Abstract
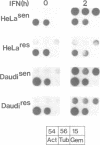
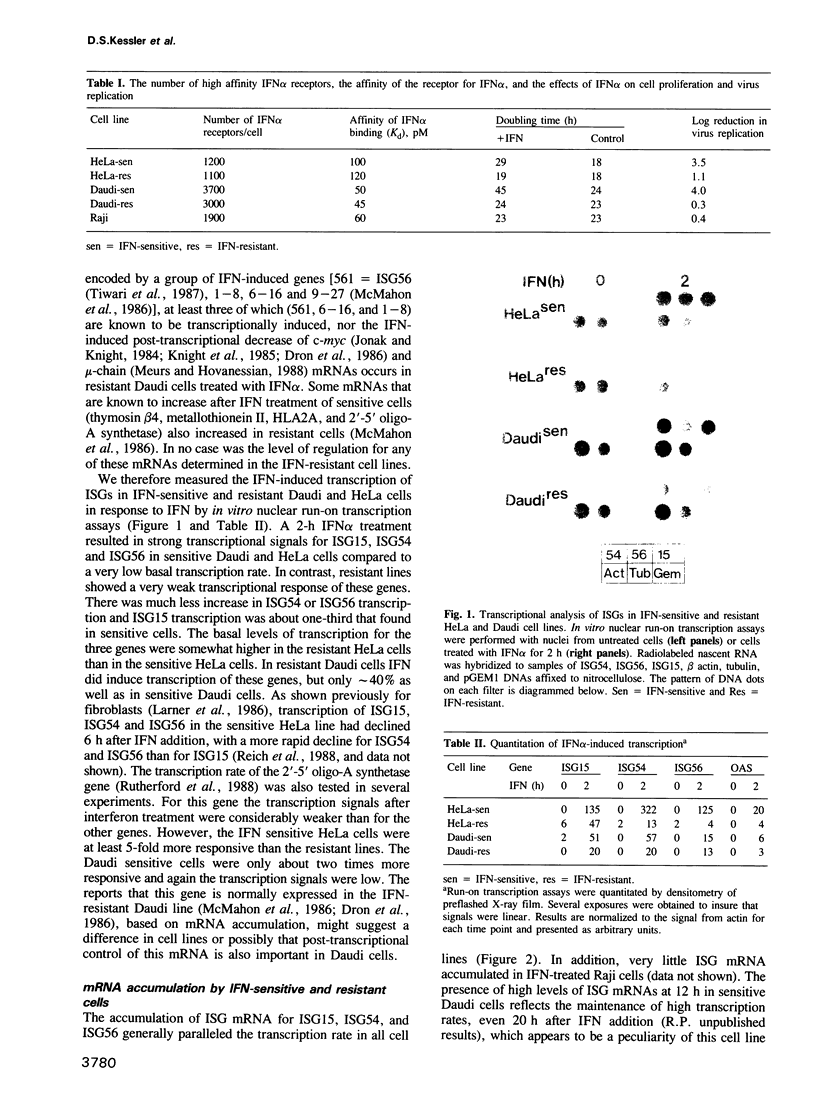
Human cultured cell lines deficient in their ability to respond to type I interferon (IFN) fail to interrupt cellular proliferation or to induce an antiviral state following exposure to IFN alpha. Comparison of non-responsive Daudi and HeLa cell lines with IFN-responsive partner cell lines and examination of non-responsive Raji cells showed that the defective cell lines expressed type I IFN receptors of typical number and affinity and bound IFN equivalently compared to the normal cells. However, transcriptional induction of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) was greatly reduced and delayed in these cell lines, leading to reduced accumulation of ISG mRNA. Furthermore, the rapid activation of IFN-stimulated promoter binding factors whose appearance correlates with ISG transcriptional induction, did not occur in non-responsive cells. Thus, the primary defect of these cells leading to an impaired physiological response to IFN appears to be an inability to activate promoter-binding factors necessary to trigger ISG transcription, an obligate early step in antiviral and antiproliferative physiology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen B., Peretz D., Vaiman D., Benech P., Chebath J. Enhancer-like interferon responsive sequences of the human and murine (2'-5') oligoadenylate synthetase gene promoters. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Modjtahedi N., Brison O., Tovey M. G. Interferon modulation of c-myc expression in cloned Daudi cells: relationship to the phenotype of interferon resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G., Eid P. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. III. Interferon-induced proteins in relation to the phenotype of interferon resistance. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):787–795. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. I. Characterization. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2641–2647. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannigan G. E., Gewert D. R., Williams B. R. Characterization and regulation of alpha-interferon receptor expression in interferon-sensitive and -resistant human lymphoblastoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9456–9460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak G. J., Knight E., Jr Selective reduction of c-myc mRNA in Daudi cells by human beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1747–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential regulation of interferon-induced mRNAs and c-myc mRNA by alpha- and gamma-interferons. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 2;153(2):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Anton E. D., Fahey D., Friedland B. K., Jonak G. J. Interferon regulates c-myc gene expression in Daudi cells at the post-transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1151–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Sen G. C. Transcriptional analyses of interferon-inducible mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):528–531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Larner A., Chaudhuri A., Babiss L. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-stimulated transcription: isolation of an inducible gene and identification of its regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8929–8933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon-induced gene expression in wild-type and interferon-resistant human lymphoblastoid (Daudi) cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.362-366.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Hovanessian A. G. Alpha-interferon inhibits the expression of heavy chain mu messenger RNA in Daudi cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1689–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Stebbing N., Donner D. B. Cytoskeletal association of human alpha-interferon-receptor complexes in interferon-sensitive and -resistant lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Pine R., Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription of interferon-stimulated genes is induced by adenovirus particles but is suppressed by E1A gene products. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.114-119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. H., Watling D., Balkwill F. R., Trowsdale J., Kerr I. M. The ppp(A2'p)nA and protein kinase systems in wild-type and interferon-resistant Daudi cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Lin S. L., Pfeffer L. M., Sehgal P. B. Interferons alpha and beta as cellular regulatory molecules. Interferon. 1987;9:13–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Sen G. C. Functional equivalents of interferon-mediated signals needed for induction of an mRNA can be generated by double-stranded RNA and growth factors. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3373–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]