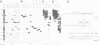Abstract
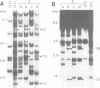
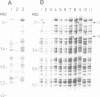
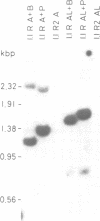
We have isolated a 5.7-kbp dispersed moderately repeated DNA sequence (TOC1) from the mutant OEE1 gene of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain FUD44. The copy number (2 to over 30) and genomic locations of TOC1 elements vary widely in different C. reinhardtii strains. Our standard laboratory photosynthetic strain exhibits a high degree of TOC1 instability during short periods of mitotic growth. TOC1 appears to be a retrotransposon: it contains LTRs and an oligonucleotide stretch that corresponds to a conserved pentapeptide of reverse transcriptase. TOC1 is an unusual retrotransposon: it is not flanked by a target site duplication in the OEE1 gene, the left end of TOC1 only contains a fraction of the LTR the remainder of which is present at its right end and TOC1 does not start with a 5' TG and end with a 3' CA. In most cases, TOC1 excision leaves behind a complete solo LTR sequence (577 bp) and in one case a deleted solo LTR sequence (191 bp). Solo LTR sequences form a separate family of repeated sequences in most of the strains tested.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello J., Handelsman K., Lodish H. F. Sequence of Dictyostelium DIRS-1: an apparent retrotransposon with inverted terminal repeats and an internal circle junction sequence. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choquet Y., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Girard-Bascou J., Kück U., Bennoun P., Rochaix J. D. Mutant phenotypes support a trans-splicing mechanism for the expression of the tripartite psaA gene in the C. reinhardtii chloroplast. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Carpenter R., Martin C. Transposable elements generate novel spatial patterns of gene expression in Antirrhinum majus. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Sequence and spacing requirements of a retrovirus integration site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. B., McCarron M., Love C., Chovnick A. Dysgenesis-induced instability of rosy locus transformation in Drosophila melanogaster: analysis of excision events and the selective recovery of control element deletions. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):95–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. Insertion of the eukaryotic transposable element Ty1 creates a 5-base pair duplication. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):352–356. doi: 10.1038/286352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J. Retroviruses and transposable elements--which came first? Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):105–106. doi: 10.1038/302105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Mitra S. W., Goff S., Baltimore D. A detailed model of reverse transcription and tests of crucial aspects. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rahire M. Sequence, evolution and differential expression of the two genes encoding variant small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann P., Klaer R., Kühn S., Starlinger P. IS4 is found between eleven or twelve base pair duplications. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):369–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00397237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harberd N P, Flavell R B, Thompson R D. Identification of a transposon-like insertion in a Glu-1 allele of wheat. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):326–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00329661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Shank P. R., Spector D. H., Kung H. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Breitman M. L. Proviruses of avian sarcoma virus are terminally redundant, co-extensive with unintegrated linear DNA and integrated at many sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1397–1410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Mottinger J., Freeling M. A low copy number, copia-like transposon in maize. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1093–1101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Ando Y., Shiba T. Unusual priming mechanism of RNA-directed DNA synthesis in copia retrovirus-like particles of Drosophila. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):824–826. doi: 10.1038/323824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchka M. R., Mayfield S. P., Rochaix J. D. Nuclear mutations specifically affect the synthesis and/or degradation of the chloroplast-encoded D2 polypeptide of photosystem II in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):319–324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE R. P., EBERSOLD W. T. The genetics and cytology of Chlamydomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1960;14:197–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.14.100160.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Terminal repeats of the Drosophila transposable element copia: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90496-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. A simplified method for preparation of mouse satellite DNA. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Bennoun P., Rochaix J. D. Expression of the nuclear encoded OEE1 protein is required for oxygen evolution and stability of photosystem II particles in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):313–318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Nelson M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r201–r207. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Löfdahl S. Transposition of Tn554 does not generate a target duplication. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):292–294. doi: 10.1038/307292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag D. K., Berg D. E. Specificity of bacteriophage Mu excision. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):395–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00331606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. Circles with two tandem LTRs are precursors to integrated retrovirus DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarca R., Haseltine W. A. Sequence similarity among retroviruses--erratum. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):728–728. doi: 10.1038/309728b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock W. J., Dennis E. S., Gerlach W. L., Sachs M. M., Schwartz D. Insertion and excision of Ds controlling elements in maize. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:347–354. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearston D. H., Gordon M., Hardman N. Transposon-like properties of the major, long repetitive sequence family in the genome of Physarum polycephalum. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3557–3562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Fink G. R. Movement of yeast transposable elements by gene conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5621–5625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E., Sivertsen A., Firtel R. A. An unusual transposon encoding heat shock inducible and developmentally regulated transcripts in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Tschudi C., Perera J., Delius H., Pirrotta V. B104, a new dispersed repeated gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and its analogies with retroviruses. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Cuypers H., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Plant transposable elements generate the DNA sequence diversity needed in evolution. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):591–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd N. S., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Blumberg vel Spalve J., Gupta M., Wienand U., Saedler H. Similarity of the Cin1 repetitive family of Zea mays to eukaryotic transposable elements. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):185–187. doi: 10.1038/307185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Sequence of retrovirus provirus resembles that of bacterial transposable elements. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):550–554. doi: 10.1038/285550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Barker C., Hunter E., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: an immunosuppressive D-type retrovirus. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Measurement of DNA length by gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Dec;100(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togasaki R. K., Levine R. P. Chloroplast structure and function in ac-20, a mutant strain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. I. CO2 fixation and ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):531–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Hayashida H., Miyata T. Sequence homology between retroviral reverse transcriptase and putative polymerases of hepatitis B virus and cauliflower mosaic virus. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):827–829. doi: 10.1038/305827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Reverse transcriptase rides again. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):583–584. doi: 10.1038/314583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C., Cappello J., Lodish H. F., George P., Chung S. Dictyostelium transposable element DIRS-1 has 350-base-pair inverted terminal repeats that contain a heat shock promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2660–2664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]