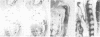Abstract
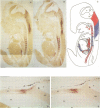
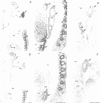
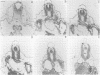
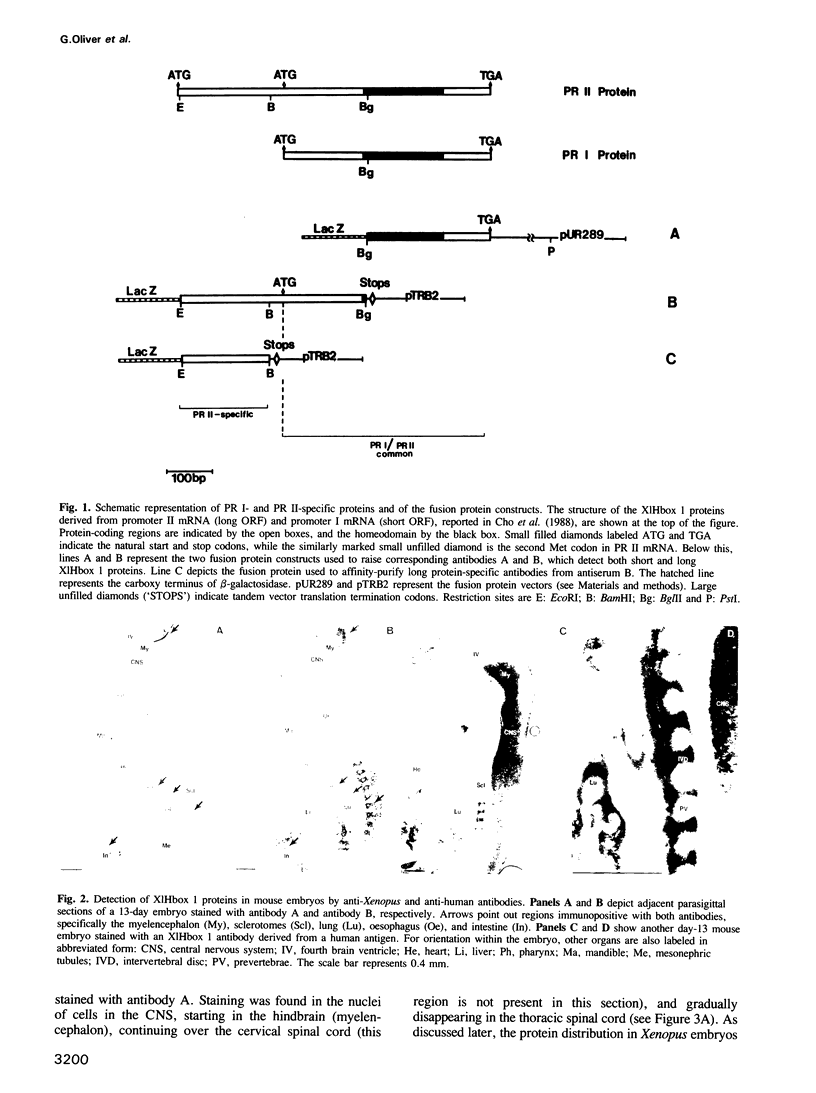
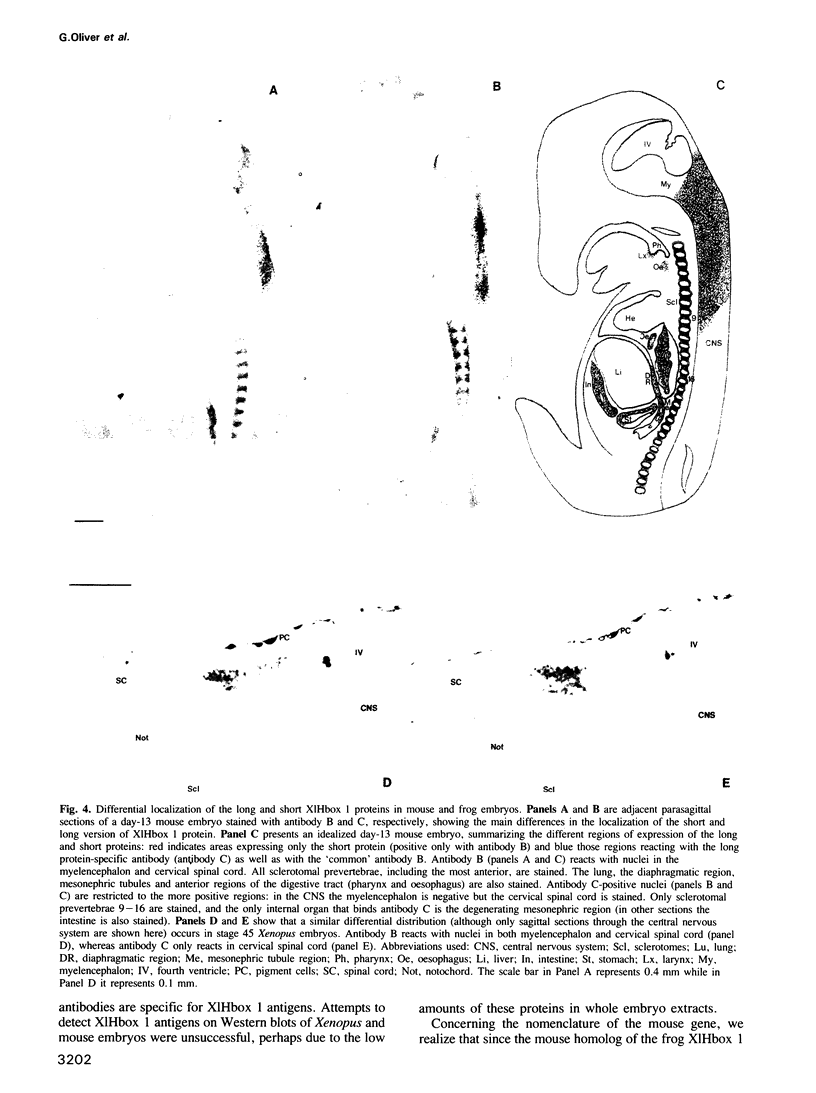
The X.laevis XlHbox 1 gene uses two functional promoters to produce a short and a long protein, both containing the same homeodomain. In this report we use specific antibodies to localize both proteins in frog embryos. The antibodies also recognize the homologous proteins in mouse embryos. In both mammalian and amphibian embryos, expression of the long protein starts more posteriorly than that of the short protein. This difference in spatial expression applies to the nervous system, the segmented mesoderm and the internal organs. This suggests that each promoter from this gene has precisely restricted regions of expression along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo. Because the long and short proteins share a common DNA-binding specificity but differ by an 82 amino acid domain, their differential distribution may have distinct developmental consequences.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awgulewitsch A., Utset M. F., Hart C. P., McGinnis W., Ruddle F. H. Spatial restriction in expression of a mouse homoeo box locus within the central nervous system. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):328–335. doi: 10.1038/320328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikel I., Roberts T. M., Bladon M. T., Green R., Amann E., Livingston D. M. Purification of biologically active simian virus 40 small tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):906–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Primary structure and developmental expression pattern of Hox 3.1, a member of the murine Hox 3 homeobox gene cluster. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1329–1336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. The nuclear migration signal of Xenopus laevis nucleoplasmin. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2617–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Croce C. M., Griffin C. A., Simeone A., Boncinelli E., Huebner K. Human homeo box-containing genes located at chromosome regions 2q31----2q37 and 12q12----12q13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):1–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., Malacinski G. M. Localization of Xenopus homoeo-box gene transcripts during embryogenesis and in the adult nervous system. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., McGinnis W., Gehring W. J., De Robertis E. M. Cloning of an X. laevis gene expressed during early embryogenesis coding for a peptide region homologous to Drosophila homeotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Goetz J., Wright C. V., Fritz A., Hardwicke J., De Robertis E. M. Differential utilization of the same reading frame in a Xenopus homeobox gene encodes two related proteins sharing the same DNA-binding specificity. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2139–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie B. G., Harland R. M. Posterior expression of a homeobox gene in early Xenopus embryos. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):93–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch U., Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Pax 1, a member of a paired box homologous murine gene family, is expressed in segmented structures during development. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90577-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Gruss P. Specific expression of the Hox 1.3 homeo box gene in murine embryonic structures originating from or induced by the mesoderm. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2965–2975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibi M., Zink B., Kessel M., Colberg-Poley A. M., Labeit S., Lehrach H., Gruss P. Coding sequence and expression of the homeobox gene Hox 1.3. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):349–359. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz A., De Robertis E. M. Xenopus homeobox-containing cDNAs expressed in early development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1453–1469. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J. Homoeobox gene Hox-1.5 expression in mouse embryos: earliest detection by in situ hybridization is during gastrulation. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Miller J. R., Powell D. J., Duboule D. Homoeobox gene expression in mouse embryos varies with position by the primitive streak stage. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):662–664. doi: 10.1038/324662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Spatially restricted patterns of expression of the homeobox-containing gene Hox 2.1. during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):159–174. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Schulze F., Fibi M., Gruss P. Primary structure and nuclear localization of a murine homeodomain protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5306–5310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Holland P. W., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):603–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Nomenclature for homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):21–22. doi: 10.1038/325021b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Taylor C. F., Palmer-Hill F. J., Friedrich V., Jr, Tani M., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a homeo domain protein in noncontact-inhibited cultured cells and postmitotic neurons. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):482–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe C. R., Fritz A., De Robertis E. M., Gurdon J. B. A homeobox-containing marker of posterior neural differentiation shows the importance of predetermination in neural induction. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe P. T., Miller J. R., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Gaunt S. J. Isolation and expression of a new mouse homeobox gene. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):397–407. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.2.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Mavilio F., Acampora D., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., D'Esposito M., Pannese M., Russo G., Boncinelli E. Two human homeobox genes, c1 and c8: structure analysis and expression in embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4914–4918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Homoeotic transformations in man: implications for the mechanism of embryonic development and for the organization of epithelia. J Theor Biol. 1985 Jun 7;114(3):463–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth L. E., Slawin K. L., Pintar J. E., Nguyen-Huu M. C. Region-specific expression of mouse homeobox genes in the embryonic mesoderm and central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6790–6794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utset M. F., Awgulewitsch A., Ruddle F. H., McGinnis W. Region-specific expression of two mouse homeo box genes. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1379–1382. doi: 10.1126/science.2881353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbout A. J. The development of the vertebral column. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1985;90:1–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69983-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]