Abstract
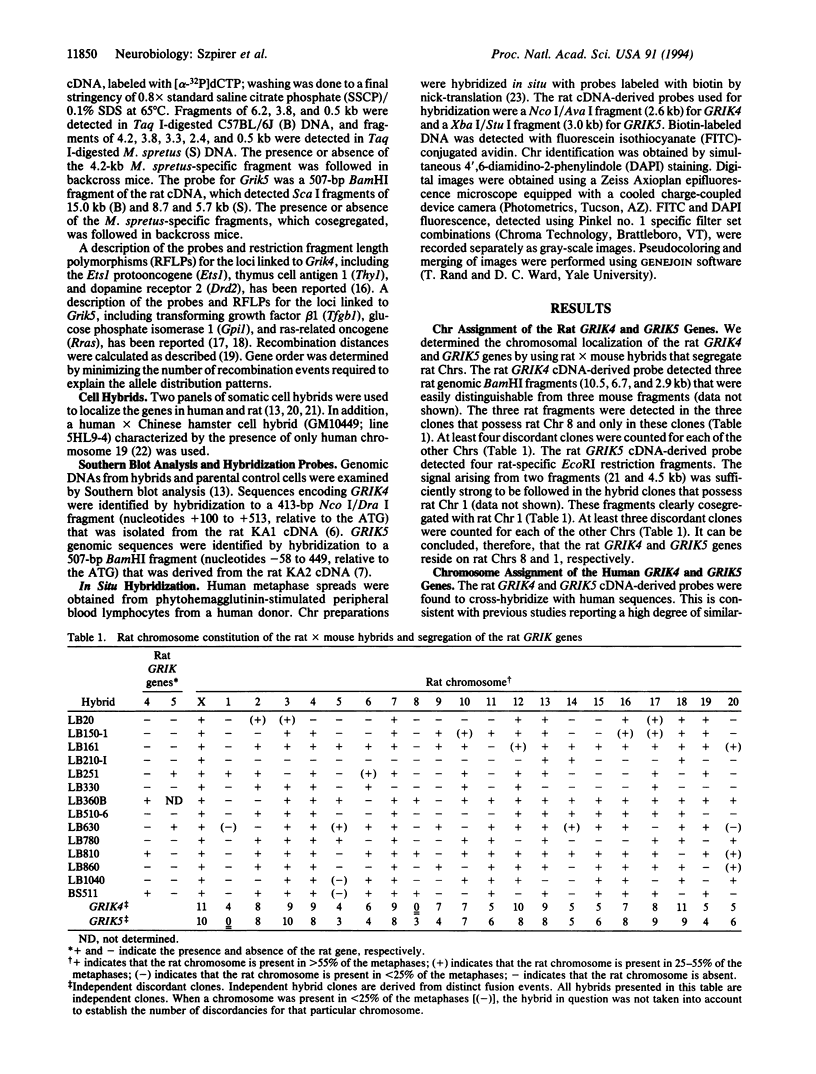
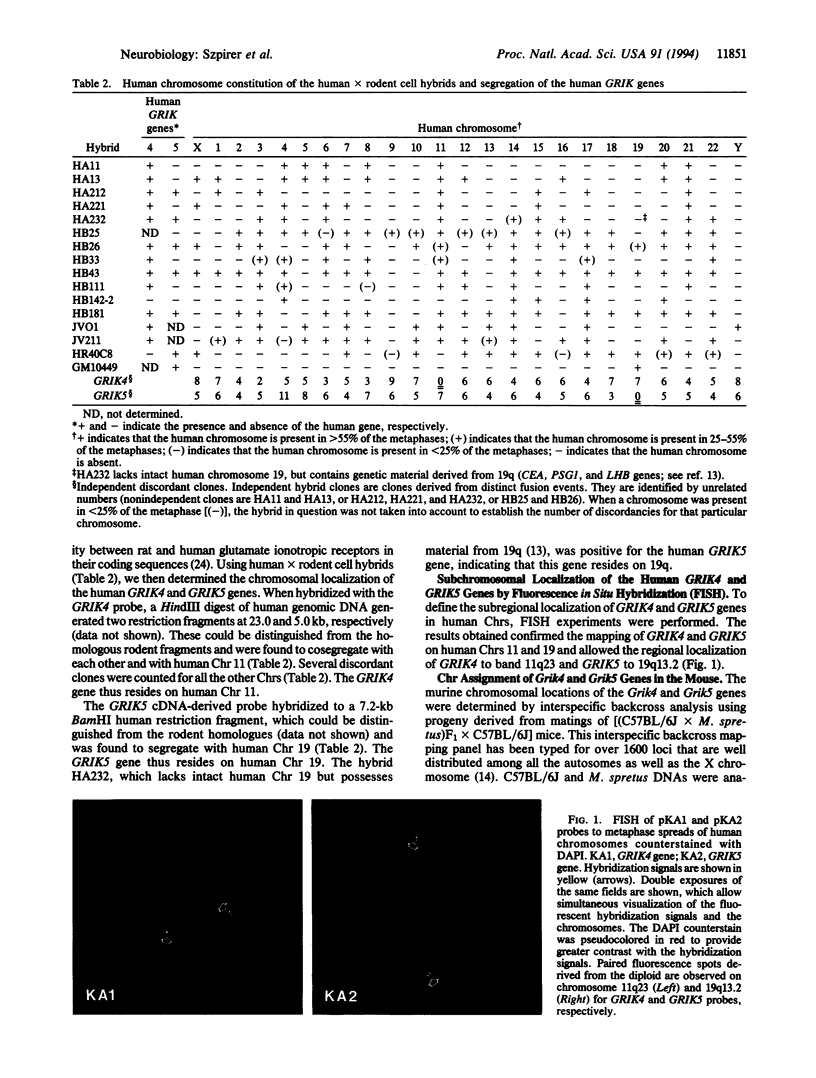
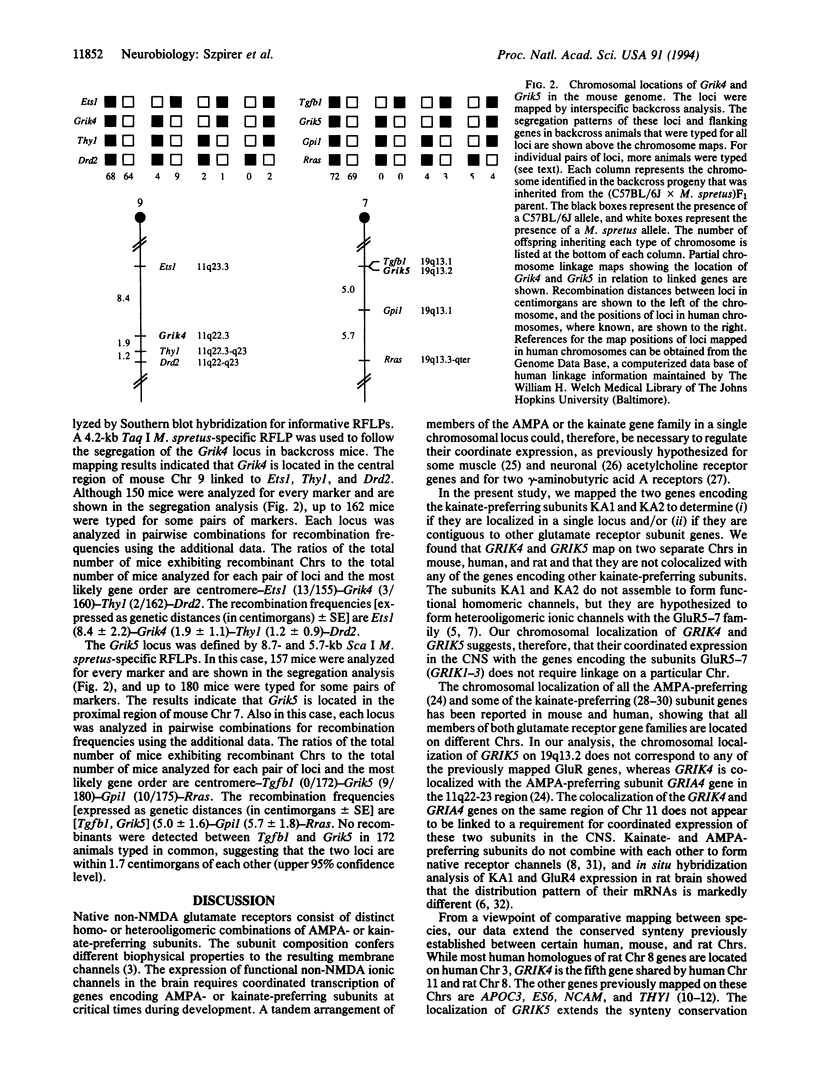
The chromosomal localization of the human and rat genes encoding the kainate-preferring glutamate receptor subunits KA1 and KA2 (GRIK4 and GRIK5, respectively) was determined by Southern analysis of rat x mouse and human x mouse somatic cell hybrid panels and by fluorescence in situ hybridization. The localization of the mouse genes (Grik4 and Grik5) was established by interspecific backcross mapping. GRIK4 and GRIK5 are located on separate chromosomes (Chrs) in all species. GRIK4 mapped to human Chr 11q22.3, mouse Chr 9, and rat Chr 8. GRIK5 mapped to human Chr 19q13.2, mouse Chr 7, and rat Chr 1. The genes encoding the (R,S)-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA)-preferring subunit GluR4, or GluRD (GRIA4), the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), the D2 dopamine receptor (DRD2), and the Thy-1 cell surface antigen (THY1) have all been previously mapped to the human Chr 11q22 region. The mapping of the human GRIK4 and GRIK5 genes confirms and extends the relationship between human Chr 11 and mouse Chr 9 and also human Chr 19 and mouse Chr 7. GRIK4 is the fifth gene shared by human Chr 11 and rat Chr 8, whereas GRIK5 is 1 out of the 12 genes that are located on both human Chr 19 and rat Chr 1. Our data extend the conserved synteny established between certain human, mouse, and rat Chrs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonacci R., Colombo I., Archidiacono N., Volta M., DiDonato S., Finocchiaro G., Rocchi M. Assignment of the gene encoding the beta-subunit of the electron-transfer flavoprotein (ETFB) to human chromosome 19q13.3. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):177–179. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Duvoisin R. M., Connolly J. G., Wada E., Jensen A., Gardner P. D., Ballivet M., Deneris E. S., McKinnon D. Alpha 3, alpha 5, and beta 4: three members of the rat neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related gene family form a gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4472–4482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle V. J., Fujita N., Ryder-Cook A. S., Derry J. M., Barnard P. J., Lebo R. V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Bateson A. N., Darlison M. G. Chromosomal localization of GABAA receptor subunit genes: relationship to human genetic disease. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Lester R. A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):143–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Eppig J. T., Maltais L. J., Miller J. C., Dietrich W. F., Weaver A., Lincoln S. E., Steen R. G. A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):57–66. doi: 10.1126/science.8211130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., McBain C. J., McNamara J. O. Excitatory amino acid receptors in epilepsy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Aug;11(8):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drwinga H. L., Toji L. H., Kim C. H., Greene A. E., Mulivor R. A. NIGMS human/rodent somatic cell hybrid mapping panels 1 and 2. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):311–314. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey C. E., Schwarzman A. L., Rise M. L., Seyfried T. N. Ceruloplasmin gene defect associated with epilepsy in EL mice. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):426–431. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P., Reeves R. H., Jabs E. W., Yang X., Dackowski W., Rochelle J. M., Brown R. H., Jr, Haines J. L., O'Hara B. F., Uhl G. R. Chromosomal localization of glutamate receptor genes: relationship to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurological disorders of mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3053–3057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Buonanno A., Geoffroy B., Robert B., Guénet J. L., Merlie J. P., Changeux J. P. Chromosomal localization of muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes in the mouse. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.3022377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law C. L., Torres R. M., Sundberg H. A., Parkhouse R. M., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Clark E. A. Organization of the murine Cd22 locus. Mapping to chromosome 7 and characterization of two alleles. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):175–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levan G., Szpirer J., Szpirer C., Klinga K., Hanson C., Islam M. Q. The gene map of the Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus) and comparative mapping with mouse and man. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):699–718. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville C. M., Formstone C. J., Hernandez D., Thick J., Taylor A. M. Fine mapping of the chromosome 11q22-23 region using PFGE, linkage and haplotype analysis; localization of the gene for ataxia telangiectasia to a 5cM region flanked by NCAM/DRD2 and STMY/CJ52.75, phi 2.22. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4335–4343. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O., Eubanks J. H., McPherson J. D., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A., Heinemann S. F. Chromosomal localization of human glutamate receptor genes. J Neurosci. 1992 Jul;12(7):2555–2562. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-07-02555.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Wisden W. Glutamate-operated channels: developmentally early and mature forms arise by alternative splicing. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):799–810. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90176-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin K. M., Patneau D. K., Winters C. A., Mayer M. L., Buonanno A. Selective modulation of desensitization at AMPA versus kainate receptors by cyclothiazide and concanavalin A. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1069–1082. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90220-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschen W., Blackstone C. D., Huganir R. L., Ross C. A. Human GluR6 kainate receptor (GRIK2): molecular cloning, expression, polymorphism, and chromosomal assignment. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):435–440. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Wright P. W., Winters C., Mayer M. L., Gallo V. Glial cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage express both kainate- and AMPA-preferring subtypes of glutamate receptor. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M. Thy-1 antigen on astrocytes in long-term cultures of rat central nervous system. Nature. 1979 Aug 23;280(5724):688–690. doi: 10.1038/280688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puranam R. S., Eubanks J. H., Heinemann S. F., McNamara J. O. Chromosomal localization of gene for human glutamate receptor subunit-7. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;19(6):581–588. doi: 10.1007/BF01233385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rise M. L., Frankel W. N., Coffin J. M., Seyfried T. N. Genes for epilepsy mapped in the mouse. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):669–673. doi: 10.1126/science.1871601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serikawa T., Kuramoto T., Hilbert P., Mori M., Yamada J., Dubay C. J., Lindpainter K., Ganten D., Guénet J. L., Lathrop G. M. Rat gene mapping using PCR-analyzed microsatellites. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):701–721. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfried T. N., Glaser G. H. A review of mouse mutants as genetic models of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1985 Mar-Apr;26(2):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1985.tb05398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Identification and applications of repetitive probes for gene mapping in the mouse. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):169–179. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Burnashev N., Verdoorn T. A., Keinänen K., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A glutamate receptor channel with high affinity for domoate and kainate. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1651–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpirer C., Riviere M., Cortese R., Nakamura T., Islam M. Q., Levan G., Szpirer J. Chromosomal localization in man and rat of the genes encoding the liver-enriched transcription factors C/EBP, DBP, and HNF1/LFB-1 (CEBP, DBP, and transcription factor 1, TCF1, respectively) and of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor gene (HGF). Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90245-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M. G., Szpirer J., Nols C. B., Clauss I. M., De Wit L., Islam M. Q., Levan G., Horisberger M. A., Content J., Szpirer C. Cloning and chromosomal location of human genes inducible by type I interferon. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Sep;14(5):415–426. doi: 10.1007/BF01534709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Chen Y., Gilbert D. J., Moore K. J., Yu L., Simon M. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Identification, chromosomal location, and genome organization of mammalian G-protein-coupled receptors. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):175–184. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. A complex mosaic of high-affinity kainate receptors in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Aug;13(8):3582–3598. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-08-03582.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada J., Kuramoto T., Serikawa T. A rat genetic linkage map and comparative maps for mouse or human homologous rat genes. Mamm Genome. 1994 Feb;5(2):63–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00292332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasue M., Serikawa T., Kuramoto T., Mori M., Higashiguchi T., Ishizaki K., Yamada J. Chromosomal assignments of 17 structural genes and 11 related DNA fragments in rats (Rattus norvegicus) by Southern blot analysis of rat x mouse somatic cell hybrid clones. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):659–664. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Abeelen J. H., Kalkhoven J. T. Behavioural ontogeny of the Nijmegen waltzer, a neurological mutant in the mouse. Anim Behav. 1970 Nov;18(4):711–718. doi: 10.1016/0003-3472(70)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



