Abstract
Some cell types have cytoplasmic storage vesicles whose fusion with the cell surface is triggered by an extracellular signal. To explore the relationship between different classes of storage vesicles, we expressed, in the neuro-endocrine cell line PC12, the facilitative glucose transporter GLUT4, which is stored in small cytoplasmic vesicles in fat and muscle cells and mobilized to the cell surface when insulin is present. PC12 cells have two known types of storage vesicles, secretory granules and synaptic vesicles, but GLUT4 is targeted to neither. It is recovered, however, in a class of small vesicles that sediment approximately twice as fast as synaptic vesicles. Immunoelectron microscopy confirmed the presence of such small vesicles in transfected PC12 cells. By velocity sedimentation analysis, GLUT4 vesicles efficiently exclude the synaptic vesicle markers synaptophysin, SV2, and synaptobrevin; the transferrin receptor, a marker of conventional endocytosis; and the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, a marker of transcytosis. The exclusion of synaptophysin and the transferrin receptor from most of the GLUT4-containing structures was confirmed by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Like synaptic vesicles, therefore, GLUT4 vesicles of PC12 cells appear to be a unique type of organelle. A GLUT4-containing organelle of identical sedimentation properties was found in transfected fibroblast cell lines and in rat adipocytes. On stimulation of the adipocytes with insulin, GLUT4 was translocated from the peak of small vesicles to faster sedimenting membranes. We propose that the class of vesicles described here is present in a wide range of cell types and is involved in transient modification of the cell surface.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apodaca G., Bomsel M., Arden J., Breitfeld P. P., Tang K., Mostov K. E. The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. A model protein to study transcytosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1877–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI115211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajjalieh S. M., Peterson K., Shinghal R., Scheller R. H. SV2, a brain synaptic vesicle protein homologous to bacterial transporters. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1271–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.1519064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini G., Hohl T., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F. Cloning of a Rab3 isotype predominantly expressed in adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5049–5052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber J. W., Lienhard G. E. Isolation of vesicles containing insulin-responsive, intracellular glucose transporters from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16180–16184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from post-Golgi compartments to the plasma membrane of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K., Kelly R. B. Identification of a transmembrane glycoprotein specific for secretory vesicles of neural and endocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1284–1294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clift-O'Grady L., Linstedt A. D., Lowe A. W., Grote E., Kelly R. B. Biogenesis of synaptic vesicle-like structures in a pheochromocytoma cell line PC-12. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1693–1703. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler D. Cell biology. Fast forward to fusion. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):287–288. doi: 10.1038/364287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feany M. B., Lee S., Edwards R. H., Buckley K. M. The synaptic vesicle protein SV2 is a novel type of transmembrane transporter. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Hanzel D. K., Urushidani T., Wolosin J. M. Pumps and pathways for gastric HCl secretion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;574:145–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb25153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. A., Setiadi H., McEver R. P., Kelly R. B. The cytoplasmic domain of P-selectin contains a sorting determinant that mediates rapid degradation in lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):435–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney P. M., Slot J. W., Piper R. C., James D. E., Mueckler M. Intracellular targeting of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT4) is isoform specific and independent of cell type. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):689–699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
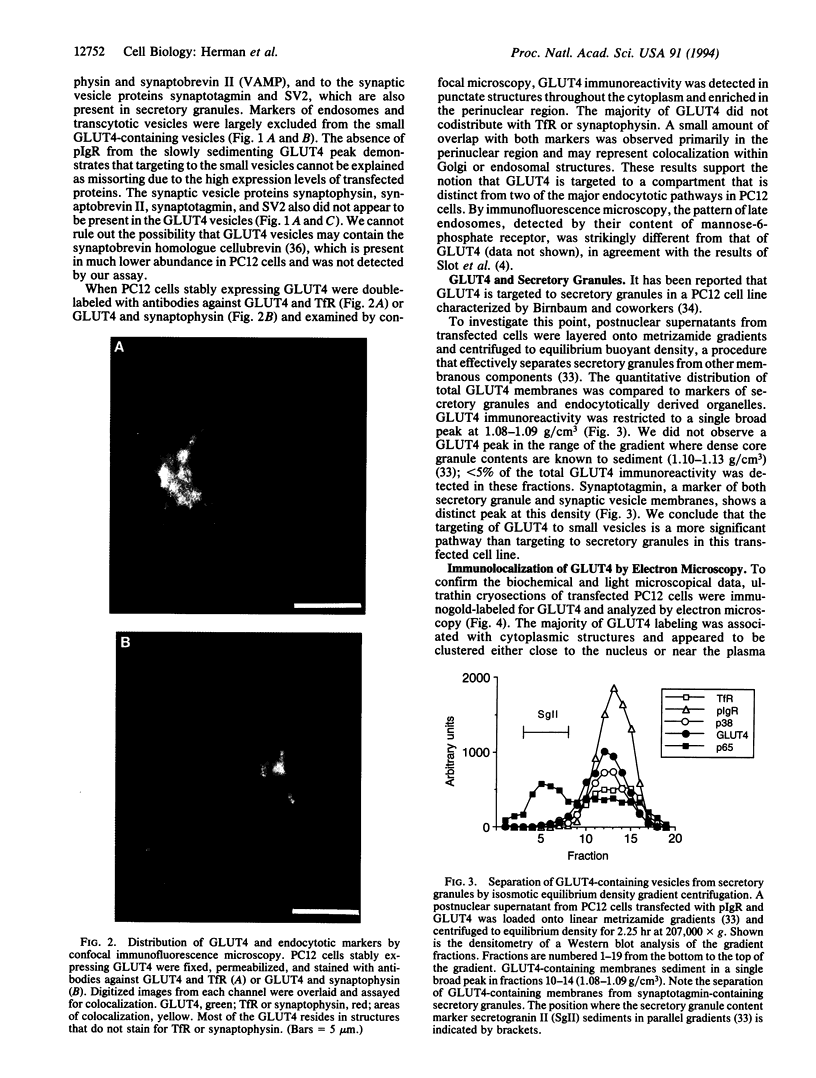
- Hudson A. W., Fingar D. C., Seidner G. A., Griffiths G., Burke B., Birnbaum M. J. Targeting of the "insulin-responsive" glucose transporter (GLUT4) to the regulated secretory pathway in PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):579–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Lederman L., Pilch P. F. Purification of insulin-dependent exocytic vesicles containing the glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11817–11824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Piper R. C., Slot J. W. Insulin stimulation of GLUT-4 translocation: a model for regulated recycling. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;4(4):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Cameron P. L., Stukenbrok H., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin is targeted to similar microvesicles in CHO and PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Grote E. Protein targeting in the neuron. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:95–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Secretion. A question of endosomes. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):487–488. doi: 10.1038/364487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Secretory granule and synaptic vesicle formation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90037-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie S. M., Cain C. C., Lienhard G. E., Castle J. D. The glucose transporter GluT4 and secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) colocalize in rat adipocytes and partially segregate during insulin stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19110–19117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S. R., Huff S. Y., Goode B. L., Marschall L., Chang J., Feinstein S. C. Molecular analysis of the nerve growth factor inducible ornithine decarboxylase gene in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Feb 15;34(3):304–314. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490340307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Hess L. J., James D. E. Differential sorting of two glucose transporters expressed in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C570–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Tai C., Slot J. W., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Huang H., James D. E. The efficient intracellular sequestration of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT-4) is conferred by the NH2 terminus. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):729–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presley J. F., Mayor S., Dunn K. W., Johnson L. S., McGraw T. E., Maxfield F. R. The End2 mutation in CHO cells slows the exit of transferrin receptors from the recycling compartment but bulk membrane recycling is unaffected. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J. Biogenesis of storage granules and vesicles. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):616–622. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90080-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnick K. J., Slot J. W., Studelska D. R., Hanpeter D. E., Robinson L. J., Geuze H. J., James D. E. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies of GLUT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6278–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Nishimura H., Clark A. E., Kozka I. J., Vannucci S. J., Simpson I. A., Quon M. J., Cushman S. W., Holman G. D. Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17820–17829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Charron M. J., Shah N., Lodish H. F., Jarett L. Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane of isolated rat adipocytes and masking of the carboxyl-terminal epitope of intracellular GLUT4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6893–6897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solari R., Kühn L., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Antibodies recognizing different domains of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1141–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S. Water channels in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:97–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S., Miller K., Hopkins C., Trowbridge I. S. Monoclonal antibodies against defined epitopes of the human transferrin receptor cytoplasmic tail. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 22;1136(1):28–34. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90081-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Rehm H., Knierim M., Becker C. M. Fractionation of synaptophysin-containing vesicles from rat brain and cultured PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]