Abstract
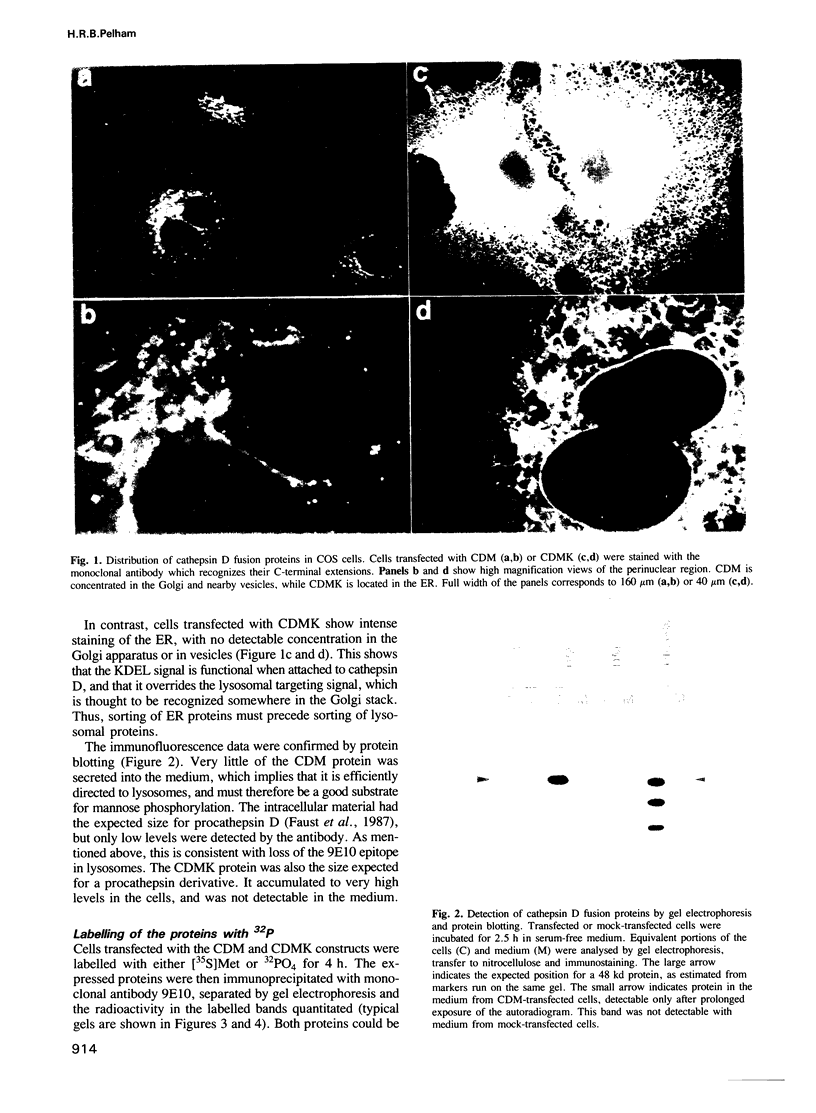
Several soluble proteins that reside in the lumen of the ER contain a specific C-terminal sequence (KDEL) which prevents their secretion. This sequence may be recognized by a receptor that either immobilizes the proteins in the ER, or sorts them from other proteins at a later point in the secretory pathway and returns them to their normal location. To distinguish these possibilities, I have attached an ER retention signal to the lysosomal protein cathepsin D. The oligosaccharide side chains of this protein are normally modified sequentially by two enzymes to form mannose-6-phosphate residues; these enzymes do not act in the ER, but are thought to be located in separate compartments within (or near) the Golgi apparatus. Cathepsin D bearing the ER signal accumulates within the ER, but continues to be modified by the first of the mannose-6-phosphate forming enzymes. Modification is strongly temperature-dependent, which is also a feature of ER-to-Golgi transport. These results support the idea that luminal ER proteins are continuously retrieved from a post-ER compartment, and that this compartment contains N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Elliott M. M., Keller D. S. ATP-coupled transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14681–14689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J., Kornfeld R. Evidence for an alpha-mannosidase in endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7907–7910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Novak E. K., Takeuchi K., Moore K., Medda S., Swank R. T. Lumenal location of the microsomal beta-glucuronidase-egasyn complex. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1571–1578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriotti A., Colman A. Binding to membrane proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum cannot explain the retention of the glucose-regulated protein GRP78 in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):633–638. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Creek K. E., Merion M., Hirschberg C. B. Subfractionation of rat liver Golgi apparatus: separation of enzyme activities involved in the biosynthesis of the phosphomannosyl recognition marker in lysosomal enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3938–3942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Wall D. A., Perara E., Lingappa V. R., Kornfeld S. Expression of human cathepsin D in Xenopus oocytes: phosphorylation and intracellular targeting. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1937–1945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabel C. A., Kornfeld S. Lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation in mouse lymphoma cell lines with altered asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10605–10612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. The phosphorylation of beta-glucuronidase oligosaccharides in mouse P388D1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13060–13067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Turco S. J., Green M. Structure and assembly of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biosynthetic sorting of endoplasmic reticulum proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6926–6931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Nishimura Y., Kato K., Kobata A. Comparative studies of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide structures of rat liver microsomal and lysosomal beta-glucuronidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez M., Hirschberg C. B. Translocation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine into vesicles derived from rat liver rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlmann R., Waheed A., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Synthesis of phosphorylated recognition marker in lysosomal enzymes is located in the cis part of Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5323–5325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Palade G. E., Farquhar M. G. Temperature-sensitive steps in the transport of secretory proteins through the Golgi complex in exocrine pancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Temperature and energy dependence of secretory protein transport in the exocrine pancreas. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1477–1482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Pohlmann R., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Subcellular location of two enzymes involved in the synthesis of phosphorylated recognition markers in lysosomal enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4150–4152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. Protein transport. Signals and salvage sequences. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):17–18. doi: 10.1038/327017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Amos W. B., Fordham M. An evaluation of confocal versus conventional imaging of biological structures by fluorescence light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):41–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Hasilik A. Lysosomal enzymes and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:167–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]