Abstract
CD22ΔE12 has emerged as a driver lesion in the pathogenesis of pediatric B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and a new molecular target for RNA therapeutics. Here we report a 43-gene CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome that shows a striking representation in primary human leukemia cells from patients with relapsed BPL. Our data uniquely indicate that CD22ΔE12 is a candidate driver lesion responsible for the activation of MAPK and PI3-K pathways in aggressive forms of B-lineage ALL. We also show that the forced expression of a CD22 RNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) markedly reduces the capacity of the leukemic stem cell fraction of CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage ALL cells to engraft and cause overt leukemia in NOD/SCID mice. We have successfully complexed our rationally designed lead CD22-RTM with PVBLG-8 to prepare a non-viral nanoscale formulation of CD22ΔE12-RTM with potent anti-cancer activity against CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage leukemia and lymphoma cells. CD22-RTM nanoparticles effectively delivered the CD22-RTM cargo into B-lineage ALL cells and exhibited significant anti-leukemic activity in vitro.
Keywords: Gene therapy, Driver lesion, Leukemogenesis, RNA trans-splicing, Alternative splicing, Leukemia, Cancer, RNA therapeutics, Nanomedicine, Personalized medicine
Highlights
-
•
The CD22ΔE12-driven transcriptome shows striking representation in relapsed B-lineage ALL
-
•
CD22 RNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) reduces the in vivo clonogenicity of leukemic stem cells
-
•
Nanoformulations of CD22-RTM show therapeutic potential against B-lineage ALL and lymphomas
1. Introduction
Contemporary treatment strategies offer > 80% long-term survival in pediatric B-lineage ALL (O'Leary et al., 2008). However, the prognosis of relapsed B-lineage ALL is very poor (Gaynon et al., 2006, Pui et al., 2012). New treatment strategies capable of improving the treatment outcomes of relapsed B-lineage ALL patients are urgently needed. Leukemic clones in aggressive forms of pediatric B-lineage ALL are characterized by CD22ΔE12, a genetic defect involving CD22, an inhibitory co-receptor of human BCP (Uckun et al., 2010, Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2015a, Ma et al., 2011). The incidence of CD22ΔE12 is also high in adult aggressive B-lineage leukemias and lymphomas (Uckun et al., 2015a). We have previously demonstrated that therapy-refractory clones in B-lineage ALL patients are CD22ΔE12+ (Ma et al., 2011). Notably, CD22ΔE12-transgenic (Tg) mice spontaneously develop B-lineage ALL which recapitulates the gene expression profile of CD22ΔE12+ human B-lineage ALL, establishing a causal relationship between CD22ΔE12 and B-lineage ALL and indicating that CD22ΔE12 is an oncogenic “driver lesion” sufficient for leukemogenesis (Uckun et al., 2014a). Functional RNA interference experiments using CD22ΔE12-specific siRNA and its nanoscale formulations have confirmed the causal link between CD22ΔE12 and the stemness features as well as aggressiveness and drug resistance of B-lineage ALL cells (Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2014b, Uckun et al., 2015b). Our most recent preliminary studies have established that the “undruggable” CD22ΔE12 genetic defect can be repaired using RNA trans-splicing molecules (RTM) (Uckun et al., 2015a). The aim of the current study was to further assess the anti-leukemic activity of CD22-RTM on clonogenic B-lineage ALL cells and to characterize a unique multi-functional nanoparticle (NP) of CD22-RTM as a novel anti-ALL nanomedicine candidate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles
The Exon 12 Index values were calculated by subtracting the median centered expression values of the Exon 10–11 plus Exon 13–14 probes from the median centered expression values of the Exon 12 probes, as previously reported (Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2015a). In order to determine the representation of the leading-edge genes of the CD22ΔE12 transcriptome in the transcriptome of primary leukemia cells from relapsed BPL patients, the RMA-normalized gene expression values for leukemia cells obtained from 49 BPL patients in relapse (GSE28460) were log2 transformed and mean-centered to the average value for the 447 diagnosis samples (GSE11877, GSE13351, GSE28460, and GSE7440) for cluster visualization. To determine the differential expression of each leading edge gene of the CD22ΔE12 transcriptome in relapsed BPL cells, linear contrasts designed from a mixed ANOVA model using RMA normalized expression values were performed, as reported (Uckun et al., 2014a).
2.2. Gene Expression Profiling of Murine BPL Cells and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
Mouse leukemia cells were isolated from markedly enlarged spleens of CD22ΔE12-Tg, BCR-ABL-Tg or Eμ-MYC Tg mice, Splenocytes from wildtype healthy C57BL/6 mice served as controls. Gene expression values for splenocytes from WT healthy C57/BL/6 mice (N = 4), leukemia cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice (N = 2), leukemia cells from BCR-ABL Tg mice (N = 2), and leukemia cells from Eμ-MYC Tg mice (N = 2) were estimated from RMA normalization of signal values following hybridization to the Affymetrix Mouse Gene 1.0 ST Array (1,102,500 probes, 35,512 genes) (GSE58874 and GSE58872), as previously reported (Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2014b). PM signal values for probesets were extracted utilizing raw CEL files matched with probe identifiers obtained from a CDF file (MoGene-1_0-st-v1, r3.cdf obtained from http://www.aroma-project.org/vignettes/GeneSTArrayAnalysis) implemented by Aroma Affymetrix statistical packages run in the R-studio environment (Version 0.97.551, R-studio Inc., running with R 3.01). The PM signals were quantified using Robust Multiarray Analysis (RMA), as previously reported (Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2014b). T-values greater than 5 (2035 genes) or less than − 5 (1973 genes) of log2 gene expression differences between BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice (N = 2) vs. other cells (N = 8; pooled data on wildtype normal splenocytes and BPL cells from BCR-ABL Tg or Eμ-MYC Tg mice) were visualized using a one-way hierarchical cluster figure to organize similar expression profiles of genes across the samples. Transcript cluster annotations for the mouse array were obtained from the NetAffx website (http://www.affymetrix.com/Auth/analysis/downloads/na33/wtgene-32_2/MoGene-1_0-st-v1.na33.2.mm9.transcript.csv.zip). In order to determine a CD22ΔE12-specific gene expression signature, the expression levels for differentially expressed genes were compared for BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice versus splenocytes from WT mice, BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg versus Eμ-MYC Tg mice and BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg versus BCR-ABL Tg mice using Student's T-tests (unequal variance correction). T- and P-values were obtained for further processing in the GSEA (accession nos. GSE 58872 and 58874).
We used 3 archived gene expression profiling datasets (i.e., GSE13159, GSE1187, and GSE13351) and log2-transformed RMA normalized gene expression values (Assay Platform: Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array) on primary leukemia cells from newly diagnosed pediatric ALL patients to perform pairwise correlations of the Exon 12 Index for each sample and signaling pathway-linked probesets for 3 cytogenetically defined high-risk BPL subsets (N = 279) – Ph+/BCR-ABL+ (N = 123), t (1;19)/E2A-PBX1+ (N = 61), multilineage leukemia gene MLL rearranged (MLL-R+) (N = 95) – and 74 normal control samples. Correlation coefficients (r) were determined between CD22 Exon 12 expression and each of the probesets for GSEA. Rank-ordered correlation coefficients were processed for enrichment of the signaling pathway (viz.: MAPK pathway, PI3-K pathway, WNT pathway) -linked gene sets obtained from the Reactome Database (c2.cp.reactome.v4.0.symbols deposited in database on broadinstitute.org servers) using a supervised approach implemented in GSEA2.08 (Broad Institute). Significance of association was assessed using weighted Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistics. The GSEA evaluated the significance of the over-representation of probesets correlated or anti-correlated with CD22 Exon 12 Index values by calculating the enrichment score (ES) values representing the difference between the observed rankings from the expected null. The null distribution assumed a random rank distribution utilizing an empirical permutation test procedure that randomly assigned probeset names to the rank ordered differences in expression (“GSEA Preranked” algorithm). Leading edge genes were identified up to and including the peak of the ES profile. Nominal P-values were computed by comparing the tails of the ES scores for observed and permutation-generated null distributions following 1000 permutations. The T-values of the gene expression differences between CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells and other cells were processed for enrichment using gene sets obtained from the Reactome Database (c2.cp.reactome.v4.0.symbols deposited in database on broadinstitute.org servers) using a supervised approach implemented in GSEA2.08 (Broad Institute), as described (Uckun et al., 2014b). T-values obtained from comparisons of CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus WT splenocytes, CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus Eμ-MYC Tg BPL cells and CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus BCR-ABL Tg BPL cells were utilized to identify consistently and uniquely dysregulated signaling pathways in CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells. In order to more directly compare gene set enrichments in BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice with loss of CD22 Exon 12 in high risk human BPL, T-values of the differences between CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus WT splenocytes, Eμ-MYC Tg BPL cells or BCR-ABL Tg BPL cells were processed for GSEA and compared to the GSEA results obtained from the correlation with Exon 12 Index values in 3 cytogenetically defined high-risk BPL subsets focusing on MAPK, PI3-K and WNT pathway signaling pathways. Significance of association was assessed using weighted Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistics. To compare the differences in gene expression levels across gene sets, normalized enrichment scores (NES) were calculated. A two-way hierarchical cluster analysis of the NES values was performed to visualize the associations between gene sets in comparisons of CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus WT splenocytes, CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus Eμ-MYC Tg BPL cells and CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells versus BCR-ABL Tg BPL cells. A more focused analysis on MAPK, WNT and PI3-K/AKT pathway genes as classified in the Reactome Database was performed because of their association with relapsed human BPL. In this comparison, nominal P-values for GSEA enrichment scores for expression changes in mouse and human transcriptomes were combined using the Fisher's method to determine the significance of the representation of signaling pathway genes in both human and mouse BPL cells (combined P-value) (Uckun et al., 2014b).
2.3. Phosphoproteome Analysis Using Antibody Microarrays
The phosphoproteome analyses were performed as previously described in detail (Uckun et al., 2014a). Data were normalized utilizing the median intensity values for the 1318 antibodies on each array (normalized data = average signal intensity of replicate spots/median signal). The normalized data were log10 transformed and mean centered to the WT samples (N = 4, 2 technical replicates for each of 2 samples) (GSE58873 and GSE 58874).
2.4. Leukemia Cells
Deidentified xenograft clones from 2 relapsed B-lineage ALL patients were used in this study. The secondary use of these clones did not meet the definition of human subject research per 45 CFR 46.102 (d and f) and the IRB (CCI) at the Children's Hospital Los Angeles (CHLA) approved our research. In addition, the B-lineage ALL cell lines ALL-1 and RAJI (B-ALL/Burkitt's leukemia) were used in some of the experiments.
2.5. Construction of the CD22 RNA-trans-splicing Molecule (RTM) Transfection of ALL Xenograft Cells from Relapsed B-lineage ALL Patients With CD22-RTM
The CD22-RTM was designed to replace the mutated segment of CD22 intron 12 and downstream portion of the CD22ΔE12 gene with mutation-free wildtype CD22 Exons 10–14 (Uckun et al., 2015a). We have constructed a plasmid that expresses an RTM with a rationally designed anti-sense binding domain (also known as the trans-splicing region or TSR) targeting a 60-nt complementary non-coding region close to the 5′ splice site of CD22 Intron 9 that confers specificity by tethering the RTM to its target pre-mRNA (Uckun et al., 2015a). B-lineage ALL xenograft cells were transfected with the CD22-RTM plasmid using standard procedures, which were previously described in detail (Uckun et al., 2015a). As in earlier work, untransfected cells, cells transfected with an empty control plasmid (EPL) as well as cells transfected with a dystrophin-RTM plasmid were used as controls (Uckun et al., 2015a). Transfection and trans-splicing in leukemia cells were confirmed by using RT-PCR as reported (Uckun et al., 2015a).
2.6. NOD/SCID (NS) Mouse Xenograft Model of Human B-lineage ALL
The anti-leukemic activity of CD22-RTM against leukemic stem cells was studied in a previously published NS mouse xenograft model of human B-lineage ALL (Uckun et al., 2013, Uckun et al., 2015b, Uckun et al., 2015c). The research was approved by the IACUC of CHLA. Our standard animal care procedures were previously reported (Uckun et al., 2015d, Uckun et al., 2015e). In 2 independent experiments, we examined the effects of CD22-RTM on the leukemia-initiating cells of the xenograft clones. Controls included untransfected cells. Immediately after transfection, cells were injected into NS mice. NS mice (6–8 weeks old, female, same age in all cohorts in each independent experiment) were inoculated intravenously (i.v) with CD22-RTM transfected B-lineage ALL xenograft cells (2 × 106 leukemia cells in 0.2 mL PBS). Mice were monitored daily and electively euthanized by CO2 asphyxia when any mouse developed morbidity. We compared the spleen size and nucleated spleen cell counts of mice according to the leukemia cells they were inoculated with. Spleens of mice were removed and measured, and cell suspensions were prepared for determination of mononuclear cell counts. For multiple group comparisons, significant treatment effects were determined using linear contrasts for all pairwise comparisons defined by an ANOVA model with one fixed factor for treatment (6 comparisons for a model consisting of 4 treatment groups: untransfected cells (N = 5), cells transfected with CD22-RTM (N = 17), EPL (N = 17), or Dystrophin-RTM (N = 5)). Two separate models were constructed for spleen size and log10 transformed nucleated spleen cell counts using previously published standard procedures (Uckun et al., 2013, Uckun et al., 2015c). Comparisons of 2 treatment groups (pooled controls (N = 27) versus CD22-RTM treated (N = 17)) were performed using a two-tailed T-test. Contingency analysis compared the proportion of mice with splenomegaly (spleen size > 3 cm) and a high nucleated spleen cell count (> 150 million nucleated cells/spleen) in pooled control versus CD22-RTM treated groups.
2.7. Preparation and Characterization of CD22-RTM Nanoparticles
PVBLG-8, a helical, cationic polypeptide, was prepared, as previously reported (Yin et al., 2013a, Yin et al., 2013b, Zheng et al., 2014, Uckun et al., 2014a). CD22-RTM was complexed with PVBLG-8 at a 1:10 weight ratio to form the NPs. Control NP were prepared with a luciferase encoding control plasmid (pLuc), Dystrophin-RTM plasmid, and empty plasmid (EPL). Size measurement by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) method and Zeta potential analyses were performed using a Malvern Zetasizer, as previously reported (Uckun et al., 2013, Yin et al., 2013b). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed using published procedures (Uckun et al., 2013, Yin et al., 2013b). CD22-RTM condensation by PVBLG-8 at a PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM weight ratio of 10:1 was evaluated by a gel retardation assay, as previously reported (Zheng et al., 2014, Zheng et al., 2015). For the CD22-RTM + serum or PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM + serum conditions, CD22-RTM or PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM were incubated with fetal bovine serum for 2 h at 37 °C, respectively. For PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM + serum/heparin, after incubation with serum, a 10-fold excess of heparin was added to remove the CD22-RTM from the NP. In order to perform a flow cytometric analysis of the cellular delivery of fluorescent-labeled CD22-RTM by PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM NP, CD22-RTM DNA was labeled with YOYO1 and YOYO1-CD22 RTM was complexed with PVBLG-8 to form the NP using previously published methods (Zheng et al., 2014, Zheng et al., 2015). Unformulated YOYO1-CD22 RTM vs. PVBLG-8/YOYO1-CD22 RTM NP were incubated with CD22ΔE12+ RAJI or ALL-1 (BCR-ABL+ B-lineage ALL) cells (0.5 μg DNA/sample) for 4 h. After 2 washes with heparin-supplemented PBS to remove the NP attached to the membrane of leukemia cells, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (4%, 100 μL) and analyzed for cell-associated fluorescence due to internalized YOYO1-CD22 RTM using flow cytometry. To evaluate the ability of CD22-RTM NP to cause transfection and trans-splicing in CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage leukemia cells, the difficult to transfect RAJI cells in 1 mL culture medium were incubated for 4 h at 37 °C with PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/CD22-RTM (5 μg), PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/Dystrophin-RTM (5 μg), or PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/empty plasmid (EPL) (5 μg). Cells were washed twice and then cultured in RPMI + 10% FBS for 48 h at 37 °C/5% CO2. Total RNA was extracted from the 48 h samples and subjected to RT-PCR analysis as described above and outlined in the figure legends. The anti-leukemic activity of the CD22-RTM against RAJI cells was evaluated using MTT assays to assess cell viability.
The CD22-RTM NP delivers expression plasmids that encode CD22-RTM. Upon delivery to the nucleus, the plasmid's CMV promoter drives expression of the RTM as RNA. If normal or mutant CD22 pre-mRNA is present in the cell, the RTM binding domain can base-pair with its complementary region in CD22 intron 9. The 3′ splice site carried by the RTM can recruit splicing factors (such as U2 and U2AF) to bind to the RTM. These factors can interact and begin the splicing process in trans — with other splicing factors (such as U1) that are bound to the 5′ splice site of the endogenous CD22 intron 9, thereby replacing the entire sequence of endogenous CD22, beginning with intron 9 and including Exon 14 as well as the 3′ UTR, with the exogenous sequence of CD22 EXONs 10 through 14 provided by the RTM. Each trans-spliced molecule of CD22ΔE12 pre-mRNA is converted or reprogrammed to encode normal CD22 mRNA. Therefore, the reduction in the amount of CD22ΔE12 mRNA is directly proportionate to the number of mutant pre-mRNA molecules trans-spliced. The total amount of trans-spliced CD22 mRNAs includes both the number of mutant and normal CD22 pre-mRNAs that are trans-spliced. Our RTM will trans-splice into both mutant and normal CD22 pre-mRNA, with the result that the mutant is corrected to encode a normal CD22 sequence, while the normal is trans-spliced into normal, although both forms will be tagged with the 3′ UTR sequence of the RTM. The net effect on the leukemic phenotype should correlate with the amount that the mutant leukemogenic CD22ΔE12 mRNA expression is reduced.
3. Results
3.1. CD22ΔE12-Driven Signature Transcriptome is a Characteristic Feature of Aggressive Leukemic Clones in Newly Diagnosed High Risk ALL as well as Relapsed B-lineage ALL
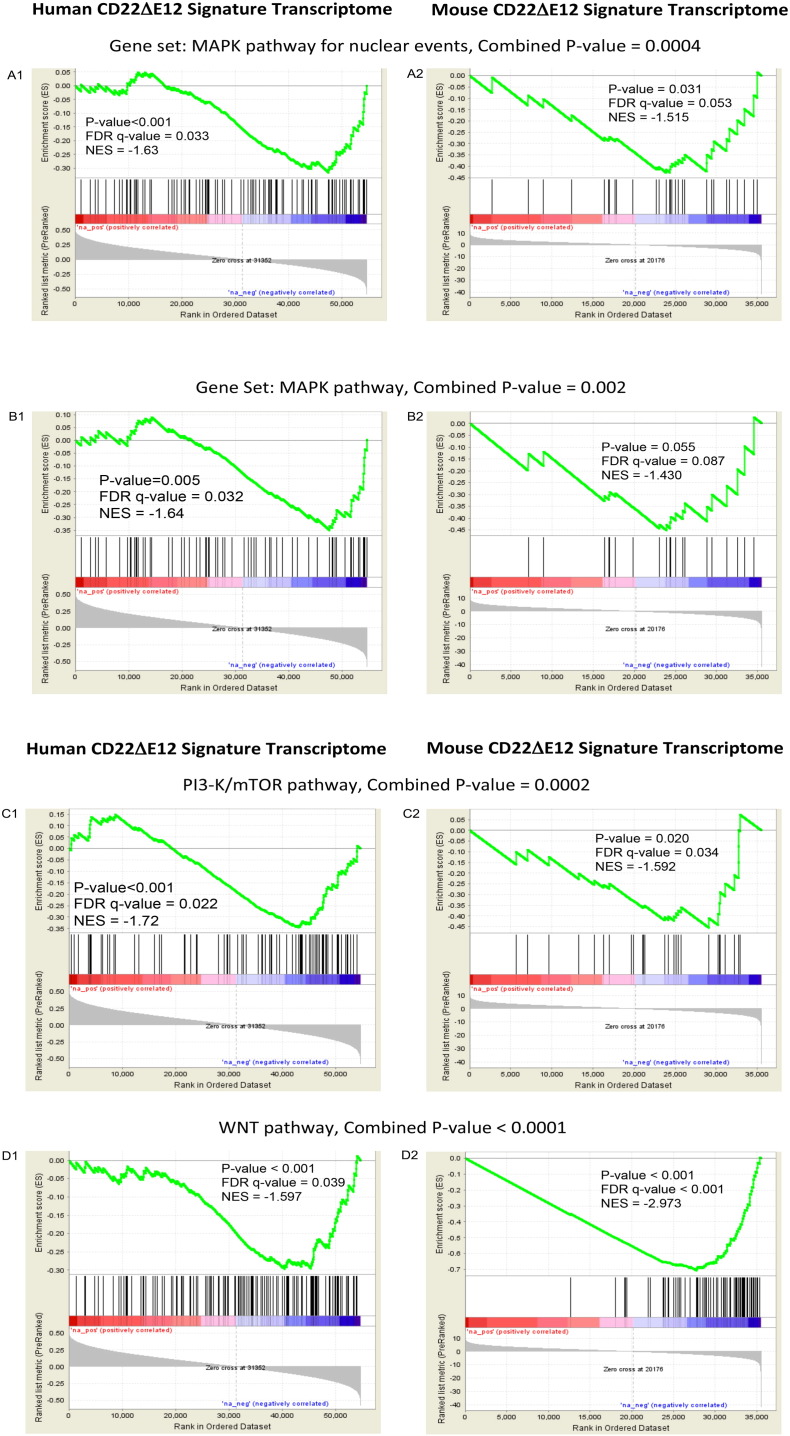
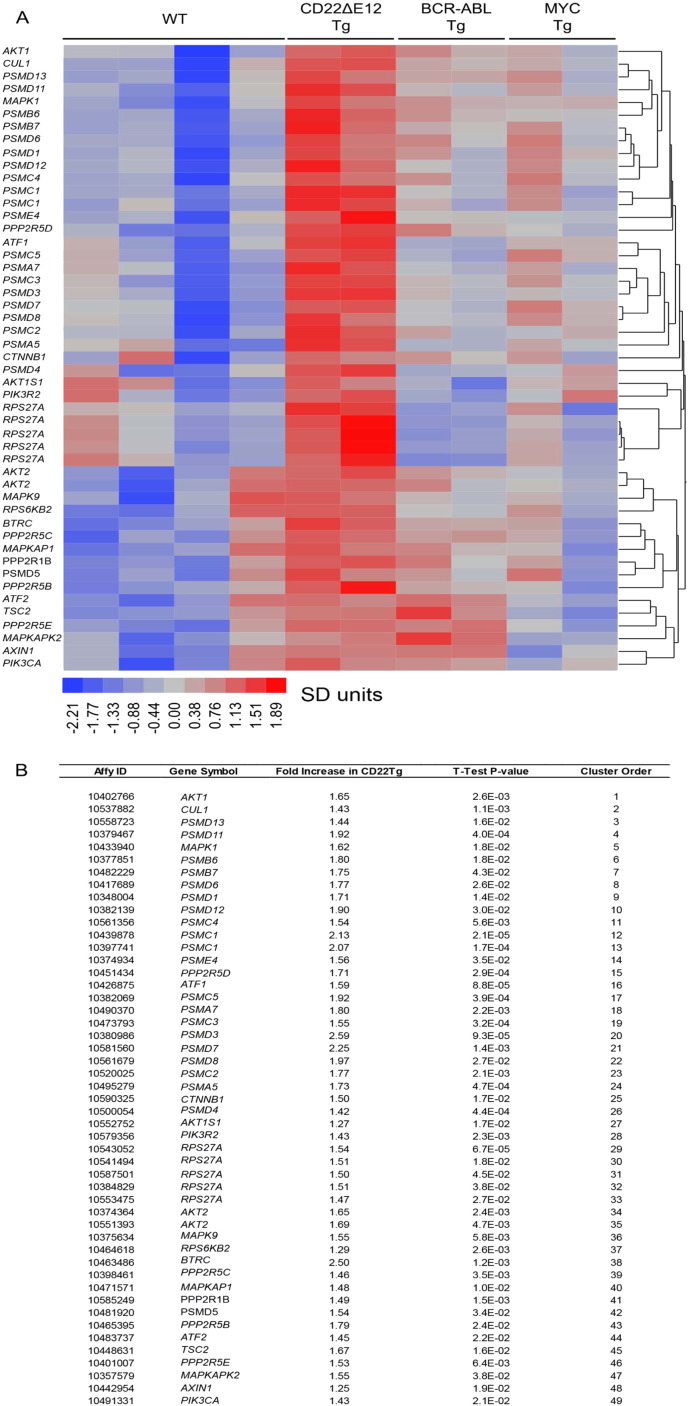
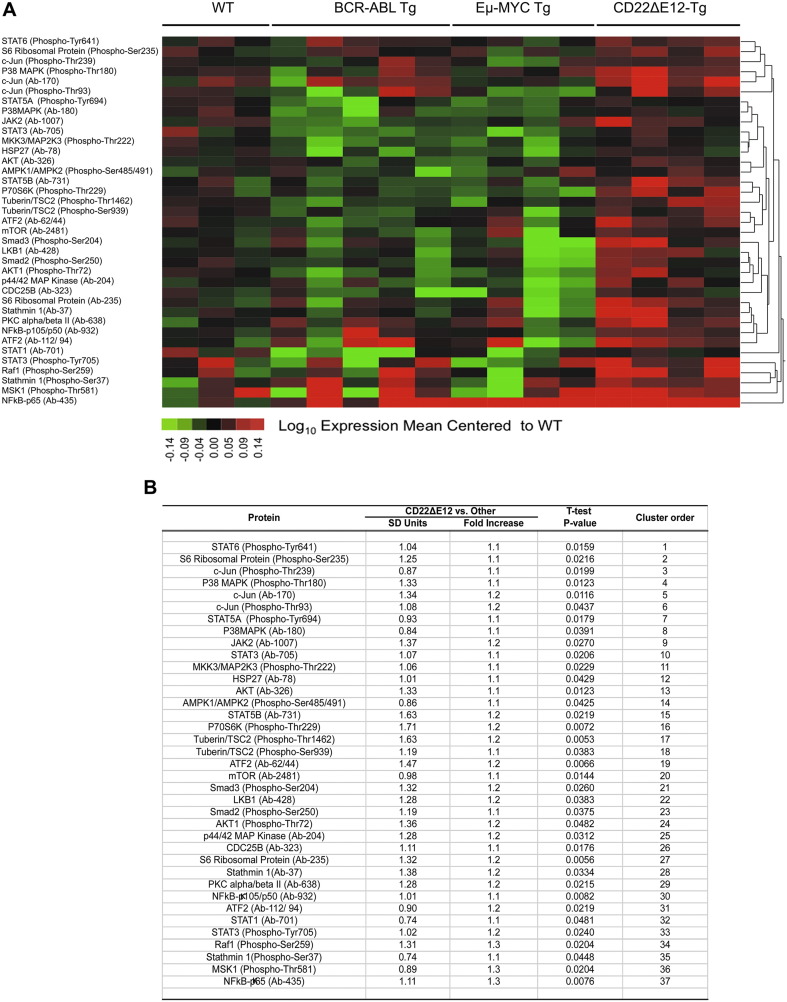
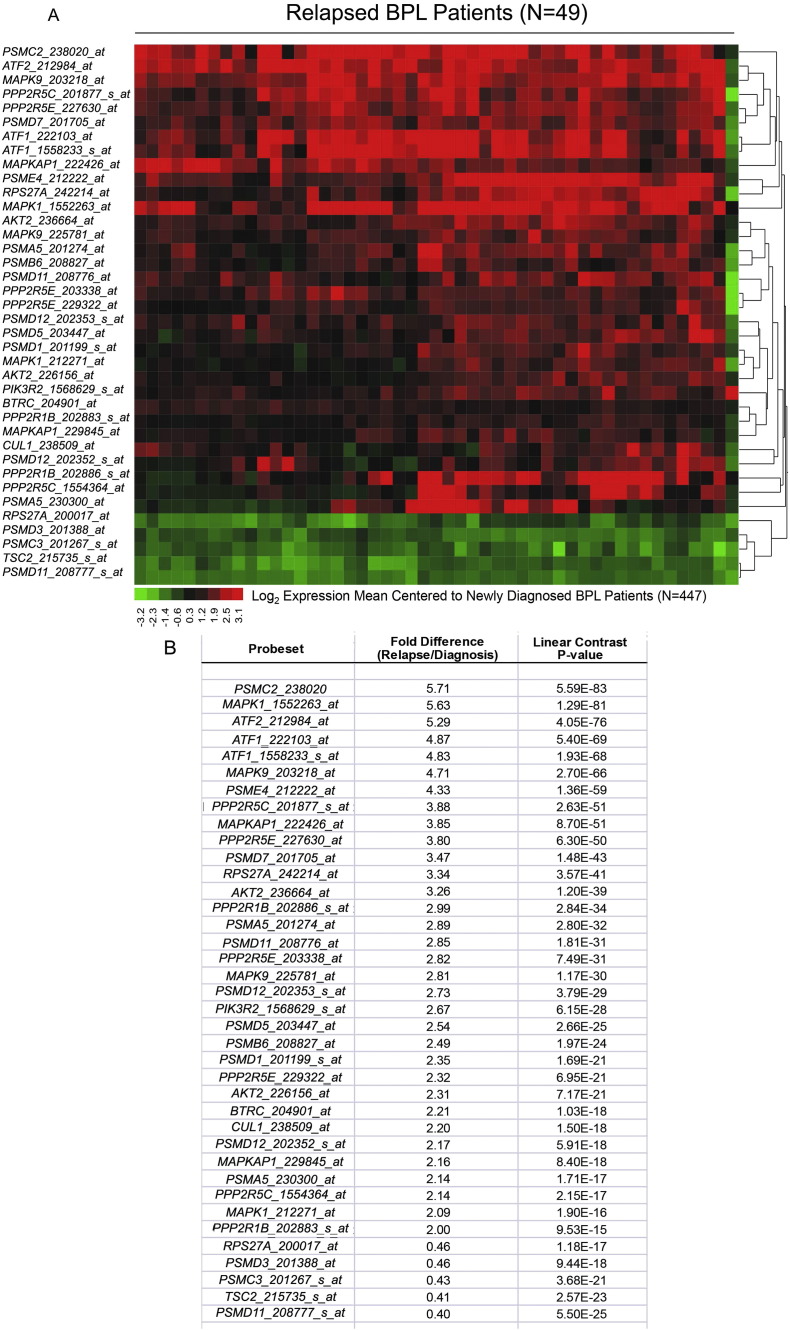
Relapse clones are characterized by constitutive activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways (Hogan et al., 2011). Likewise, constitutive activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K), Akt and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (PI3-K/Akt/mTOR) network is a characteristic feature of aggressive BPL cells (Badura et al., 2013, Neri et al., 2013). However, the driver lesion that causes these transcriptome changes in aggressive BPL cells has remained elusive. The GSEA of primary leukemia cells from 279 cytogenetically defined high-risk BPL patients and normal hematopoietic cells in 74 control samples showed that the expression of genes related to MAPK, PI3-K/mTOR, and WNT pathways was differentially upregulated upon the loss of the CD22 Exon 12 (Fig. 1). Gene expression profiling and GSEA revealed differential upregulation of the mouse homologs of these genes in BPL cells from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice – but not in BPL cells from Eμ-MYC Tg or BCR-ABL Tg mice – closely mimicking the transcriptome of primary leukemia cells from high-risk BPL patients (Fig. 1, Fig. 2A). We identified a CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome based on the significantly affected expression values of the leading edge genes from the GSEA by comparing CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells with BPL cells from Eμ-MYC Tg or BCR-ABL Tg mice as well as wildtype splenocytes (Fig. 2A): T-tests documented that 49 probesets representing 43 signaling pathway genes in MAPK, PI3-K and WNT signaling networks were significantly upregulated in CD22ΔE12-Tg mice (P < 0.05) (Fig. 2B). A comparative proteomic profiling with phosphoprotein antibody arrays demonstrated that 37 phosphoproteins in MAPK and PI3-K signaling networks were uniquely overexpressed in CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells (Fig. 3; GSE58873 and GSE58874). These changes collectively demonstrate that the regulation of multiple signaling networks is corrupted in CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells. We next examined the representation of the unique CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome in primary cancer cells from patients with relapsed BPL by comparing the gene expression profiles of primary leukemia cells from 447 newly diagnosed BPL patients vs. primary leukemia cells from 49 relapsed BPL patients using a mixed model ANOVA. Notably, there was a significant overall increase in expression of 110 probesets in aggressive BPL cells from relapsed BPL patients (F1,494 = 68.7, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 4). Our findings indicate that the CD22ΔE12 genetic defect is the likely genetic cause for the activation of MAPK, PI3-K/mTOR and WNT pathways in primary leukemia cells from relapsed BPL patients. CD22ΔE12 may therefore have clinical utility as a molecular biomarker of aggressive relapse clones in high-risk BPL patients and a potential molecular target for more effective treatment of poor prognosis B-lineage ALL.
Fig. 1.
CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome in human and mouse BPL cells.
Depicted are GSE plots comparing the human vs. mouse CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptomes in BPL cells. Rank-ordered correlation coefficients (y-axis expression of each probeset plotted against CD22 Exon 12 Index on the x-axis) were processed for enrichment of the signaling pathway-linked gene sets obtained from the Reactome Database (c2.cp.reactome.v4.0.symbols deposited in database on broadinstitute.org servers) using a supervised approach implemented in GSEA2.08 (Broad Institute). Probesets for (i) “MAPK targets/nuclear events mediated by MAP kinases” pathway (panel A), (ii) MAPK pathway (panel B), (iii) PI3-K/mTOR activation pathway (panel C), and (iv) WNT pathway (panel D) negatively correlated with Exon 12 transcript levels in human BPL samples from high-risk ALL patients indicating that the transcripts were differentially upregulated upon loss of CD22 Exon 12 (enrichment observed towards the negative correlation co-efficient values). The mouse homologs of these genes were also upregulated in murine BPL cells derived from CD22ΔE12-Tg mice (enrichment observed towards negative T-values depicting genes downregulated in WT/BCR-ABL/Eμ-MYC Tg mice). Nominal P-values for GSEA enrichment scores for expression change in mouse and human transcriptomes were combined using Fisher's method to determine the significance of the representation of the pathway in both human and mouse cells (combined P-value).
Fig. 2.
Signature transcriptome of CD22ΔE12 transgenic (Tg) BPL cells.
Gene expression values for splenocytes from WT healthy C57BL/6 mice (N = 4), leukemia cells from CD22ΔE12 Tg mice (N = 2), leukemia cells from BCR-ABL Tg mice (N = 2), and leukemia cells from MYC Tg mice (N = 2) were estimated from RMA normalization of signal values following hybridization to the Affymetrix Mouse Gene 1.0 ST Array (1102500 probes, 35512 genes). Expression values for each probeset were standardized across the 10 samples and differences in expression were visualized using a one-way hierarchical cluster figure to organize similar expression profiles of genes across the samples. Heat map depicts up- and downregulated transcripts ranging from red to blue respectively and clustered according to average distance metric (panel A). We determined a unique CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome from significantly affected expression values comparing CD22ΔE12 Tg BPL cells with BPL cells from Eμ-MYC Tg or BCR-ABL Tg mice as well as WT splenocytes. T-tests documented that 49 probesets representing 43 signaling pathway genes in MAPK, PI3-K and WNT signaling networks were significantly upregulated in CD22ΔE12-Tg mice (P < 0.05).
Fig. 3.
Signature phosphoproteome of CD22ΔE12 transgenic mouse BPL cells.
The phosphoprotein profiles of CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells were compared side-by-side with those of Eμ-MYC Tg BPL cells, BCR-ABL Tg BPL cells as well as WT splenocytes from healthy C57BL/6 mice by using the Phospho Explorer Antibody Array platform (Full Moon BioSystems, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA), as described in Materials and Methods. Data were normalized utilizing the median intensity values for the 1318 antibodies on each array. The normalized data were log10 transformed and mean centered to the WT C57BL/6 splenocyte samples (N = 4, 2 technical replicates for each of 2 samples). (A) Heat map depicts up- and downregulated protein expression levels ranging from red to green respectively. Expression values were mean centered to WT samples and clustered according to average distance metric. (B) Student's T-tests (unequal variance correction, Microsoft Excel) compared mean-centered, log10 transformed protein expression levels in BPL cells from CD22ΔE12 Tg mice vs. splenocytes from WT mice and BPL cells from BCR-ABL Tg or MYC Tg mice. P-values and effect sizes in SD units are shown for differentially expressed proteins.
Fig. 4.
Expression of CD22ΔE12 transcriptome in relapsed BPL cells.
The 43-gene mouse CD22ΔE12-Tg transcriptome was represented by 110 probesets on the human U133 Plus 2.0 Array. The RMA-normalized gene expression values for leukemia cells from 49 BPL patients in relapse (GSE28460) were log2 transformed and mean-centered to the average value for the 447 diagnosis samples (GSE11877, GSE13351, GSE28460, and GSE7440). Mixed model ANOVA showed significant overall increase in expression of 110 probesets in relapsed cases (F1,494 = 68.7, P < 0.0001). (A) The gene expression values were clustered according to average distance metric. Heat map depicts up- and downregulated transcripts ranging from red to green respectively for expression values mean centered to diagnosis samples. (B) To determine the differential expression of each leading edge gene of the CD22ΔE12 transcriptome in relapsed BPL cells, linear contrasts were performed for the RMA normalized values (P < 0.05 deemed significant). 33 probesets were upregulated and 5 downregulated with P < 0.0001 and fold change greater than 2.
3.2. Effects of CD22-RTM Mediated Trans-splicing on In Vivo Clonogenic CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage Leukemia Cells
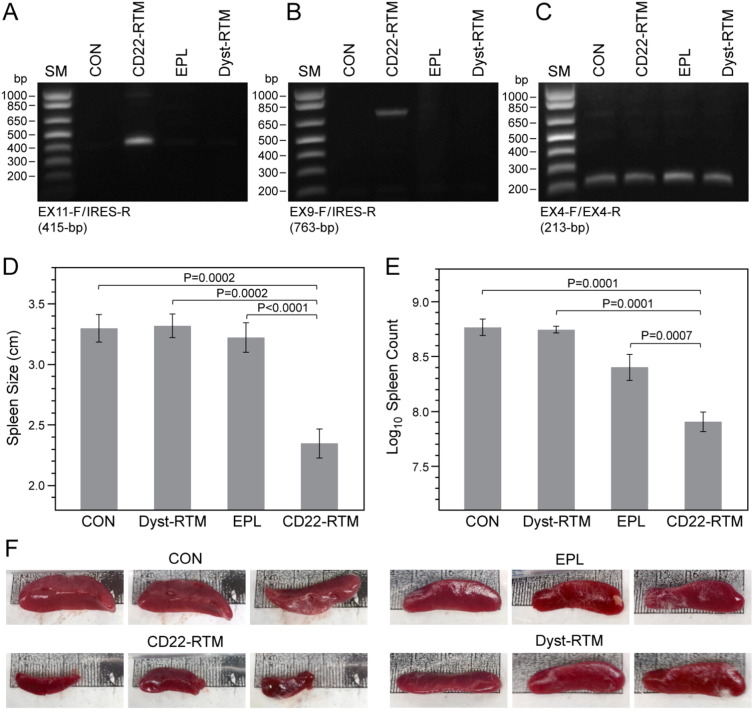
We recently demonstrated that transfection of BPL cells with CD22-RTM causes selective depletion of the CD22ΔE12-mRNA and clonogenic death in vitro (Uckun et al., 2015a). These promising results prompted us to examine the anti-leukemic potency of CD22-RTM mediated trans-splicing against the leukemia-initiating cells (LIC) (i.e., putative “leukemic stem cell fraction”) of chemotherapy-resistant aggressive xenograft clones from 2 patients with relapsed B-lineage ALL. Xenograft clones were transfected with CD22-RTM, Dystrophin-RTM (negative control), or empty plasmid (EPL, another negative control). RT-PCR assays performed 48 h after transfection confirmed successful transfection and trans-splicing in xenograft cells (Fig. 5A–C). Immediately after transfection, an aliquot of xenograft cells was injected into NS mice. All of the 27 control mice injected with untransfected (N = 5), EPL-transfected (N = 17), or Dystrophin-RTM transfected xenograft cells (N = 5) invariably developed fatal leukemia between 57 and 58 days. Necropsy revealed massive (> 3 cm) splenomegaly at the time of death in 26 of these 27 mice (Fig. 5D–F). In contrast, only 3 of 17 NS mice developed overt leukemia within the same time frame after reinjection with CD22-RTM transfected xenograft cells (2-Tailed Fisher's exact, P < 0.0001). The spleens of the control mice injected with untransfected xenograft cells were very large (3.3 ± 0.1 cm) with a very high leukemia burden (622 ± 110 × 106 cells/spleen) (Fig. 5D). Likewise, the spleens were large and contained large numbers of leukemia cells (3.3 ± 0.1 cm/562 ± 40 × 106 cells and 3.2 ± 0.1 cm/335 ± 41 × 106 cells, respectively) in control mice injected with xenograft cells that were transfected with an irrelevant RTM (viz.: Dystrophin-RTM) or EPL (Fig. 5E). For the entire group of 27 control mice, the mean ± SEM values for the spleen size and leukemia burden were 3.3 ± 0.1 cm and 430 ± 41 × 106 cells/spleen, respectively. In contrast to the control mice, the spleens of the 17 test mice injected with CD22-RTM transfected xenograft cells had a significantly smaller size (2.3 ± 0.1 cm, P-value < 0.0001) and leukemia burden (110 ± 21 × 106 cells/spleen, P-value < 0.0001), respectively (Fig. 5D &E). While 26 of the 27 control mice had very high (> 150 × 106 cells/spleen) nucleated spleen cell counts consistent with their large leukemia burden, only 4 of the 17 mice inoculated with CD22-RTM transfected xenograft cells had such high nucleated spleen cell counts (2-Tailed Fisher's exact, P < 0.0001). Thus, transfection with CD22-RTM markedly reduced the in vivo clonogenicity of the leukemic stem cell fraction of CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage ALL cells.
Fig. 5.
CD22-RTM abrogates the ability of leukemia-initiating ALL xenograft cells derived from B-lineage ALL patients to cause leukemia in NS mice.
B-lineage ALL xenograft cells (2 × 106 cells/sample) were transfected with 5 μg CD22-RTM plasmid DNA using the Amaxa Nucleofector Kit and then inoculated into NS mice (N = 17) intravenously via tail vein injections in a 200 μL total volume. Controls included NS mice inoculated with untransfected xenograft cells (N = 5), xenograft cells transfected with 5 μg empty plasmid (EPL) (N = 17) or xenograft cells transfected with 5 μg Dystrophin-RTM (N = 5) prior to inoculation. Mice were monitored for signs of leukemia and all mice in a given experiment were sacrificed when any mouse developed morbidity. (A–C) RT-PCR analyses of xenograft clone #1 transfected with CD22-RTM vs. control plasmids confirming transfection and successful completion of trans-splicing. Total RNA for the PCR was extracted 2 days after transfection. CON: untransfected cells. (A) An agarose gel is depicted showing the RT-PCR amplification of a 415-bp RTM-specific RNA-segment amplified by RT-PCR using a CD22 Exon 11 primer as forward primer (EX11-F) and the RTM IRES primer RTM-4494-5263 as a reverse primer (IRES-R). The detection of the amplicon provides evidence for the successful transfection of ALL xenograft cells with the CD22-RTM. (B) Successful completion of selective CD22 RTM-induced trans-splicing in B-lineage ALL xenograft cells was evidenced by specifically amplifying a 763-bp trans-spliced mRNA segment using an Exon 9 forward primer (EX9-F) and a reverse primer in the IRES sequence of the RTM (IRES-R), as previously reported (Uckun et al., 2015a). (C) An agarose gel of the RT-PCR products obtained with the EX4-F/EX4-R primer set that was used as a positive control of RNA integrity is shown. (D and E) The cumulative results for the average spleen size and nucleated spleen cell count are shown for each treatment group, respectively. (F) Spleen images from representative mice are shown. The spleen images were obtained using an iPhone 4S equipped with an 8-megapixel iSight camera.
3.3. Development and Characterization of a Polypeptide-based CD22-RTM Nanoparticle Formulation as an Anti-leukemic Precision Nanomedicine
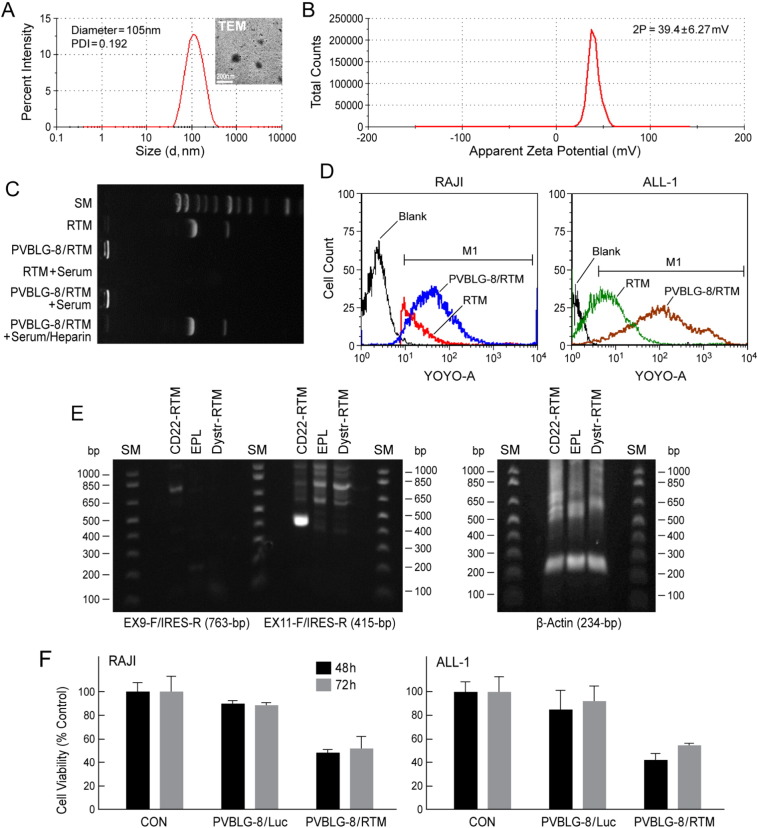
We have successfully complexed CD22-RTM with PVBLG-8 at a PVBLG-8/RTM weight ratio of 10:1 to prepare a nanoparticle (NP) formulation capable of delivering CD22-RTM to B-lineage ALL cells (Fig. 6). The generated PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM nanoparticles had a diameter of 105 nm, as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Fig. 6A), and a positive surface charge with a Zeta potential of 39.4 mV in solution (Fig. 6B). The capacity of the cationic PVBLG-8 to condense CD22-RTM plasmid DNA was first evaluated using the gel retardation assay, as previously reported (Zheng et al., 2015). As shown in Fig. 6C, DNA migration in the 1% agarose gel was completely restricted to the loading well, indicating complete condensation of the CD22-RTM by the positively charged PVBLG-8. Furthermore, while the naked RTM DNA rapidly degraded in the presence of serum, the formulated CD22-RTM did not (compare RTM + serum vs. PVBLG-8/RTM + serum). The NP formulation effectively delivered CD22-RTM into leukemia cells (Fig. 6D), effectively triggered trans-splicing (Fig. 6E), and exhibited anti-leukemic activity, as documented by loss of leukemic cell viability within 48 h after a 4 h incubation period with the NP (Fig. 6F).
Fig. 6.
PVBLG-8-based nanoparticle (NP) formulation (NPF) of CD22-RTM.
(A) DLS analysis of PVBLG-8/RTM (weight ratio 10:1) nanoparticles, showing a particle size around 105-nm in diameter and with a narrow polydispersity index of 0.192. Insert: TEM image of PVBLG-8/RTM NP. (B) Zeta-potential result of PVBLG-8/RTM NP, showing that the NP were positively charged. (C) CD22-RTM condensation by PVBLG-8 at a PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM weight ratio of 10:1, as evaluated by a gel retardation assay, as previously reported (Zheng et al., 2014). For the CD22-RTM + serum or PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM + serum conditions, CD22-RTM or PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM was incubated with serum for 2 h at 37 °C, respectively. For PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM + serum/heparin, after incubation with serum, a 10-fold excess heparin was added to remove the CD22-RTM from the NP. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of the cellular delivery of fluorescent-labeled CD22-RTM by PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM NP. Unformulated YOYO1-CD22 RTM vs. PVBLG-8/YOYO1-CD22 RTM NP were incubated with CD22ΔE12+ RAJI (Burkitt's lymphoma/leukemia) or ALL-1 (BCR-ABL+ B-lineage ALL) cells (0.5 μg DNA/sample) for 4 h. After 2 washes with heparin-containing PBS to remove membrane-bound NP, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (4%, 100 μL) and analyzed for cell-associated fluorescence caused by internalized YOYO1-CD22 RTM using flow cytometry. Markedly improved CD22-RTM delivery to RAJI and ALL-1 cells was confirmed for the NP formulation by the higher cell-associated fluorescence intensity in samples incubated with PVBLG-8/YOYO1-CD22 RTM vs. unformulated YOYO1-CD22 RTM. RTM: in this figure, abbreviation for CD22-RTM. (E) RAJI cells in 1 mL culture medium were incubated for 4 h at 37 °C with PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/CD22-RTM (5 μg), PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/Dystrophin-RTM (5 μg), or PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/empty plasmid (EPL) (5 μg). Cells were washed twice and then cultured in RPMI + 10% FBS for 48 h at 37 °C/5% CO2. Total RNA was extracted from the 48 h samples and subjected to RT-PCR analysis. Depicted is an agarose gel that shows the RT-PCR evidence for successful transfection and trans-splicing, as described in the legend of Fig. 5. Also depicted is an agarose gel showing the RT-PCR amplification of β-actin mRNA (as a control for RNA integrity) with a forward primer 5′-GGACTTCGAGCAAGAGATGG-3′, and a reverse primer 5′-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG-3′. This primer set amplifies a 234-bp region at the junction between Exon 4 and Exon 5 of the human beta actin gene. (F) Anti-leukemic activity of PVBLG-8/CD22-RTM nanoparticles. Depicted are the MTT viability assay data showing the anti-leukemic effects of PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/CD22-RTM (5 μg) NP vs. control NP PVBLG-8 (50 μg)/pLuc (5 μg) on RAJI and ALL-1 cells.
4. Discussion
We are reporting that the CD22ΔE12 genetic defect is the likely genetic cause for the activation of MAPK, PI3-K/m-TOR and WNT pathways in primary leukemia cells from relapsed BPL patients. These pathways have been associated with chemotherapy resistance and aggressiveness of BPL cells. By comparing CD22ΔE12-Tg BPL cells with BPL cells from Eμ-MYC Tg or BCR-ABL Tg mice as well as wildtype splenocytes, we have identified a unique 43-gene CD22ΔE12 signature transcriptome that showed a striking representation in primary human leukemia cells from patients with relapsed BPL. CD22ΔE12 may therefore have clinical utility as a molecular biomarker of aggressive relapse clones in high-risk BPL patients and a potential molecular target for more effective treatment of poor prognosis B-lineage ALL.
RNA trans-splicing has been used to repair several mutant genes linked to human disease (Tahara et al., 2004, Mitchell and McGarrity, 2005, He et al., 2015). We have also documented CD22ΔE12 as an oncogenic driver lesion and an undruggable molecular target in aggressive B-lineage leukemia cells (Uckun et al., 2014a, Uckun et al., 2014b, Uckun et al., 2015a, Uckun et al., 2015b). Our CD22-RTM was designed to replace the mutated segment of CD22 intron 12 and the downstream portion of the CD22ΔE12 gene with mutation-free wildtype CD22 Exons 10–14 (Uckun et al., 2015a). Here we show that the forced expression of the CD22-RTM markedly reduces the in vivo clonogenicity of the leukemic stem cell fraction of CD22ΔE12+ B-lineage ALL cells.
We have recently developed a highly efficient nucleic acid delivery platform based on a class of rationally designed cell-penetrating cationic helical polypeptides (Lu et al., 2011, Gabrielson et al., 2012, Yin et al., 2013a, Yin et al., 2013b, Uckun et al., 2014a, Zheng et al., 2014). These polypeptide-based novel nanomaterials exhibit unprecedented thermodynamic and physicochemical stability and unique biological properties with exceptional endosomal escape and nucleic acid delivery efficiency. The high molecular weight, cationic, α-helical polypeptide PVBLG-8 was identified as the top-performing peptide for nucleic acid delivery in vivo with favorable safety, biocompatibility, PK, and biodistribution profiles (Yin et al., 2013a, Yin et al., 2013b, Zheng et al., 2014). We have successfully complexed our rationally designed lead CD22-RTM with PVBLG-8 to prepare a “non-viral” nanoscale formulation of CD22-RTM with potent anti-cancer activity against CD22ΔE12 B-lineage leukemia and lymphoma cells. CD22-RTM nanoparticles effectively delivered the CD22-RTM cargo into B-lineage ALL cells and exhibited significant anti-leukemic activity in vitro.
The focus of our future preclinical proof of concept studies in animal models of B-lineage ALL studies will be a stepwise evaluation of the safety, biocompatibility, pharmacodynamics features, and efficacy of this polypeptide-based nanoscale formulation of CD22-RTM. We aim to establish spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing using polypeptide-based multifunctional nanoparticles of the CD22-RTM as a therapeutic innovation to treat chemotherapy-resistant B-lineage ALL. Therapeutic nanoformulations containing CD22-RTM may facilitate the development of effective treatments for patients with relapsed B-lineage ALL. The CD22-RTM technology is applicable to all B-lineage ALL patients both high risk and standard risk. That is because CD22ΔE12 is a characteristic feature of leukemic clones that escape chemotherapy and cause relapse in both high risk and low risk subgroups of patients. The technology therefore has the potential (i) for prevention of relapses by selectively killing the clones that are most likely to escape chemotherapy and cause relapse as well as (ii) for treatment of relapses in ALL.
5. Author Contributions
All authors have made significant contributions. All authors reviewed and revised the paper. F.M.U. was the NIH-funded Principal Investigator who designed, directed and supervised this study and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. F.M.U., L.G.M., S.Q., H.M. and J.C. have equally contributed to the work. Z.S., N.Z., Y.L. and J.C. prepared the polypeptide-based nanoformulation of CD22-RTM. L.G.M. designed CD22-RTM. Z.S., N.Z., Y.L., H.M., D.E.M. and F.M.U. evaluated effects of CD22-RTM and its nanoformulation on leukemia cells. S.Q. performed the statistical analyses.
Acknowledgments
The project described was supported by the DHHS grant R43CA177067 (L.M., F.M.U.) from the National Cancer Institute. F.M.U. was also supported in part by DHHS grants P30CA014089, U01-CA-151837, R01CA-154471 and R21-CA-164098 (F.M.U.) from the National Cancer Institute; and by the V-Foundation, Nautica Triathlon as well as the Ronald McDonald House Charities of Southern California. J.C. was supported by NSF-CHE 1308485 for the advance of polypeptide synthesis and design, and by NIH Director's New Innovator Award 1DP2OD007246 for the study of polypeptide/CD22-RTM formulation. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or the National Institutes of Health.
References
- Badura S., Tesanovic T., Pfeifer H., Wystub S., Nijmeijer B.A., Liebermann M., Falkenburg J.H., Ruthardt M., Ottmann O.G. Differential effects of selective inhibitors targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielson N.P., Lu H., Yin L.C., Li D., Wang F., Cheng J.J. Reactive and bioactive cationic α-helical polypeptide template for nonviral gene delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:1143–1147. doi: 10.1002/anie.201104262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynon P.S., Harris R.E., Altman A.J., Bostrom B.C., Brenneman J.C., Hawks R., Steele D., Zipf T., Stram D.O., Villaluna D., Trigg M.E. Bone marrow transplantation versus prolonged intensive chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and an initial bone marrow relapse within 12 months of the completion of primary therapy: Children's Oncology Group Study CCG-1941. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:3150–3156. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.5856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Liu F., Yan J., Zhang Y., Yan J., Shang H., Dou Q., Zhao Q., Song Y. Trans-splicing repair of mutant p53 suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:8705. doi: 10.1038/srep08705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan L.E., Meyer J.A., Yang J., Wang J., Wong N., Yang W., Condos G., Hunger S.P., Raetz E., Saffery R., Relling M.V., Bhojwani D., Morrison D.J., Carroll W.L. Integrated genomic analysis of relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals therapeutic strategies. Blood. 2011;118(19):5218–5226. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-345595. Epub 2011 Sep 14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Wang J., Bai Y.G., Lang J.W., Liu S.Y., Lin Y., Cheng J.J. Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability. Nat. Commun. 2011;2:206. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Qazi S., Ozer Z., Gaynon P., Reaman G.H., Uckun F.M. CD22 Exon 12 deletion is a characteristic genetic defect of therapy-refractory clones in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2011 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08901.x. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell L.G., McGarrity G. Progress & prospects: reprograming gene expression by trans-splicing. Gene Ther. 2005;12(20):1477–1485. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri L.M., Cani A., Martelli A.M., Simioni C., Junghanss C., Tabellini G., Ricci F., Tazzari P.L., Pagliaro P., McCubrey J.A., Capitani S. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its therapeutic potential. Leukemia. 2013 doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary M., Krailo M., Anderson J.R., Reaman G.H., Children's Oncology Group Progress in childhood cancer: 50 years of research collaboration, a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Semin. Oncol. 2008;35(5):484–493. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2008.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C.H., Mullighan C.G., Evans W.E., Relling M.V. Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: where are we going and how do we get there? Blood. 2012;120(6):1165–1174. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-378943. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Review. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara M., Pergolizzi R.G., Kobayashi H., Krause A., Luettich K., Lesser M.L., Crystal R.G. Trans-splicing repair of CD40 ligand deficiency results in naturally regulated correction of a mouse model of hyper-IgM X-linked immunodeficiency. Nat. Med. 2004;10:835–841. doi: 10.1038/nm1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Goodman P., Ma H., Dibirdik I., Qazi S. CD22 Exon 12 deletion as a novel pathogenic mechanism of human B-precursor leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010;107:16852–16857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007896107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Qazi S., Cely I., Sahin K., Shahidzadeh A., Ozercan I., Yin Q., Gaynon P., Termuhlen A., Cheng J., Yiv S. Nanoscale liposomal formulation of a SYK P-site inhibitor against B-precursor leukemia. Blood. 2013;121(21):4348–4354. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-11-470633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Qazi S., Ma H., Yin L., Cheng J. A rationally designed CD22ΔE12-siRNA nanoparticle for RNAi therapy in B-lineage lymphoid malignancies. EBioMedicine. 2014;1(2–3):141–155. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2014.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Ma H., Ozer Z., Goodman P., Zhang J., Qazi S. A previously unknown unique challenge for inhibitors of Syk Atp-binding site: role of Syk as a cell cycle checkpoint regulator. EBioMedicine. 2014;1(1):16–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2014.10.019. Nov 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Qazi S., Ma H., Reaman G.H., Mitchell L. CD22ΔE12 as a molecular target for corrective repair using RNA trans-splicing: anti-leukemic activity of a rationally designed RNA trans-splicing molecule. Integr. Biol. (Camb.) 2015;7:237–249. doi: 10.1039/c4ib00221k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Myers D.E., Qazi S., Ozer Z., Rose R., D'Cruz O., Ma H. Recombinant human CD19L-sTRAIL protein effectively targets B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Invest. 2015;125(3):1006–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI76610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Myers D.E., Cheng J., Qazi S. Liposomal nanoparticles of a spleen tyrosine kinase P-site inhibitor amplify the potency of low dose total body irradiation against aggressive B-precursor leukemia and yield superior survival outcomes in mice. EBioMedicine. 2015;2:554–562. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Ma H., Cheng J., Myers D.E., Qazi S. CD22ΔE12 as a molecular target for RNAi therapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2015 doi: 10.1111/bjh.13306. Article first published online: 6 FEB 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F.M., Myers D.E., Ma H., Rose R., Qazi S. Low dose total body irradiation combined with recombinant CD19-ligand × soluble TRAIL fusion protein is highly effective against radiation-resistant B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in mice. EBiomedicine. 2015;2:306–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin L., Song Z., Kim K., Zheng N., Gabrielson N.P., Cheng J. Non-viral gene delivery via membrane penetrating, mannose-targeting supramolecular self-assembled nanocomplexes. Adv. Mater. 2013;25:3063–3070. doi: 10.1002/adma.201205088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin L., Song Z., Qu Q., Kim K., Zheng N., Yao C., Chaudhary I., Tang H., Gabrielson N.P., Uckun F.M., Cheng J. Supramolecular self-assembled nanoparticles (SSNPs) mediate oral delivery of therapeutic TNF-α siRNA against systemic inflammation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013 doi: 10.1002/anie.201209991. (Apr 22) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng N., Yin L., Song Z., Ma L., Tang H., Gabrielson N.P., Lu H., Cheng J. Maximizing gene delivery efficiencies of cationic helical polypeptides via balanced membrane penetration and cellular targeting. Biomaterials. 2014;35:1302–1314. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng N., Song Z., Liu Y., Zhang R., Zhang R., Yao C., Uckun F.M., Yin L., Cheng J. Redox-responsive, reversibly-crosslinked thiolated cationic helical polypeptides for efficient siRNA encapsulation and delivery. J. Control. Release. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.014. pii: S0168-3659(15)00114-5, [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]