Abstract
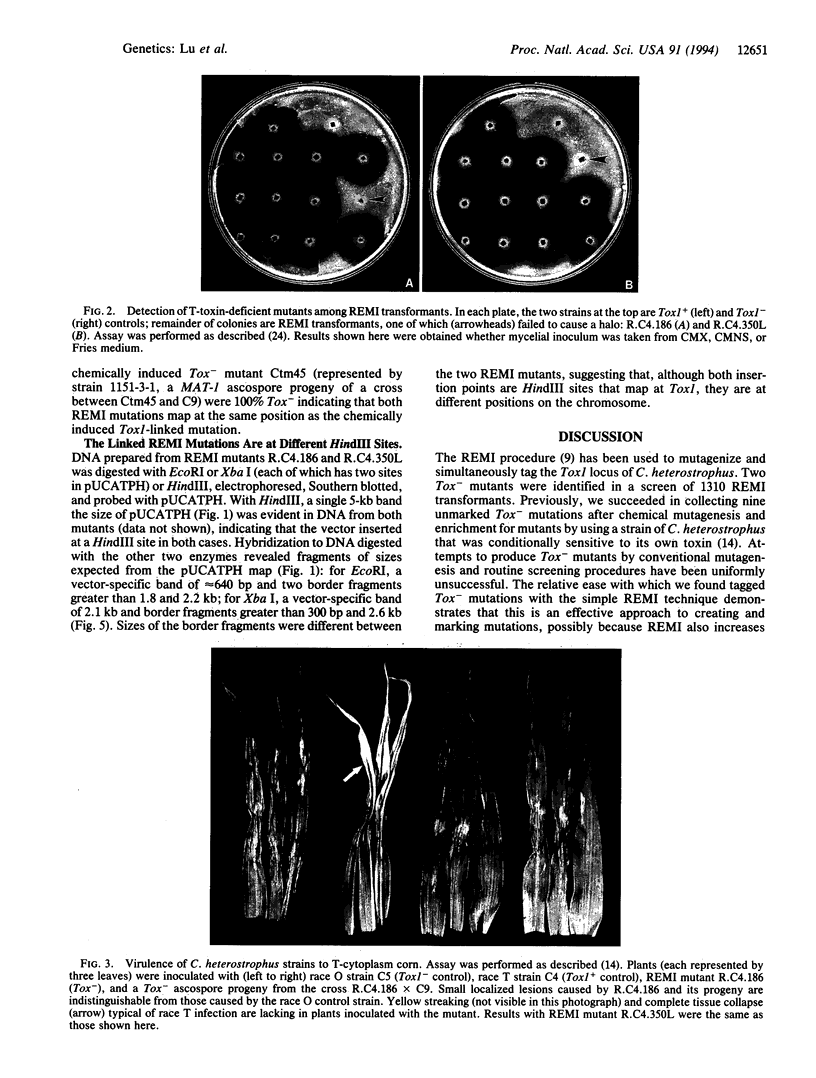
We have used the restriction enzyme-mediated integration insertional mutagenesis procedure to tag the Tox1 locus in the filamentous Ascomycete Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Mutations at other, unselected, loci were also identified and a high proportion (30-50%) of them were tagged. This procedure may be of general utility for simultaneously mutating and tagging genes in fungi and in other eukaryotes. The Tox1 locus of C. heterostrophus has been defined by Mendelian analysis as a single genetic element that controls production of T toxin, a linear polyketide involved in virulence of the fungus to its host plant, corn. To tag Tox1, protoplasts of a Tox1+ (T-toxin producing) strain were transformed with a linearized, nonhomologous plasmid along with an excess of the restriction enzyme used to linearize the plasmid. Of 1310 transformants recovered, two produced no detectable T toxin in culture or on corn plants. In each of these transformants, the Tox- mutation mapped at Tox1, was tagged with the selectable marker (hygB) on the transforming plasmid, and was tightly linked to the other tagged Tox- mutation. The two mutations, however, represent two different points of plasmid insertion at the Tox1 locus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cullen D., Leong S. A., Wilson L. J., Henner D. J. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans with the hygromycin-resistance gene, hph. Gene. 1987;57(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daboussi M. J., Langin T., Brygoo Y. Fot1, a new family of fungal transposable elements. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):12–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00299131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diallinas G., Scazzocchio C. A gene coding for the uric acid-xanthine permease of Aspergillus nidulans: inactivational cloning, characterization, and sequence of a cis-acting mutation. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):341–350. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donadio S., Staver M. J., McAlpine J. B., Swanson S. J., Katz L. Modular organization of genes required for complex polyketide biosynthesis. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.2024119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynes J. L., Clark A. M., Shaulsky G., Kuspa A., Loomis W. F., Firtel R. A. LagC is required for cell-cell interactions that are essential for cell-type differentiation in Dictyostelium. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):948–958. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsey J. A., Helber J. Isolation of a transposable element from Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Loomis W. F. Tagging developmental genes in Dictyostelium by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8803–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levings C. S., 3rd, Siedow J. N. Molecular basis of disease susceptibility in the Texas cytoplasm of maize. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):135–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00015611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil D. J., Occi J. L., Gewain K. M., MacNeil T., Gibbons P. H., Ruby C. L., Danis S. J. Complex organization of the Streptomyces avermitilis genes encoding the avermectin polyketide synthase. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHale M. T., Roberts I. N., Noble S. M., Beaumont C., Whitehead M. P., Seth D., Oliver R. P. CfT-I: an LTR-retrotransposon in Cladosporium fulvum, a fungal pathogen of tomato. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):337–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00265429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Petes T. D. Integration of DNA fragments by illegitimate recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7585–7589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilburn J., Roussel F., Scazzocchio C. Insertional inactivation and cloning of the wA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):81–90. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turgeon B. G., Bohlmann H., Ciuffetti L. M., Christiansen S. K., Yang G., Schäfer W., Yoder O. C. Cloning and analysis of the mating type genes from Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(1-2):270–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00279556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng T. H., Lyngholm L. K., Ford C. F., Bronson C. R. A restriction fragment length polymorphism map and electrophoretic karyotype of the fungal maize pathogen Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Genetics. 1992 Jan;130(1):81–96. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang G., Turgeon B. G., Yoder O. C. Toxin-deficient mutants from a toxin-sensitive transformant of Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Genetics. 1994 Jul;137(3):751–757. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]