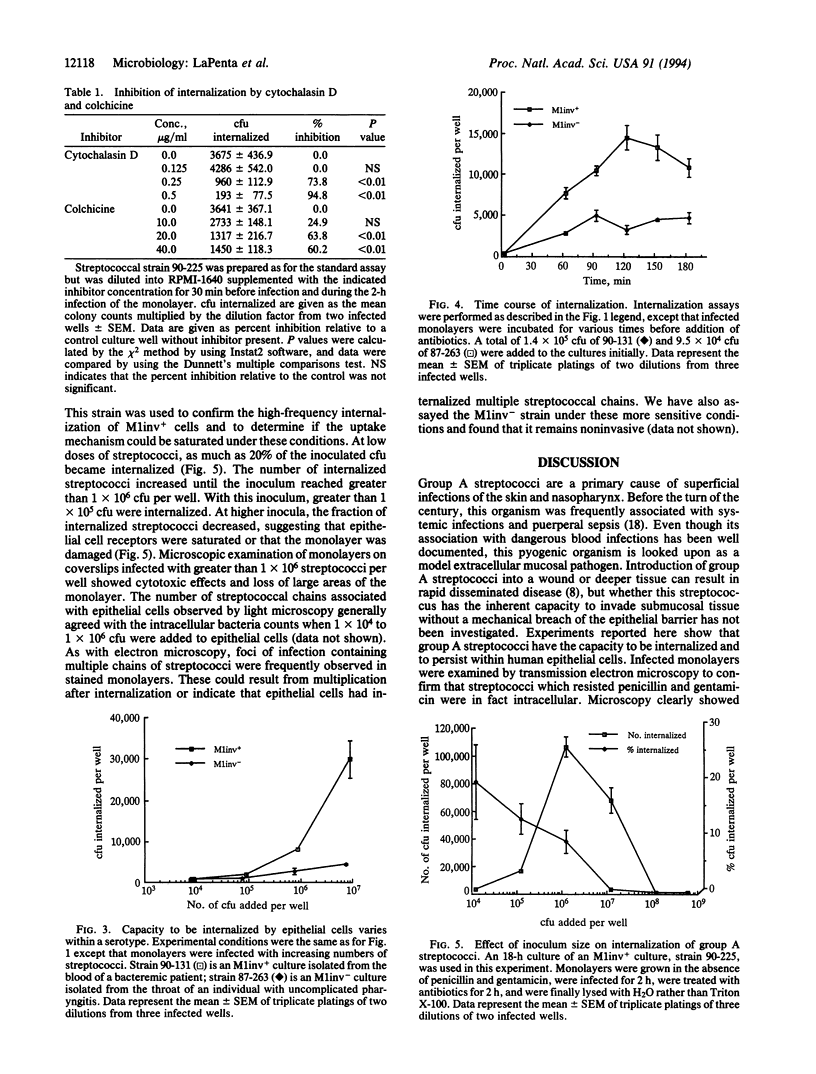
Abstract
Although infection by group A streptococci is a model of extracellular mucosal pathogenesis, these organisms can be associated with highly invasive infections resulting in sepsis and shock. Over the last 6 yr this species has renewed its reputation as a significant cause of sepsis and has piqued interest in the mechanism by which some strains are better able to breach mucosal barriers to gain access to the bloodstream than are others. An internalization assay was developed on the basis of resistance of intracellular streptococci to penicillin and gentamicin. Experiments showed that stationary-phase, as opposed to logarithmic-phase, bacteria are efficiently internalized and can persist in cultured human cells. Electron microscopy confirmed that streptococci were contained within intracellular vacuoles. Various strains of streptococci revealed significant differences in their capacity to be internalized. Two type M1 streptococci isolated from blood infections were internalized at frequencies equal to those reported for Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes and greater than the frequency of a clonal variant from a case of pharyngitis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Handley J. P., Wlazlo A., Kim M. H., Hauser A. R., Schlievert P. M. Clonal basis for resurgence of serious Streptococcus pyogenes disease in the 1980s. Lancet. 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):518–521. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90003-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaworzewska E., Colman G. Changes in the pattern of infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Apr;100(2):257–269. doi: 10.1017/s095026880006739x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. L., Lee M. K., Soderland C., Chi E. Y., Rubens C. E. Group B streptococci invade endothelial cells: type III capsular polysaccharide attenuates invasion. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):478–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.478-485.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Caparon M. Protein F, a fibronectin-binding protein, is an adhesin of the group A streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulse M. L., Smith S., Chi E. Y., Pham A., Rubens C. E. Effect of type III group B streptococcal capsular polysaccharide on invasion of respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4835–4841. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4835-4841.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Stevens D. L., Kaplan E. L. Epidemiologic analysis of group A streptococcal serotypes associated with severe systemic infections, rheumatic fever, or uncomplicated pharyngitis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):374–382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters J. G., Mulders-Kremers G. A., van Doornik C. E., van der Zeijst B. A. Effects of multiplicity of infection, bacterial protein synthesis, and growth phase on adhesion to and invasion of human cell lines by Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5013–5020. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5013-5020.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Raff H. V., Jackson J. C., Chi E. Y., Bielitzki J. T., Hillier S. L. Pathophysiology and histopathology of group B streptococcal sepsis in Macaca nemestrina primates induced after intraamniotic inoculation: evidence for bacterial cellular invasion. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):320–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Smith S., Hulse M., Chi E. Y., van Belle G. Respiratory epithelial cell invasion by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5157–5163. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5157-5163.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALLMAN B. The process of hyaluronidase formation by hemolytic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1951 Dec;62(6):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.6.741-746.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Tilney M. S. The wily ways of a parasite: induction of actin assembly by Listeria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Apr;1(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90021-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanHeyningen T., Fogg G., Yates D., Hanski E., Caparon M. Adherence and fibronectin binding are environmentally regulated in the group A streptococci. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1213–1222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. R., Stinson M. W. M protein mediates streptococcal adhesion to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1994 Feb;62(2):442–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.2.442-448.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




