a combination of nuclear run-off and poly(A) site competition assays, that transcriptional termination occurs between the closely spaced human complement genes, C2 and Factor B, soon after the C2 poly(A) site. A comparison of the C2 termination signal with a functionally similar sequence downstream of the human alpha 2 globin gene reveals that both signals function in an orientation dependent manner, with subfragments of the whole signal displaying partial effects. In the case of the C2 termination sequence a protein binds within it, and is partially responsible for the termination effect. We further demonstrate that the same (or closely related) protein binds to the ME1a1 site in the murine c-myc promoter, which has been implicated in c-myc attenuation. We suggest that the termination/pause sequences positioned downstream of a gene's poly(A) site may constitute the general signals that elicit transcriptional termination in genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselin C., Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Molecular requirements for transcriptional initiation of the murine c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baek K. H., Sato K., Ito R., Agarwal K. RNA polymerase II transcription terminates at a specific DNA sequence in a HeLa cell-free reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7623–7627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A CCAAT box sequence in the adenovirus major late promoter functions as part of an RNA polymerase II termination signal. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. A functional mRNA polyadenylation signal is required for transcription termination by RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):440–452. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Manley J. L. RNA polymerase II transcription termination is mediated specifically by protein binding to a CCAAT box sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5254–5259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Structural features of the murine dihydrofolate reductase transcription termination region: identification of a conserved DNA sequence element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4113–4125. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Cribbs D. L., Schibler U. Termination of transcription in the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-2a occurs at multiple sites downstream of the polyadenylation site. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Sollner-Webb B. A transcriptional terminator is a novel element of the promoter of the mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Analysis of the signals for transcription termination by purified RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):269–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription boundaries of U1 small nuclear RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2332–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Acheson N. H. A rabbit beta-globin polyadenylation signal directs efficient termination of transcription of polyomavirus DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2515–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt N., Briggs D., Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Definition of an efficient synthetic poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1019–1025. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Falck-Pedersen E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Shenk T. A poly(A) addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Hart R. P., Wong W. W., Nevins J. R. Sequences capable of restoring poly(A) site function define two distinct downstream elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Transcription termination at the chicken beta H-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5369–5377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E., Jr The definition of a large viral transcription unit late in Ad2 infection of HeLa cells: mapping of nascent RNA molecules labeled in isolated nuclei. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):611–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Proudfoot N. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a poly(A) site mutation reveals that transcriptional termination is linked to 3' end processing in the human alpha 2 globin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2915–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Bishop J. M. DNA sequences that mediate attenuation of transcription from the mouse protooncogene myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. C., Morley B. J., Campbell R. D. Cell-specific expression of the human complement protein factor B gene: evidence for the role of two distinct 5'-flanking elements. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]