Abstract
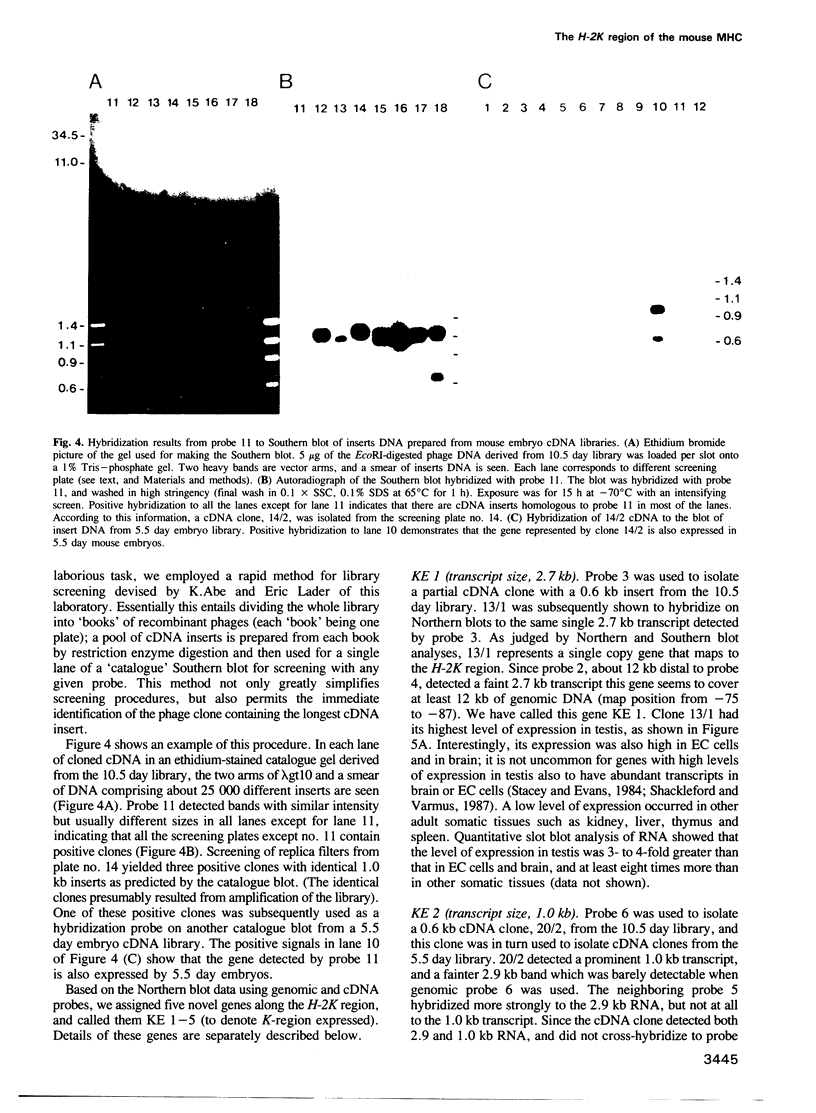
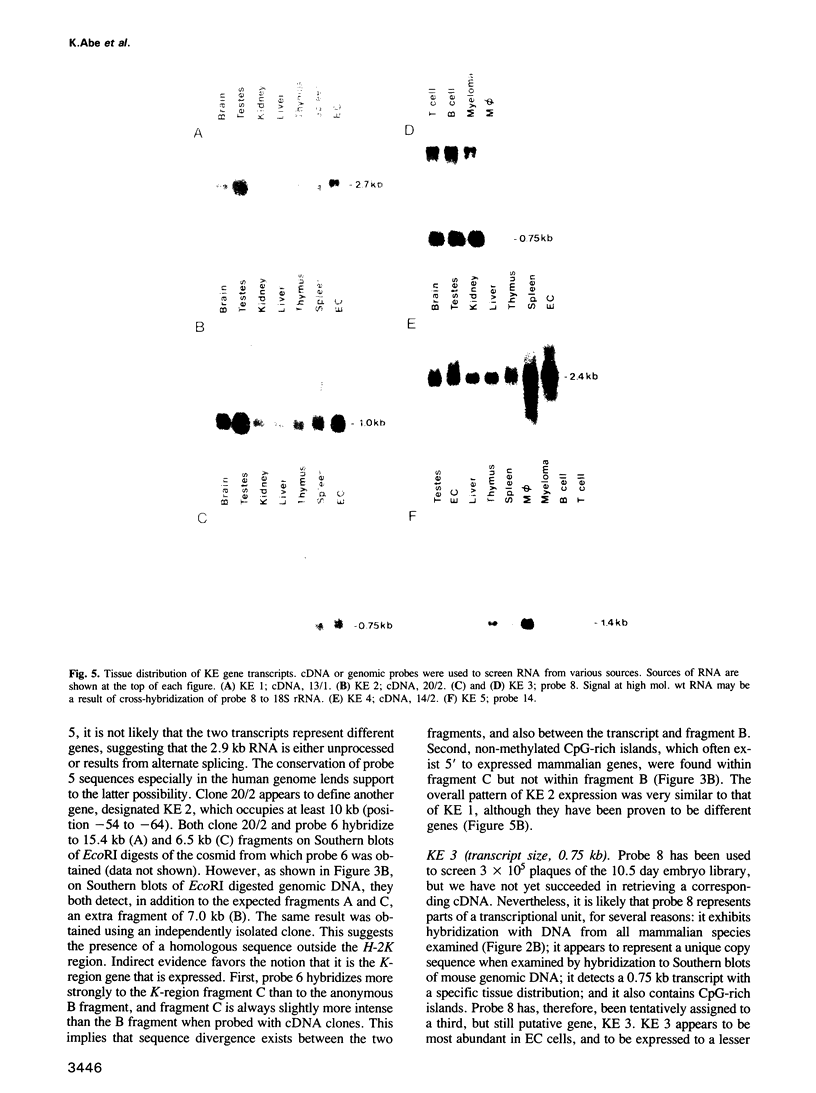
We have searched for expressed genes in 170 kb of cosmid cloned DNA from the H-2K region of the mouse MHC. This region is known to contain two genes, H-2K and K2. We identified unique/low copy sequences evenly spaced along the cloned DNA, and used these as probes to search for conserved sequences in Southern blots from a variety of mammalian species. The majority of the unique sequences were found to have homologues and most of these were associated with CpG non-methylated islands. Northern blot analysis and isolation of clones from 5.5 and 10.5-day embryo cDNA libraries showed five additional genes encoded in the H-2K region. Four of these are abundant in embryos; the fifth is exclusively expressed in lymphoid cells. Our data indicate a minimum of seven genes in 170 kb, an unexpectedly high gene density. These results differ from two recent studies where similar lengths of cloned DNA were examined for expressed genes, and only one, or a part of one gene was found. The combined data suggest that the spatial organization of genes in the mammalian genome may not be random.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman A., Sferruzza A., Weiner R. G., Katz D. H. Constitutive and mitogen-induced production of T cell growth factor by stable T cell hybridoma lines. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1365–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artzt K., Abe K., Uehara H., Bennett D. Intra-H-2 recombination in t haplotypes shows a hot spot and close linkage of 1tw5 to H-2K. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(1):30–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00372526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artzt K. Gene mapping within the T/t complex of the mouse. III: t-Lethal genes are arranged in three clusters on chromosome 17. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90463-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Oudshoorn-Snoek M. H-2 class I antigen expression on mouse teratocarcinoma cell lines. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(6):543–552. doi: 10.1007/BF00430302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida H., Miyata T. Unusual evolutionary conservation and frequent DNA segment exchange in class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2671–2675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes C. E., Bach F. H. I-N: a newly described H-2 I subregion between K and I-A. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):481–485. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Y. C. In vitro development of individually cultured whole mouse embryos from blastocyst to early somite stage. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. L., Clipson L. J., Dove W. F., Feilbach J., Maher L. J., Shedlovsky A. Teratocarcinoma transplantation antigens are encoded in the H-2 region. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(2):137–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00368542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavia P., Macleod D., Bird A. Coincident start sites for divergent transcripts at a randomly selected CpG-rich island of mouse. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Wiley L. M., Damjanov I. The development of cystic embryoid bodies in vitro from clonal teratocarcinoma stem cells. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):230–244. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Aldridge J., Fischbeck K. H., Bartlett R., Pericak-Vance M. A., Roses A. D., Kunkel L. M. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):842–845. doi: 10.1038/316842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. Identification of a fourth class of proteins linked to the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3001–3005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. The LMP antigens: a stable MHC-controlled multisubunit protein complex. Hum Immunol. 1986 Apr;15(4):416–426. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser A. R., Shedlovsky A., Johnson L. L. H-2 class I and Gt (H-2) antigens are identical: evidence from H-2 mutant mice. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):271–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00373023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Stephan D., Philippsen P., Steinmetz M. Orientation and molecular map position of the complement genes in the mouse MHC. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):369–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Reverse genetics and human disease. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):845–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold G. A., Stubbs L., Labeit S., Crkvenjakov R. B., Lehrach H. Identification of a testis-specific gene from the mouse t-complex next to a CpG-rich island. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1975–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard H. W., Gutman G. A. Rat kappa-chain J-segment genes: two recent gene duplications separate rat and mouse. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Bennett D., Artzt K. Gene mapping within the T/t complex of the mouse. IV: The inverted MHC is intermingled with several t-lethal genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90464-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin H. S., Flaherty L., Artzt K., Bennett D., Ravetch J. Inversion in the H-2 complex of t-haplotypes in mice. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):380–383. doi: 10.1038/306380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey A. J., Evans M. J. A gene sequence expressed only in undifferentiated EC, EK cells and testes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2279–2285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tykocinski M. L., Max E. E. CG dinucleotide clusters in MHC genes and in 5' demethylated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4385–4396. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara H., Abe K., Park C. H., Shin H. S., Bennett D., Artzt K. The molecular organization of the H-2K region of two t-haplotypes: implications for the evolution of genetic diversity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):83–90. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04722.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widera G., Flavell R. A. The I region of the C57BL/10 mouse: characterization and physical linkage to H-2K of an SB beta-like class II pseudogene, psi A beta 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5500–5504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. K., Masters J. N., Attardi G. Human dihydrofolate reductase gene organization. Extensive conservation of the G + C-rich 5' non-coding sequence and strong intron size divergence from homologous mammalian genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):169–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]