Abstract
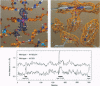
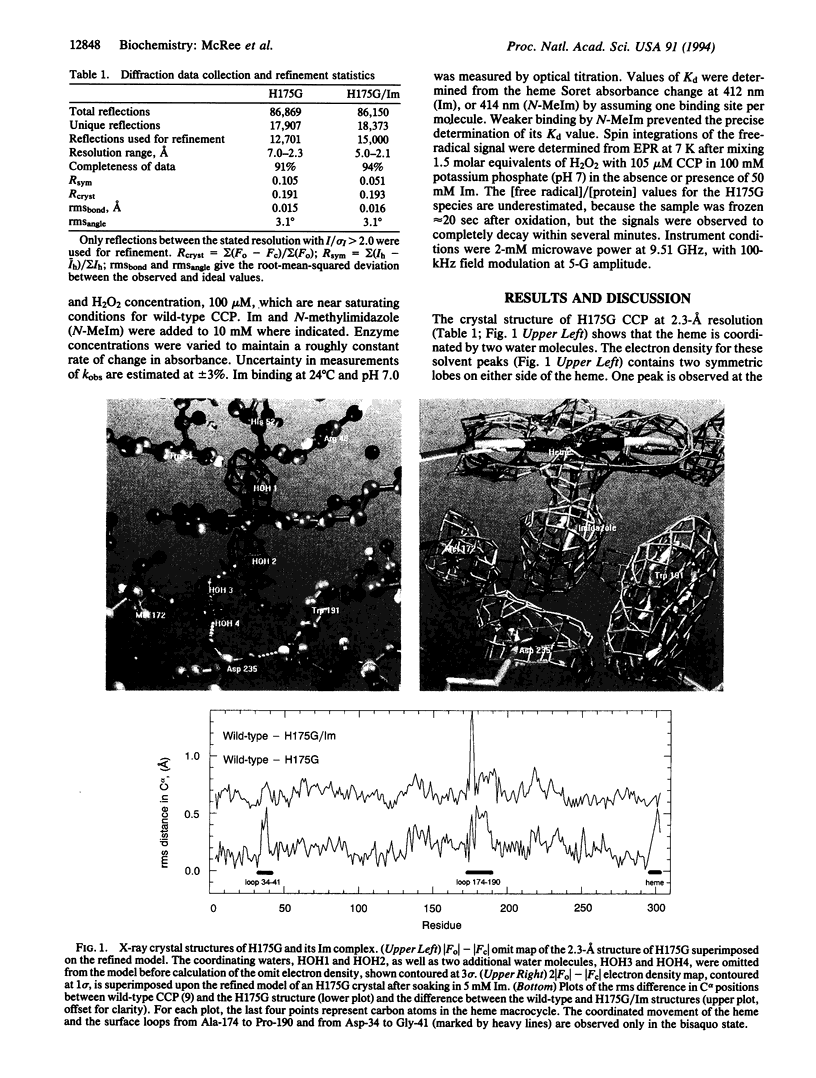
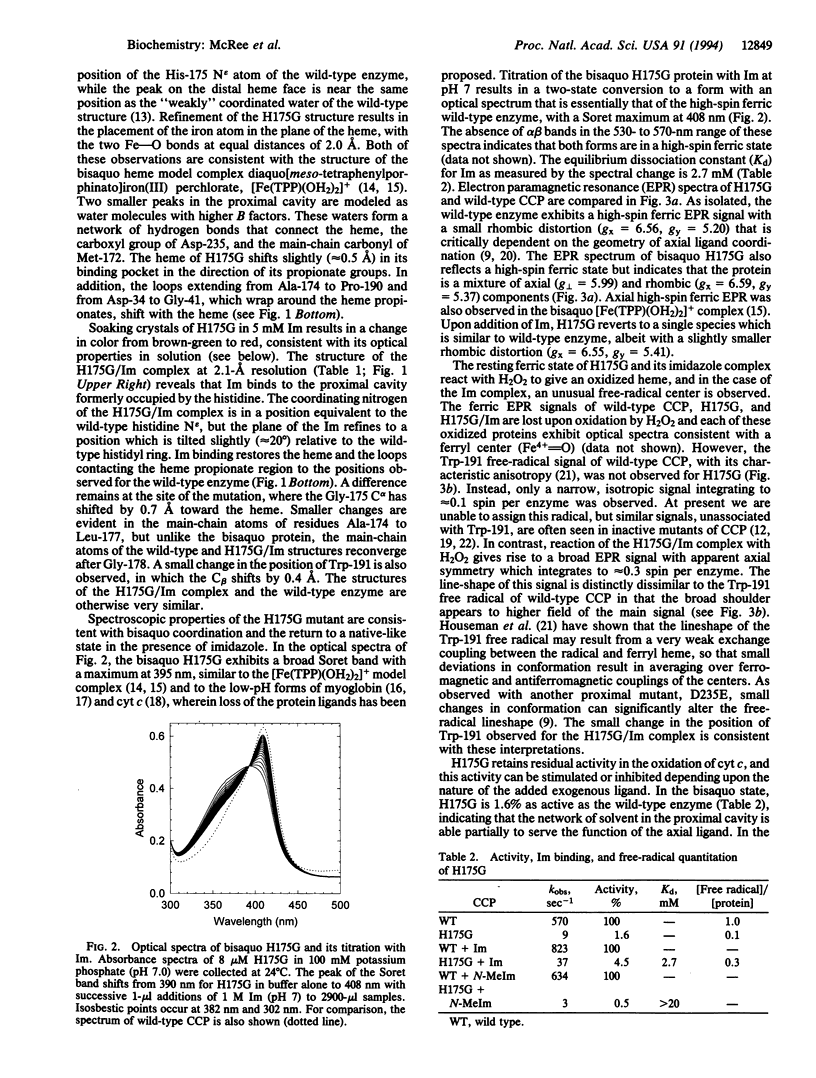
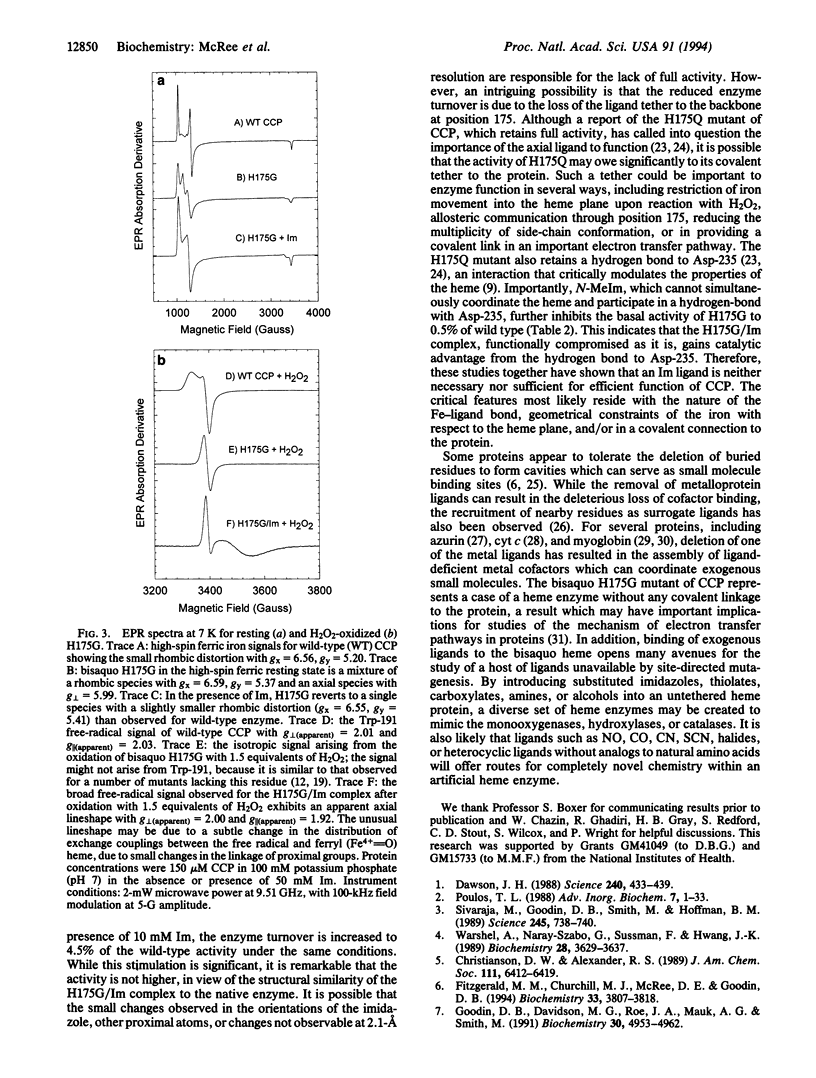
The crystal structure of the His-175-->Gly (H175G) mutant of cytochrome-c peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.5), missing its only heme ligand, reveals that the histidine is replaced by solvent to give a bisaquo heme protein. This protein retains some residual activity, which can be stimulated or inhibited by addition of exogenous ligands. Structural analysis confirms the binding of imidazole to the heme at the position of the wild-type histidine ligand. This imidazole complex reacts readily with hydrogen peroxide to produce a radical species with novel properties. However, reactivation in this complex is incomplete (approximately 5%), which, in view of the very similar structures of the wild-type and the H175G/imidazole forms, implies a critical role for tethering of the axial ligand in catalysis. This study demonstrates the feasibility of constructing heme enzymes with no covalent link to the protein and with unnatural ligand replacements. Such enzymes may prove useful in studies of electron transfer mechanisms and in the engineering of novel heme-based catalysts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrick D. Replacement of the proximal ligand of sperm whale myoglobin with free imidazole in the mutant His-93-->Gly. Biochemistry. 1994 May 31;33(21):6546–6554. doi: 10.1021/bi00187a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratan D. N., Onuchic J. N., Winkler J. R., Gray H. B. Electron-tunneling pathways in proteins. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1740–1741. doi: 10.1126/science.1334572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury K., Sundaramoorthy M., Mauro J. M., Poulos T. L. Conversion of the proximal histidine ligand to glutamine restores activity to an inactive mutant of cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25656–25659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. H. Probing structure-function relations in heme-containing oxygenases and peroxidases. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):433–439. doi: 10.1126/science.3358128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Wozniak J. A., Matthews B. W. A cavity-containing mutant of T4 lysozyme is stabilized by buried benzene. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):371–373. doi: 10.1038/355371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzel B. C., Poulos T. L., Kraut J. Crystal structure of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase refined at 1.7-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13027–13036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel L. A., Farnum M. F., Mauro J. M., Miller M. A., Kraut J., Liu Y. J., Tan X. L., Scholes C. P. Compound I radical in site-directed mutants of cytochrome c peroxidase as probed by electron paramagnetic resonance and electron-nuclear double resonance. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1986–1996. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. M., Churchill M. J., McRee D. E., Goodin D. B. Small molecule binding to an artificially created cavity at the active site of cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 5;33(13):3807–3818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodin D. B., Davidson M. G., Roe J. A., Mauk A. G., Smith M. Amino acid substitutions at tryptophan-51 of cytochrome c peroxidase: effects on coordination, species preference for cytochrome c, and electron transfer. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4953–4962. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodin D. B., Mauk A. G., Smith M. The peroxide complex of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase contains two distinct radical species, neither of which resides at methionine 172 or tryptophan 51. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7719–7724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodin D. B., McRee D. E. The Asp-His-Fe triad of cytochrome c peroxidase controls the reduction potential, electronic structure, and coupling of the tryptophan free radical to the heme. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3313–3324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Yonetani T. Powder and single-crystal electron paramagnetic resonance studies of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase and its peroxide and its peroxide compound, Compound ES. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houseman A. L., Doan P. E., Goodin D. B., Hoffman B. M. Comprehensive explanation of the anomalous EPR spectra of wild-type and mutant cytochrome c peroxidase compound ES. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4430–4443. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanir A., Aviram I. Proton magnetic relaxation and anion effect in solutions of acid ferricytochrome c. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Feb;166(2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Casimiro D. R., Bren K. L., Richards J. H., Gray H. B. Structurally engineered cytochromes with unusual ligand-binding properties: expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Met-80-->Ala iso-1-cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11456–11459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín A. E., Burgess B. K., Stout C. D., Cash V. L., Dean D. R., Jensen G. M., Stephens P. J. Site-directed mutagenesis of Azotobacter vinelandii ferredoxin I: [Fe-S] cluster-driven protein rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):598–602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Minasian E., Appleby C. A., Leach S. J. Circular dichroism studies of myoglobin and leghemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5141–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage J. T., Morikis D., Champion P. M. Spectroscopic studies of myoglobin at low pH: heme structure and ligation. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1227–1237. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidt W. R., Cohen I. A., Kastner M. E. A structural model for heme in high-spin ferric hemoproteins. Iron atom centering, porphinato core expansion, and molecular stereochemistry of high-spin diaquo(meso-tetraphenylporphinato)iron(III) perchlorate. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3546–3552. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraja M., Goodin D. B., Smith M., Hoffman B. M. Identification by ENDOR of Trp191 as the free-radical site in cytochrome c peroxidase compound ES. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):738–740. doi: 10.1126/science.2549632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traylor T. G., Deardurff L. A., Coletta M., Ascenzi P., Antonini E., Brunori M. Reactivity of ferrous heme proteins at low pH. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12147–12148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Naray-Szabo G., Sussman F., Hwang J. K. How do serine proteases really work? Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3629–3637. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]