Abstract
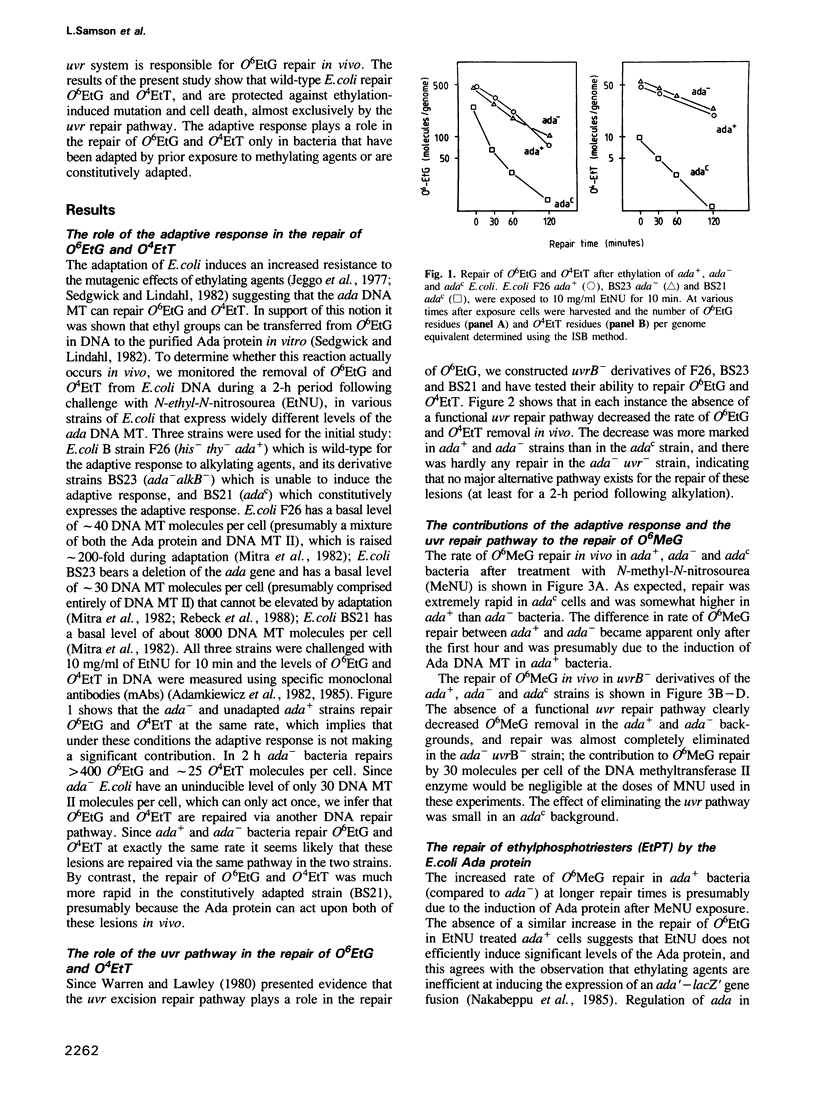
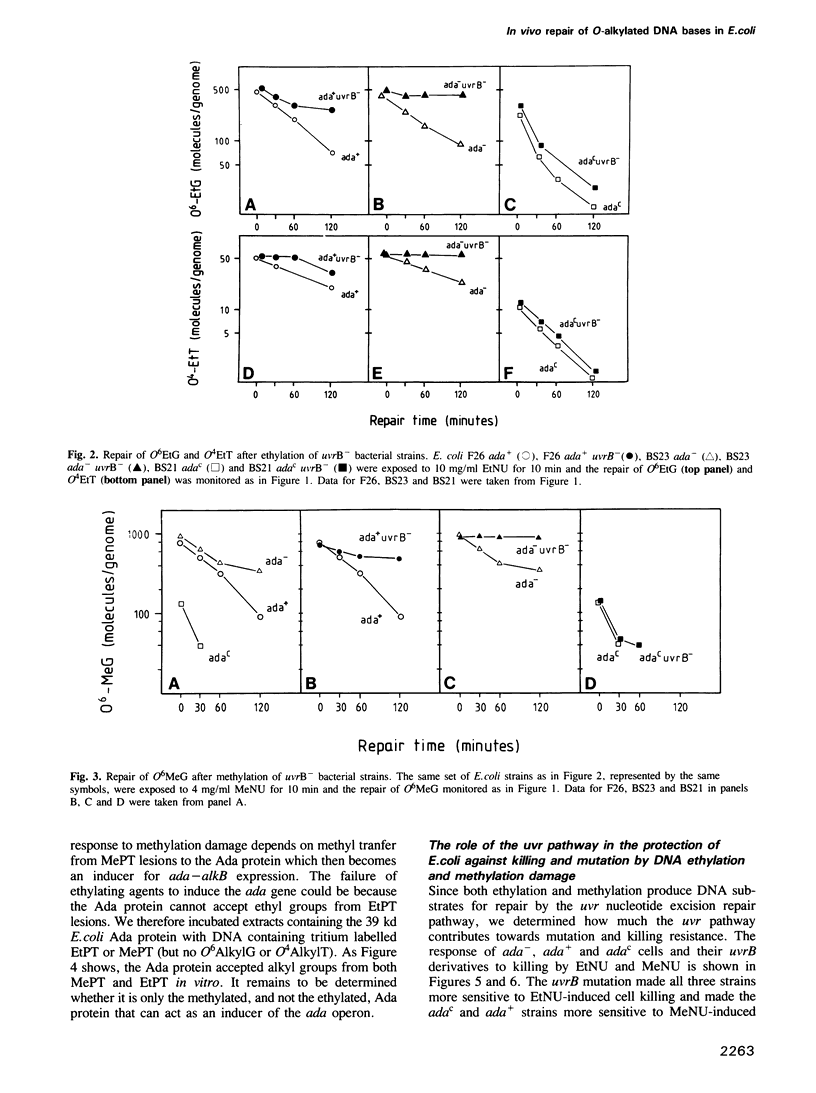
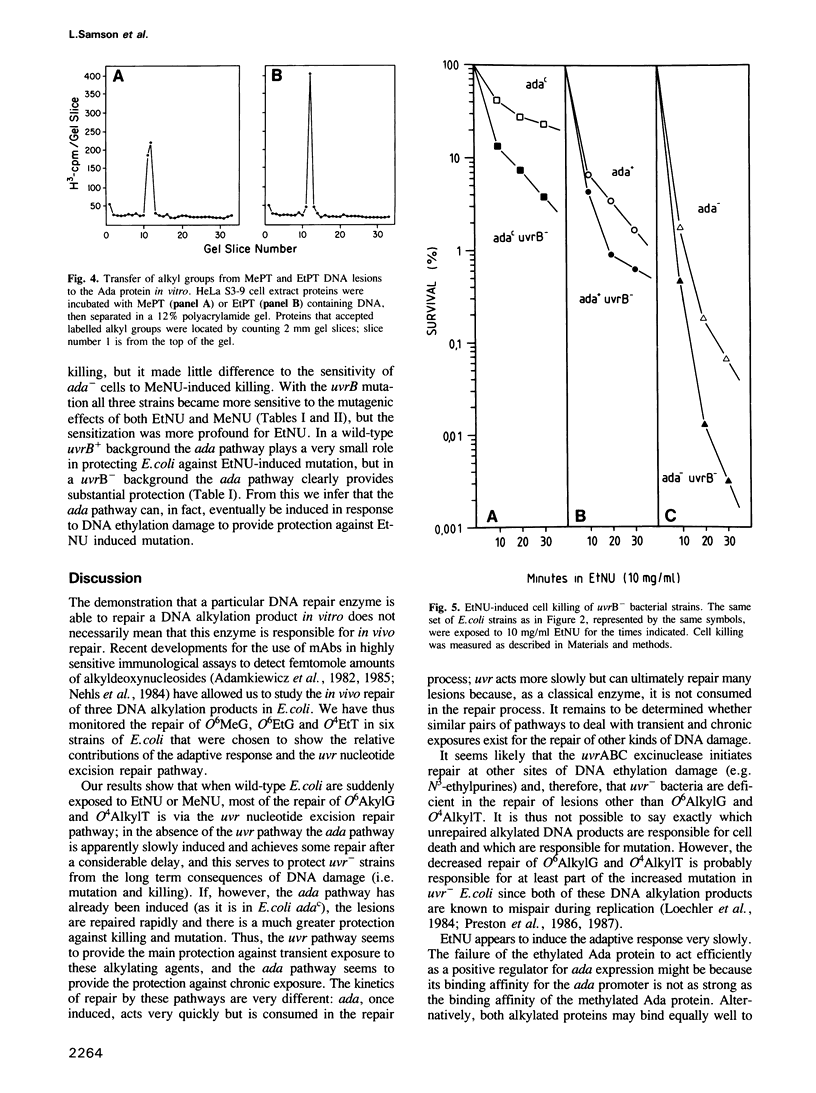
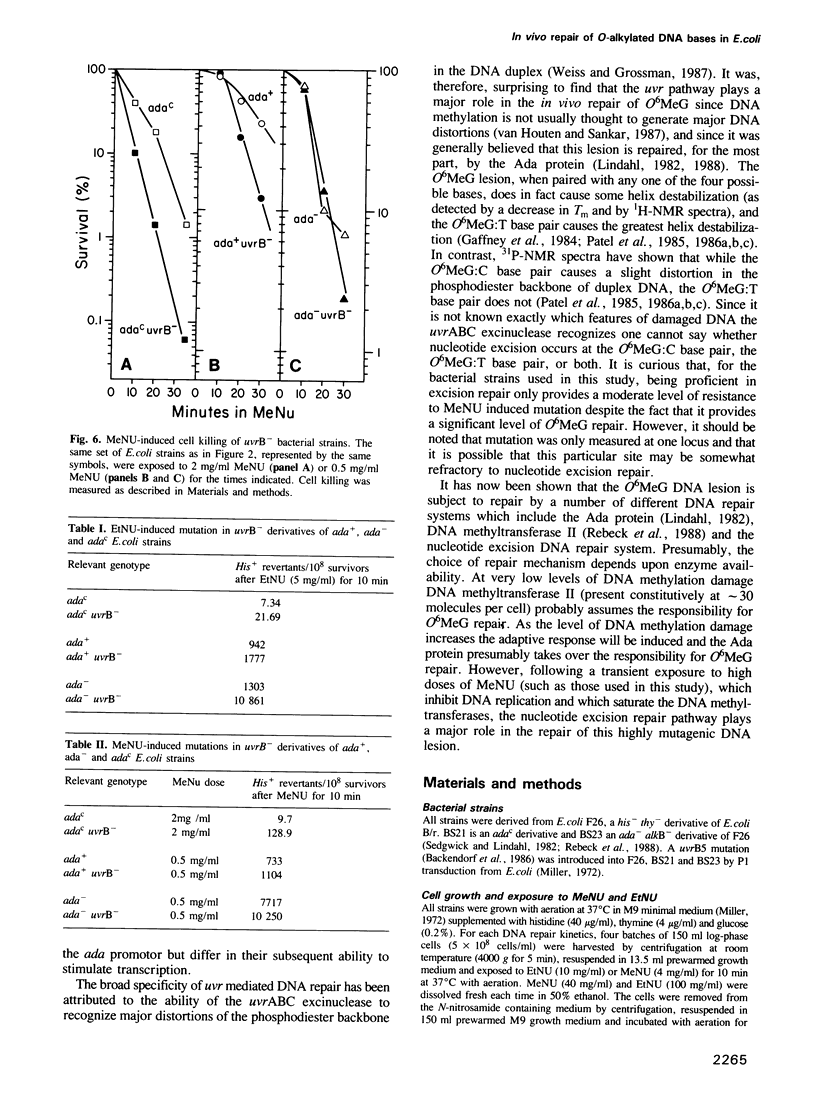
The in vivo removal of three different O-alkylated bases from DNA was measured in Escherichia coli. Using monoclonal antibodies specific for O6-methylguanine, O6-ethylguanine and O4-ethylthymine we have monitored the removal of these lesions from six different strains to assess the relative contributions of the adaptive response and of nucleotide excision repair. During the first hour after DNA alkylation, O6-methylguanine, O6-ethylguanine and O4-ethylthymine lesions were repaired almost exclusively by nucleotide excision, except when the adaptive response was being constitutively expressed. In wild-type E. coli the adaptive response began to contribute to O6-methylguanine repair about one hour after alkylation, the time required for the full induction of the ada DNA methyltransferase. In contrast, the adaptive response did not play such a large role in the repair of O6-ethylguanine and O4-ethylthymine in wild-type E. coli, presumably because DNA ethylation damage is a poor inducer of the adaptive response; possible reasons for this poor induction are discussed. The repair of all three O-alkylated lesions was virtually absent in ada- uvr- bacteria suggesting that no alternative pathway is available for their repair, at least during the first two hours after alkylation. When the repair of O-alkylated bases was compromised by an ada- or by a uvr- mutation, the bacteria became more sensitive to alkylation induced killing and mutation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamkiewicz J., Ahrens O., Huh N., Nehls P., Rajewsky M. F., Spiess E. High-affinity monoclonal antibodies for the specific recognition and quantification of deoxynucleosides structurally modified by N-nitroso compounds. IARC Sci Publ. 1984;(57):581–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamkiewicz J., Eberle G., Huh N., Nehls P., Rajewsky M. F. Quantitation and visualization of alkyl deoxynucleosides in the DNA of mammalian cells by monoclonal antibodies. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Oct;62:49–55. doi: 10.1289/ehp.856249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backendorf C., Spaink H., Barbeiro A. P., van de Putte P. Structure of the uvrB gene of Escherichia coli. Homology with other DNA repair enzymes and characterization of the uvrB5 mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2877–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Jacobsson A., Olsson M., Robins P., Lindahl T. Repair of alkylated DNA in Escherichia coli. Physical properties of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13776–13780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen G., Seeberg E. Adaptation to alkylation resistance involves the induction of a DNA glycosylase. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):773–775. doi: 10.1038/296773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote R. S., Mitra S., Pal B. C. Demethylation of O6-methylguanine in a synthetic DNA polymer by an inducible activity in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):654–659. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney B. L., Marky L. A., Jones R. A. Synthesis and characterization of a set of four dodecadeoxyribonucleoside undecaphosphates containing O6-methylguanine opposite adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5686–5691. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N., Rajewsky M. F. Enzymatic elimination of O6-ethylguanine and stability of O4-ethylthymine in the DNA of malignant neural cell lines exposed to N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea in culture. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Mar;7(3):435–439. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P., Defais T. M., Samson L., Schendel P. An adaptive response of E. coli to low levels of alkylating agent: comparison with previously characterised DNA repair pathways. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 29;157(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00268680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants unable to induce the adaptive response to simple alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):783–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.783-791.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Lindahl T., Ofsteng I., Evensen G. B., Seeberg E. Escherichia coli mutants deficient in 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):101–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Demple B., Robins P. Suicide inactivation of the E. coli O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1359–1363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loechler E. L., Green C. L., Essigmann J. M. In vivo mutagenesis by O6-methylguanine built into a unique site in a viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Karran P., Lindahl T. Inducible repair of O-alkylated DNA pyrimidines in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):545–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. Methyl phosphotriesters in alkylated DNA are repaired by the Ada regulatory protein of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2683–2698. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Pal B. C., Foote R. S. O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in wild-type and ada mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):534–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.534-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Rajewsky M. F. Antibodies specific for DNA components structurally modified by chemical carcinogens. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;102(2):99–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00410662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Rajewsky M. F. Immunological quantification by high-affinity antibodies of O6-ethyldeoxyguanosine in DNA exposed to N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):887–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Mine Y., Sekiguchi M. Regulation of expression of the cloned ada gene in Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1985 Sep;146(2):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Regulatory mechanisms for induction of synthesis of repair enzymes in response to alkylating agents: ada protein acts as a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6297–6301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls P., Adamkiewicz J., Rajewsky M. F. Immuno-slot-blot: a highly sensitive immunoassay for the quantitation of carcinogen-modified nucleosides in DNA. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1984;108(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00390969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson M., Lindahl T. Repair of alkylated DNA in Escherichia coli. Methyl group transfer from O6-methylguanine to a protein cysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10569–10571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L., Kozlowski S. A., Gaffney B. L., Jones R. A. Covalent carcinogenic O6-methylguanosine lesions in DNA. Structural studies of the O6 meG X A and O6meG X G interactions in dodecanucleotide duplexes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):677–692. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L., Kozlowski S. A., Gaffney B. L., Jones R. A. Structural studies of the O6meG.C interaction in the d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-O6meG-C-G) duplex. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1027–1036. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Shapiro L., Kozlowski S. A., Gaffney B. L., Jones R. A. Structural studies of the O6meG.T interaction in the d(C-G-T-G-A-A-T-T-C-O6meG-C-G) duplex. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1036–1042. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter P. M., Wilkinson M. C., Fitton J., Carr F. J., Brennand J., Cooper D. P., Margison G. P. Characterisation and nucleotide sequence of ogt, the O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9177–9193. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Singer B., Loeb L. A. Comparison of the relative mutagenicities of O-alkylthymines site-specifically incorporated into phi X174 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13821–13827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Singer B., Loeb L. A. Mutagenic potential of O4-methylthymine in vivo determined by an enzymatic approach to site-specific mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8501–8505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins P., Cairns J. Quantitation of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):74–76. doi: 10.1038/280074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):281–283. doi: 10.1038/267281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Derfler B., Waldstein E. A. Suppression of human DNA alkylation-repair defects by Escherichia coli DNA-repair genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5607–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. A novel repair enzyme: UVRABC excision nuclease of Escherichia coli cuts a DNA strand on both sides of the damaged region. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schendel P. F., Robins P. E. Repair of O6-methylguanine in adapted Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6017–6020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Lindahl T. A common mechanism for repair of O6-methylguanine and O6-ethylguanine in DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Demple B., Li B., Lindahl T. Induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli: the ada+ gene product serves both as a regulatory protein and as an enzyme for repair of mutagenic damage. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Kilpatrick M. W., McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. The intracellular signal for induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B., Sancar A. Repair of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced DNA damage by ABC excinuclease. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.540-545.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Nguyen D. C. Induction of specific Escherichia coli genes by sublethal treatments with alkylating agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4110–4114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarosh D. B., Fornace A. J., Day R. S., 3rd Human O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase fails to repair O4-methylthymine and methyl phosphotriesters in DNA as efficiently as does the alkyltransferase from Escherichia coli. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Jul;6(7):949–953. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.7.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


