Abstract
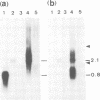
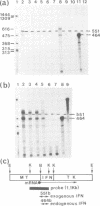
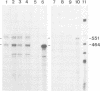
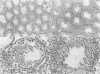
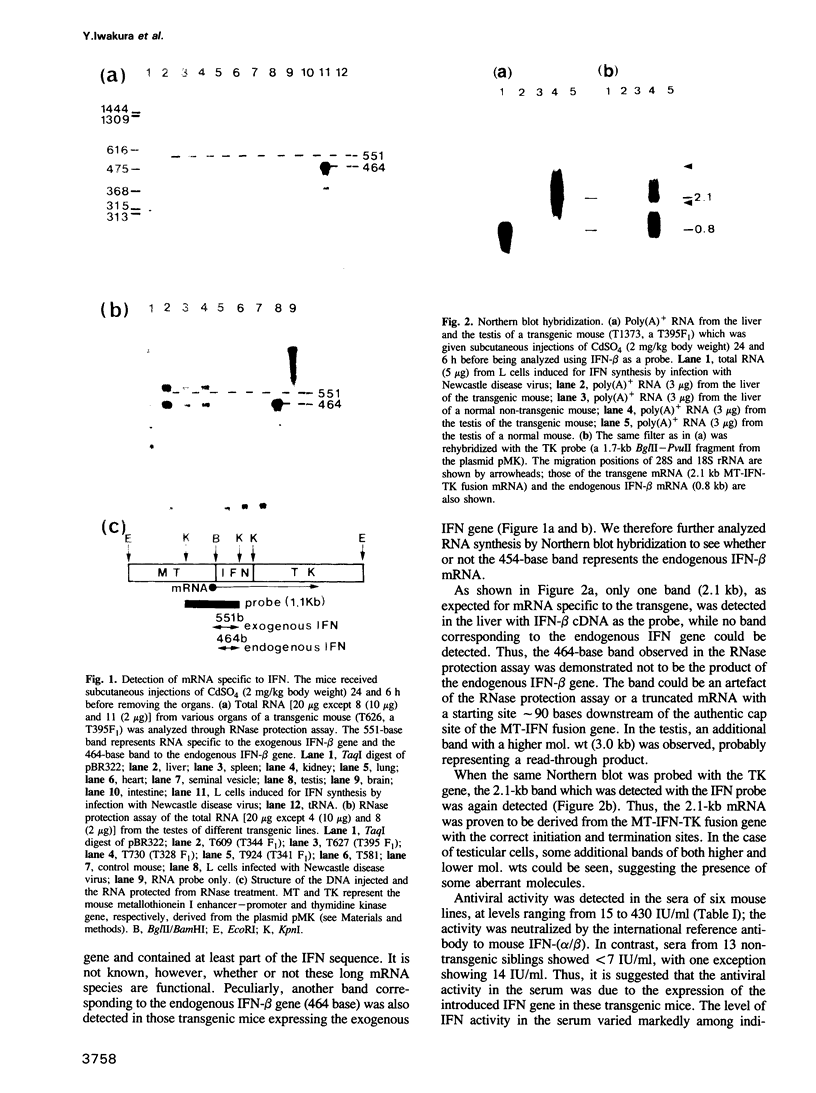
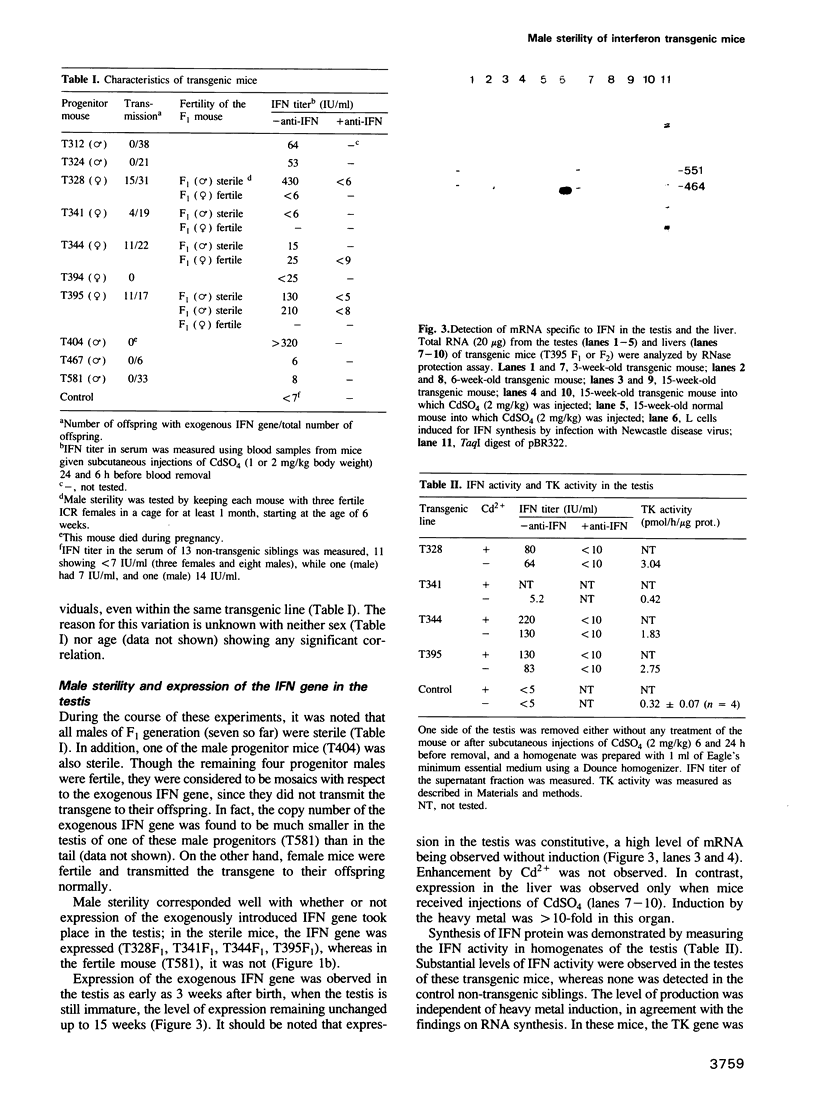
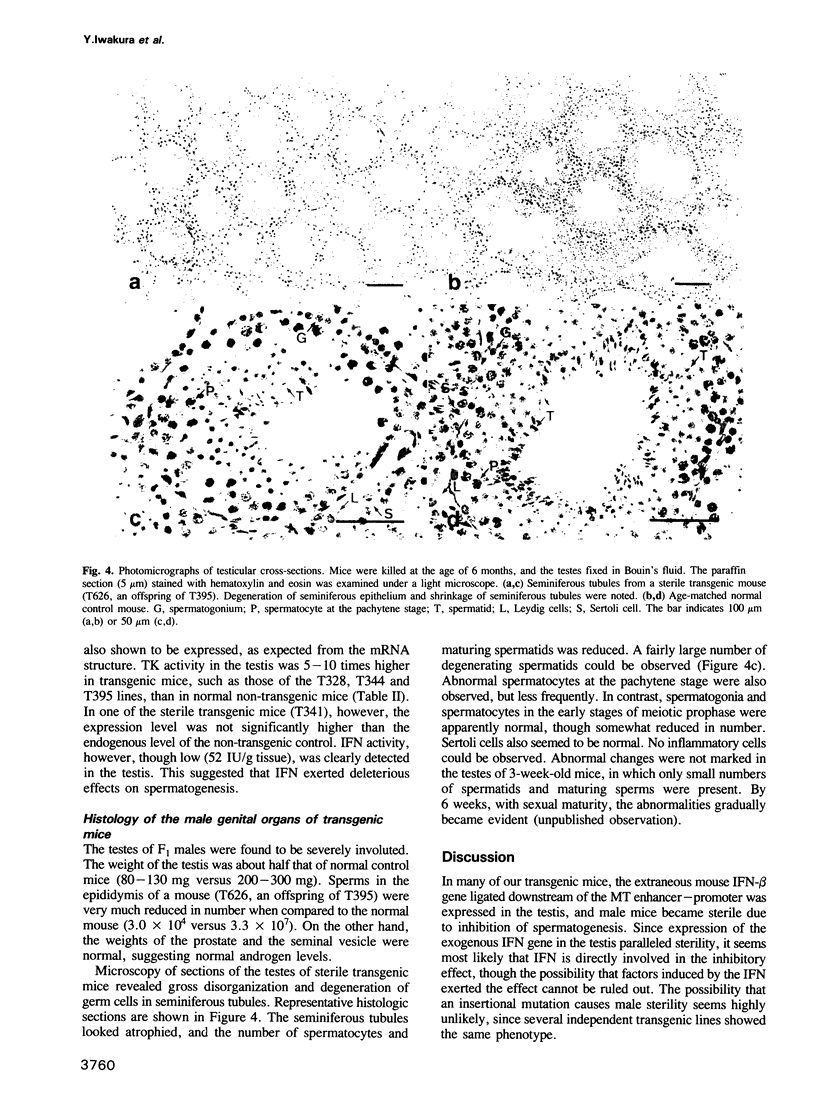
As an approach to elucidating the roles of interferon (IFN) in the normal physiology and diseases of animals, transgenic mice carrying extra mouse IFN-beta genes under the control of a mouse metallothionein I enhancer-promoter were constructed. Upon induction with Cd2+, IFN activity (15-430 IU/ml) was detected in the sera of six out of ten transgenic mouse lines so far obtained. Synthesis of mRNA of the transgene was observed in the liver, the testis and less abundantly in the brain. Interestingly, IFN mRNA was constitutively synthesized in the testis where substantial levels of IFN accumulated without heavy metal induction, whereas synthesis in the liver was mostly dependent on induction by CD2+. Since IFN activity in the serum also depended on heavy metal induction, the IFN in the serum may be produced mainly in the liver. All males expressing the IFN gene in the testis were found to be sterile. Testes were involuted and contained few mature sperm, and degeneration of spermatocytes and spermatids was observed. These findings suggest that high levels of IFN are harmful to spermatogenesis and can cause male sterility.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Warren R., Sarthy A., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein--thymidine kinase fusion plasmids injected into mouse eggs. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):39–42. doi: 10.1038/296039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucchini D., Ripoche M. A., Stinnakre M. G., Desbois P., Lorès P., Monthioux E., Absil J., Lepesant J. A., Pictet R., Jami J. Pancreatic expression of human insulin gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2511–2515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Immunomodulation by interferons: recent developments. Interferon. 1985;6:69–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolei A., Capobianchi M. R., Ameglio F. Human interferon-gamma enhances the expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex products in neoplastic cells more effectively than interferon-alpha and interferon-beta. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):172–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.172-176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc-Goiran P., Robert-Galliot B., Lopez J., Chany C. Unusual apparently constitutive interferons and antagonists in human placental blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. Can interferon induce disease? Interferon. 1982;4:95–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura Y., Nozaki M. Effects of tunicamycin on preimplantation mouse embryos: prevention of molecular differentiation during blastocyst formation. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura Y., Yonehara S., Kawade Y. Purification of mouse L cell interferon. Essentially pure preparations with associated cell growth inhibitory activity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5074–5079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawade Y. An analysis of neutralization reaction of interferon by antibody: a proposal on the expression of neutralization titer. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):61–70. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuribayashi K., Hikata M., Hiraoka O., Miyamoto C., Furuichi Y. A rapid and efficient purification of poly(A)-mRNA by oligo(dT)30-Latex. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1988;(19):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magram J., Chada K., Costantini F. Developmental regulation of a cloned adult beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):338–340. doi: 10.1038/315338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):343–345. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Wilkie T. M., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Transmission distortion and mosaicism in an unusual transgenic mouse pedigree. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Widera G., Cowing C., Heber-Katz E., Palmiter R. D., Flavell R. A., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific, inducible and functional expression of the E alpha d MHC class II gene in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2225–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Hatat D., Abadie A., Wallach D., Revel M., Fellous M. Differential regulation of HLA-DR mRNAs and cell surface antigens by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1585–1589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Streuli M., Gresser I., Gugenheim J., Blanchard B., Guymarho J., Vignaux F., Gigou M. Interferon messenger RNA is produced constitutively in the organs of normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J. Adverse effects of interferon in virus infections, autoimmune diseases and acquired immunodeficiency. Prog Med Virol. 1984;30:62–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: distinct antigenicity of the two L cell interferon species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]