Abstract
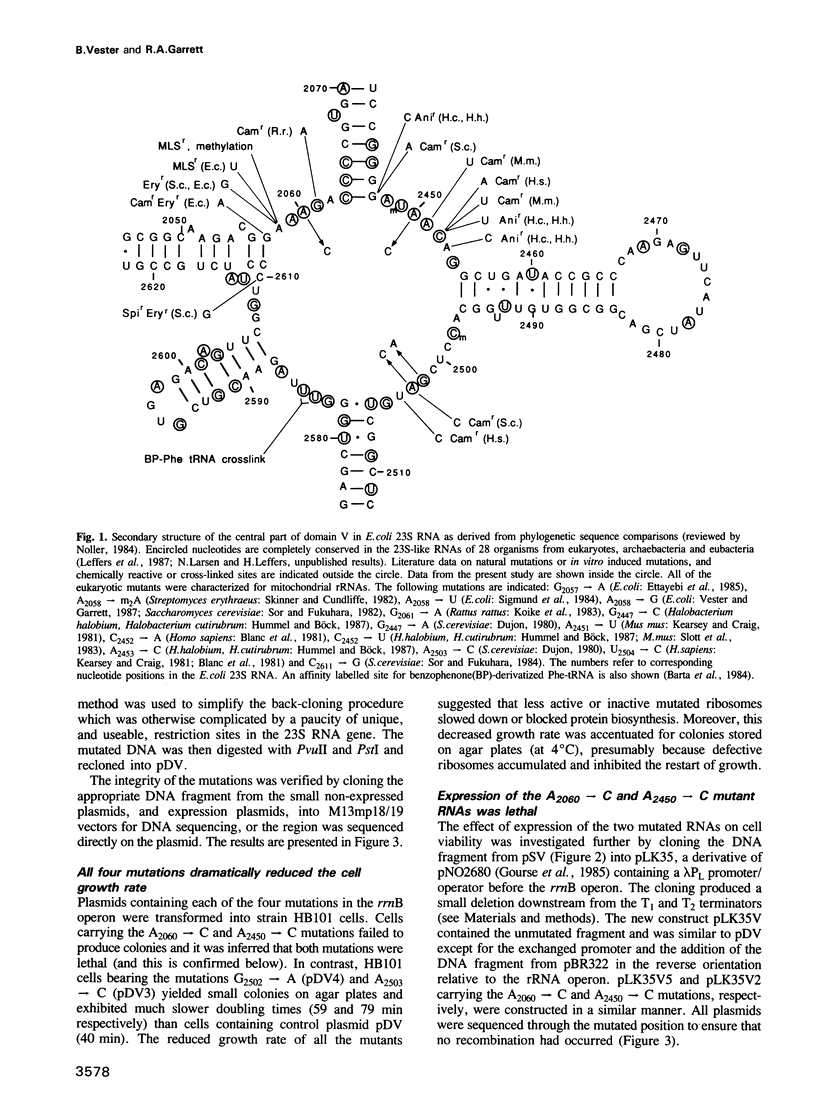
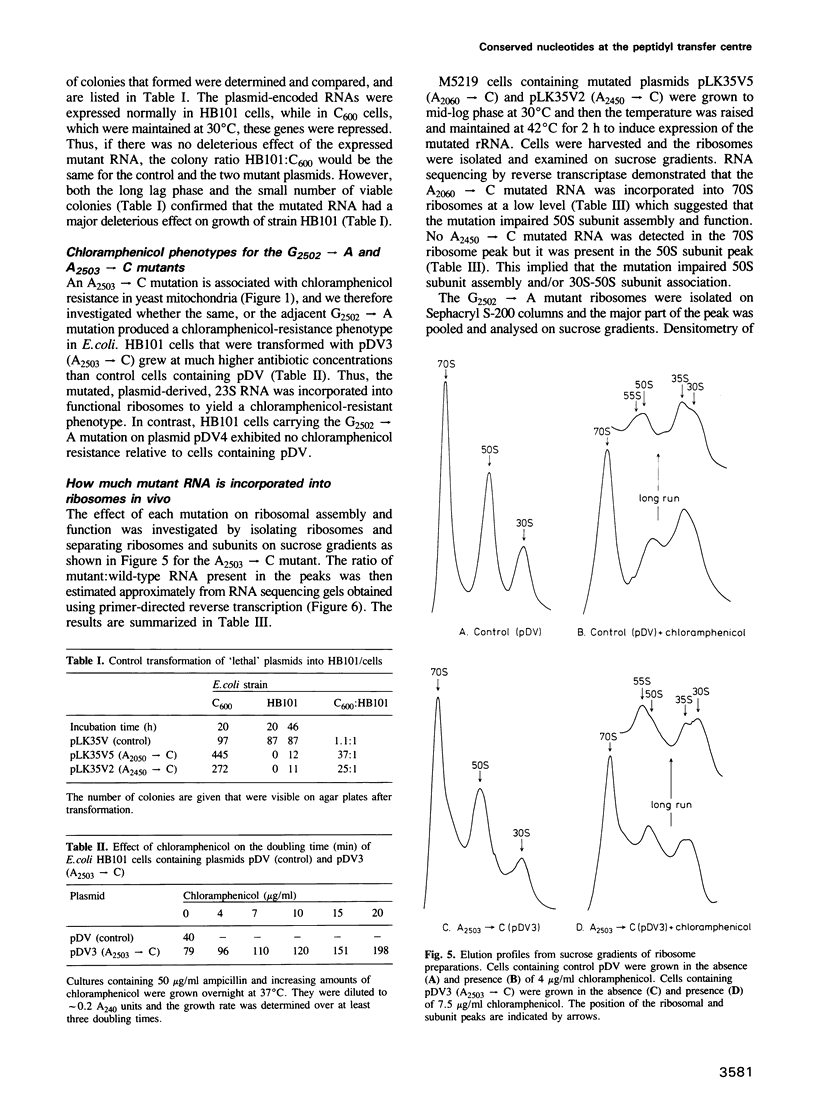
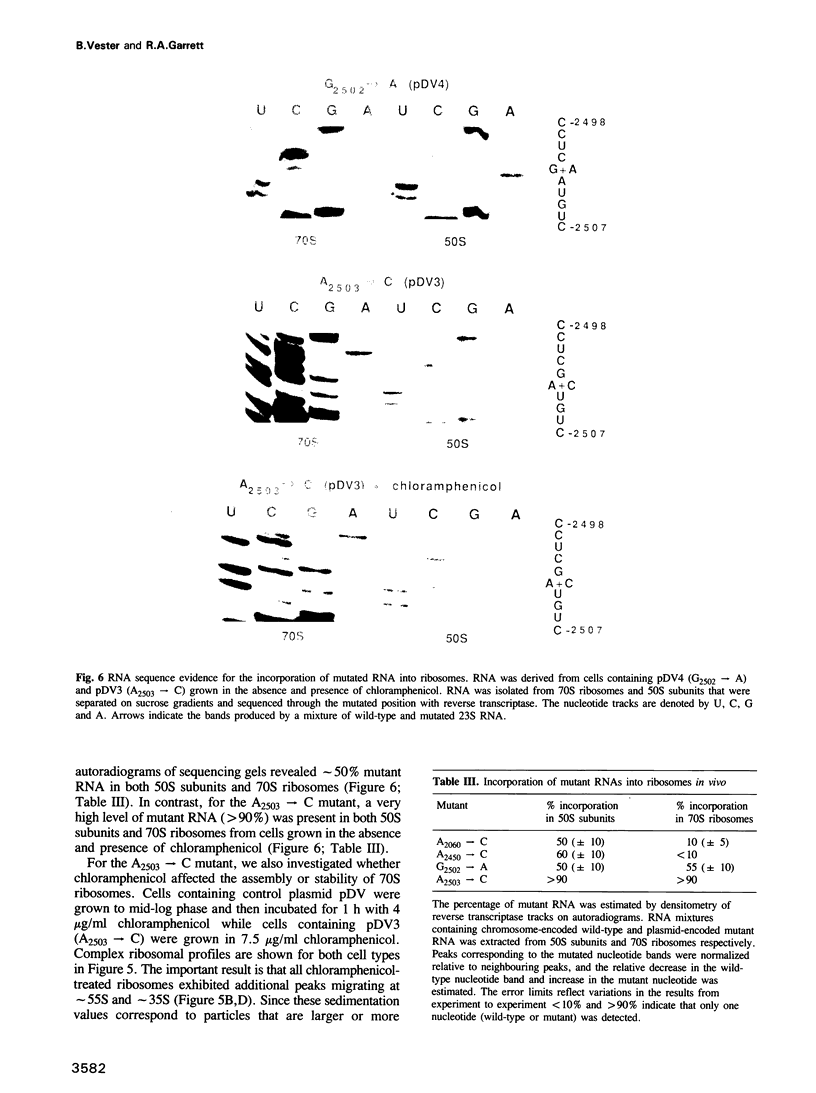
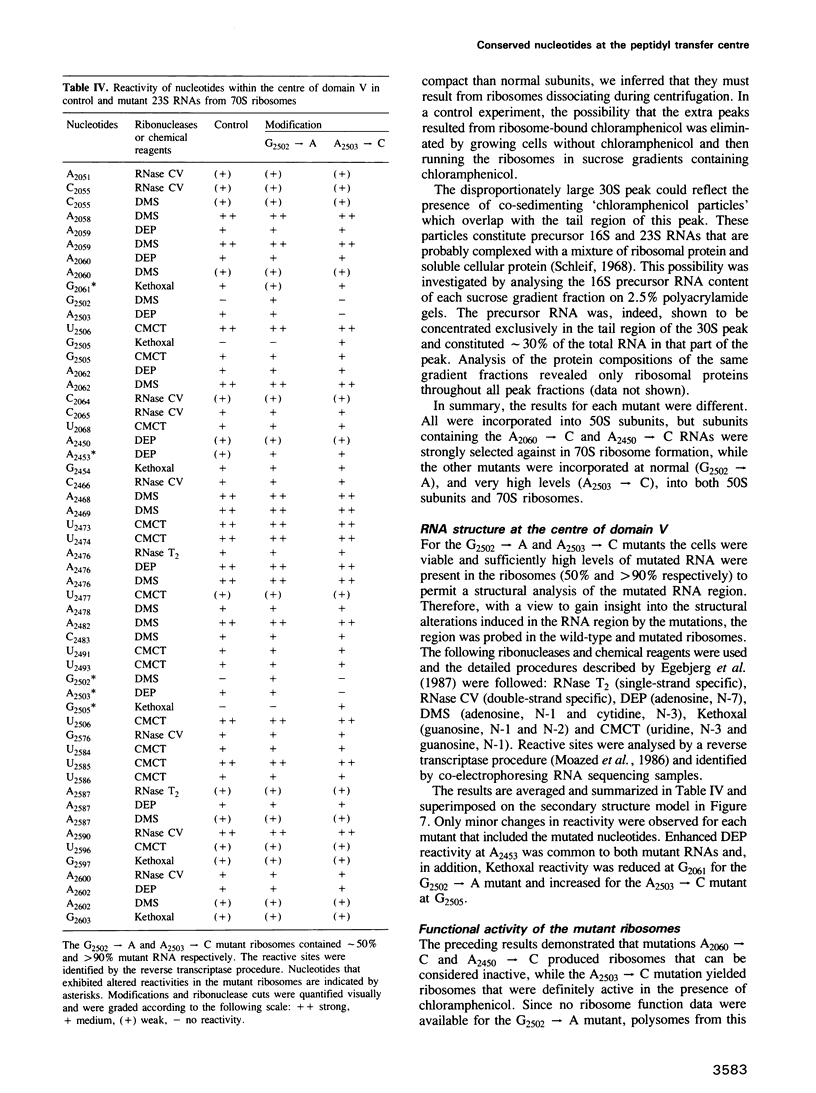
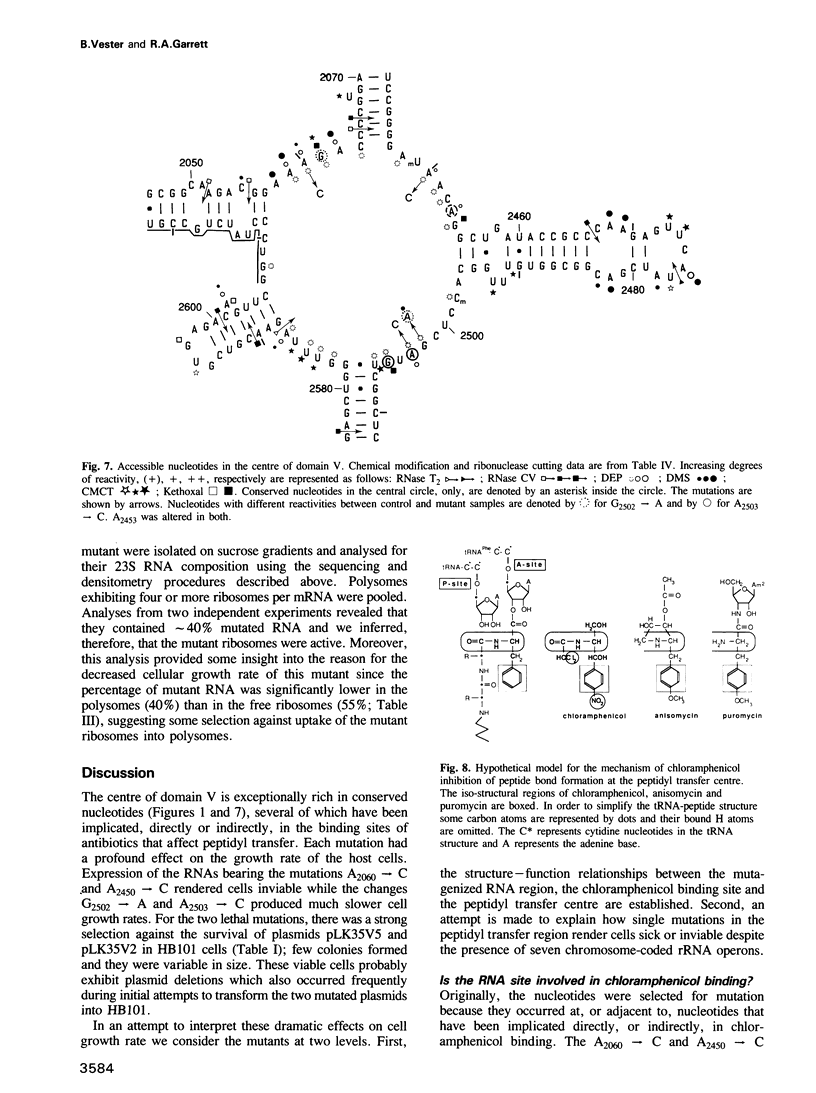
The peptidyl transfer site has been localized at the centre of domain V of 23S-like ribosomal RNA (rRNA) primarily on the basis of a chloramphenicol binding site. The implicated region constitutes an unstructured circle in the current secondary structural model which contains several universally conserved nucleotides. With a view to investigate the function of this RNA region further, four of these conserved nucleotides, including one indirectly implicated in chloramphenicol binding, were selected for mutation in Escherichia coli 23S rRNA using oligonucleotide primers. Mutant RNAs were expressed in vivo on a plasmid-encoded rRNA (rrnB) operon and each one yielded dramatically altered phenotypes. Cells exhibiting A2060----C or A2450----C transversions were inviable and it was shown by inserting the mutated genes after a temperature-inducible promoter that the mutant RNAs were directly responsible. In addition, a G2502----A transition caused a decreased growth rate, probably due to a partial selection against mutant ribosome incorporation into polysomes, while an A2503----C transversion produced a decreased growth rate and conferred resistance to chloramphenicol. All of the mutant RNAs were incorporated into 50S subunits, but while the two lethal mutant RNAs were strongly selected against in 70S ribosomes, the plasmid-encoded A2503----C RNA was preferred over the chromosome-encoded RNA, contrary to current regulatory theories. The results establish the critical structural and functional importance of highly conserved nucleotides in the chloramphenicol binding region. A mechanistic model is also presented to explain the disruptive effect of chloramphenicol (and other antibiotics) on peptide bond formation at the ribosomal subunit interface.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barta A., Steiner G., Brosius J., Noller H. F., Kuechler E. Identification of a site on 23S ribosomal RNA located at the peptidyl transferase center. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3607–3611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc H., Adams C. W., Wallace D. C. Different nucleotide changes in the large rRNA gene of the mitochondrial DNA confer chloramphenicol resistance on two human cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5785–5795. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Ullrich A., Raker M. A., Gray A., Dull T. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Construction and fine mapping of recombinant plasmids containing the rrnB ribosomal RNA operon of E. coli. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Olsson C. L., Hershey J. W., Grunberg-Manago M., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Requirement for initiation factor IF2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Sequence of the intron and flanking exons of the mitochondrial 21S rRNA gene of yeast strains having different alleles at the omega and rib-1 loci. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Leffers H., Christensen A., Andersen H., Garrett R. A. Structure and accessibility of domain I of Escherichia coli 23 S RNA in free RNA, in the L24-RNA complex and in 50 S subunits. Implications for ribosomal assembly. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90515-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettayebi M., Prasad S. M., Morgan E. A. Chloramphenicol-erythromycin resistance mutations in a 23S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):551–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.551-557.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Sinsheimer R. L. Use of Brij lysis as a general method to prepare polyribosomes from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 19;149(2):489–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Takebe Y., Sharrock R. A., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and accumulation of free ribosomes after conditional expression of rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1069–1073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel H., Böck A. 23S ribosomal RNA mutations in halobacteria conferring resistance to the anti-80S ribosome targeted antibiotic anisomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2431–2443. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob W. F., Santer M., Dahlberg A. E. A single base change in the Shine-Dalgarno region of 16S rRNA of Escherichia coli affects translation of many proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4757–4761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelenc P. C. Rapid purification of highly active ribosomes from Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Expression of rRNA and tRNA genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for feedback regulation by products of rRNA operons. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):865–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUCAN Z., LIPMANN F. DIFFERENCES IN CHLORAMPHENICOL SENSITIVITY OF CELL-FREE AMINO ACID POLYMERIZATION SYSTEMS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:516–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. E., Craig I. W. Altered ribosomal RNA genes in mitochondria from mammalian cells with chloramphenicol resistance. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):607–608. doi: 10.1038/290607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Kjems J., Ostergaard L., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria. A comparative study of 23 S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile and a thermophilic methanogen. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chao S., Bremer H. Effect of the bacterial growth rate on replication control of plasmid pBR322 in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):143–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00330395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Transfer RNA shields specific nucleotides in 16S ribosomal RNA from attack by chemical probes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):985–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90813-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Stern S., Noller H. F. Rapid chemical probing of conformation in 16 S ribosomal RNA and 30 S ribosomal subunits using primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Chaires J. B. Functional modification of 16S ribosomal RNA by kethoxal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3115–3118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Antibiotics as probes of ribosome structure: binding of chloramphenicol and erythromycin to polyribosomes; effect of other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):255–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Stanssens P., Fiers W. Plasmid vectors for high-efficiency expression controlled by the PL promoter of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. F. Origin of chloramphenicol particle protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Holland I. B. Effect of colicin E3 upon the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):959–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4653–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slott E. F., Jr, Shade R. O., Lansman R. A. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial DNA in a mouse cell line resistant to chloramphenicol and oligomycin. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1694–1702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Erythromycin and spiramycin resistance mutations of yeast mitochondria: nature of the rib2 locus in the large ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8313–8318. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Identification of two erythromycin resistance mutations in the mitochondrial gene coding for the large ribosomal RNA in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6571–6577. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Antibiotics affecting chloramphenicol uptake by bacteria. Their effect on amino acid incorporation in a cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vester B., Garrett R. A. A plasmid-coded and site-directed mutation in Escherichia coli 23S RNA that confers resistance to erythromycin: implications for the mechanism of action of erythromycin. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]