Abstract
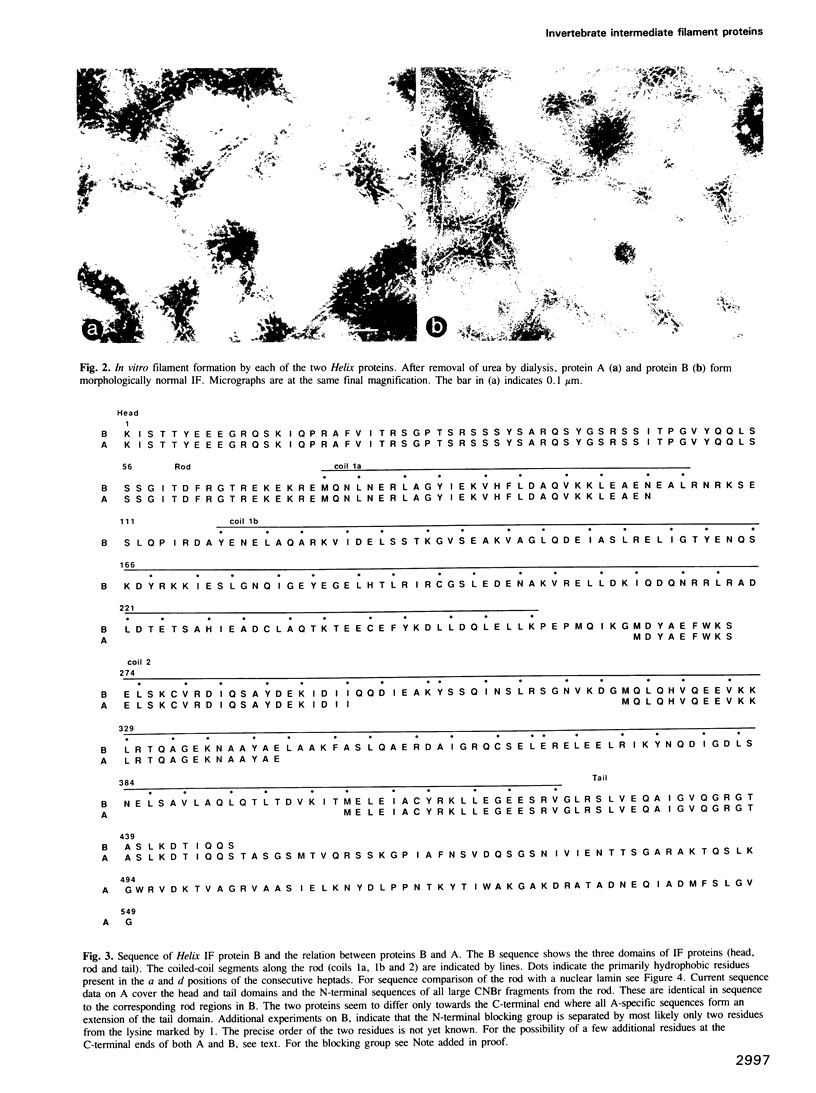
Intermediate filaments (IF) isolated from the oesophagus epithelium of the snail Helix pomatia contain two polypeptides of mol. wt 66,000 (A) and 52,000 (B), which we have now characterized by in vitro self-assembly studies and by protein sequences. A and B can each form morphologically normal IF and share extended regions of sequence identity. All A-specific sequences seem to locate to an extension of the carboxyl-terminal domain. Although the Helix protein(s) reveal the IF-consensus sequences at the ends of the coiled-coil, the remainder of the rod domain shows conservation of sequence principles rather than extended homology, when compared with any subtype of vertebrate IF proteins. Interestingly, the Helix proteins have the longer coil 1b domain found in nuclear lamins and not in cytoplasmic IF proteins of vertebrates. They lack, however, the karyophilic signal sequence typical for lamins. Obvious implications for IF evolution and structure are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Cohn J., Buhle L., Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):560–564. doi: 10.1038/323560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader B. L., Magin T. M., Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence and gene organization of cytokeratin no. 19, an exceptional tail-less intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1865–1875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarek J. M., Cowan N. J. Structure of the mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein gene: implications for the evolution of the intermediate filament multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5527–5543. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnik E., Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate filaments in muscle and epithelial cells of nematodes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2033–2041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
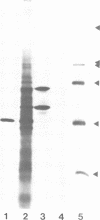
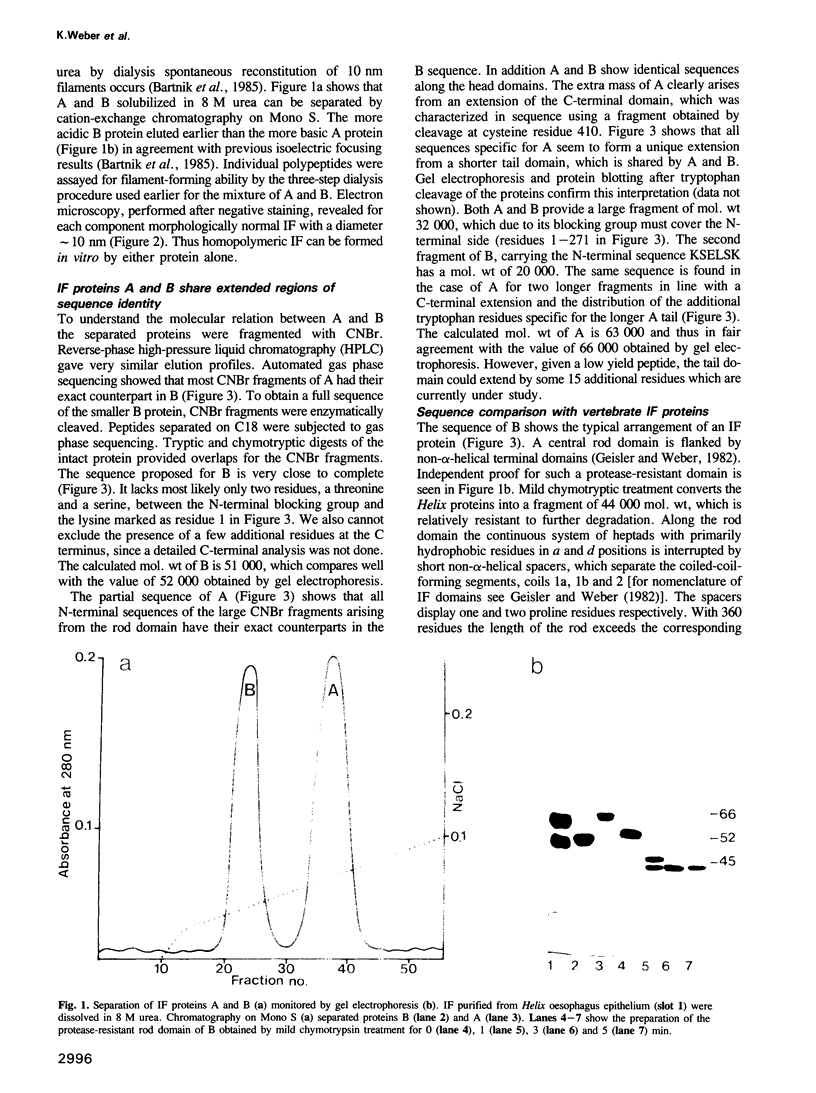
- Bartnik E., Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate filaments in non-neuronal cells of invertebrates: isolation and biochemical characterization of intermediate filaments from the esophageal epithelium of the mollusc Helix pomatia. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):427–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R., Bonitz P., Sun T. T. Classification of epidermal keratins according to their immunoreactivity, isoelectric point, and mode of expression. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1388–1396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R., Sun T. T., Aebi U. The role of keratin subfamilies and keratin pairs in the formation of human epidermal intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1767–1777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M., Krull L. H., Cavins J. F. The chromatographic determination of cystine and cysteine residues in proteins as s-beta-(4-pyridylethyl)cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3868–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Marchuk D. Type I and type II keratins have evolved from lower eukaryotes to form the epidermal intermediate filaments in mammalian skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Fischer S., Vandekerckhove J., Plessmann U., Weber K. Hybrid character of a large neurofilament protein (NF-M): intermediate filament type sequence followed by a long and acidic carboxy-terminal extension. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2701–2706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of the major mammalian neurofilament protein (NF-L). FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Phosphorylation of desmin in vitro inhibits formation of intermediate filaments; identification of three kinase A sites in the aminoterminal head domain. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice G. J., Fuchs E. The transfection of epidermal keratin genes into fibroblasts and simple epithelial cells: evidence for inducing a type I keratin by a type II gene. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Landesman Y., Drees B., Bare J. W., Saumweber H., Paddy M. R., Sedat J. W., Smith D. E., Benton B. M., Fisher P. A. Drosophila nuclear lamin precursor Dm0 is translated from either of two developmentally regulated mRNA species apparently encoded by a single gene. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):585–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Pair formation and promiscuity of cytokeratins: formation in vitro of heterotypic complexes and intermediate-sized filaments by homologous and heterologous recombinations of purified polypeptides. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1826–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heid H. W., Werner E., Franke W. W. The complement of native alpha-keratin polypeptides of hair-forming cells: a subset of eight polypeptides that differ from epithelial cytokeratins. Differentiation. 1986;32(2):101–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Wolin S. L., McKeon F. D., Franke W. W., Kirschner M. W. Nuclear lamin LI of Xenopus laevis: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and binding specificity of a member of the lamin B subfamily. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Gorham J. D., Cole P., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. A nerve growth factor-regulated messenger RNA encodes a new intermediate filament protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):181–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Genetics, evolution, and expression of the 68,000-mol-wt neurofilament protein: isolation of a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):843–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M. H., O'Guin W. M., Hardy C., Mak L., Sun T. T. Acidic and basic hair/nail ("hard") keratins: their colocalization in upper cortical and cuticle cells of the human hair follicle and their relationship to "soft" keratins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2593–2606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magin T. M., Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Analysis of cytokeratin domains by cloning and expression of intact and deleted polypeptides in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2607–2615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. W., Lazzarini R. A., Lee V. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Nelson D. L. The human mid-size neurofilament subunit: a repeated protein sequence and the relationship of its gene to the intermediate filament gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1617–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Liem R. K. The differential appearance of neurofilament triplet polypeptides in the developing rat optic nerve. Dev Biol. 1984 May;103(1):200–210. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Steven A. C., Steinert P. M. The coiled-coil molecules of intermediate filaments consist of two parallel chains in exact axial register. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):1012–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Files J. G., Weber K. Lac repressor. Specific proteolytic destruction of the NH 2 -terminal region and loss of the deoxyribonucleic acid-binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):110–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier M. M., de Néchaud B., Gros F. Peripherin, a new member of the intermediate filament protein family. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(6):335–344. doi: 10.1159/000112360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Heuvel R., Egberts W. V., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. Intermediate filament cDNAs from BHK-21 cells: demonstration of distinct genes for desmin and vimentin in all vertebrate classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5970–5974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan R. A., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Achtstätter T., Moll R., Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Patterns of expression and organization of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:282–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F., Dodemont H., Vorstenbosch P., Bloemendal H. Classification of rat lens crystallins and identification of proteins encoded by rat lens mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):503–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Weber K. Differential expression of neurofilament triplet proteins in brain development. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):277–279. doi: 10.1038/298277a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]