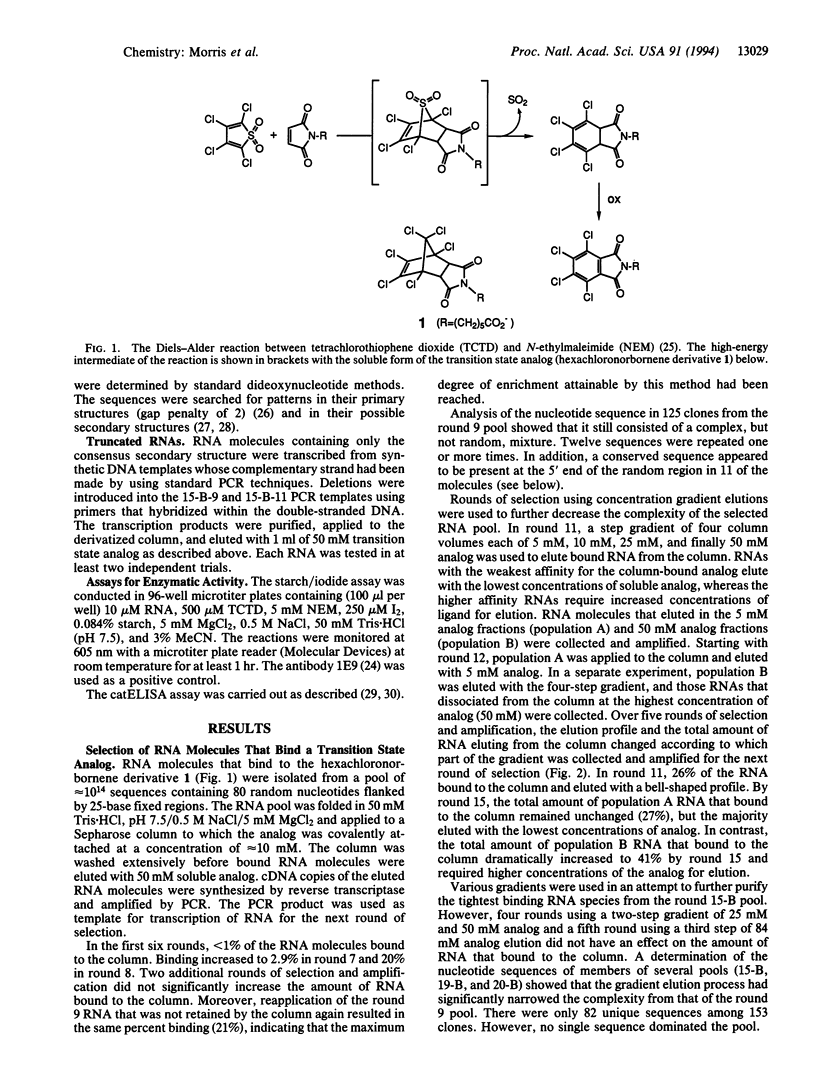
Abstract
RNA molecules that bind a transition state analog for a Diels-Alder reaction (Kd = 0.35 +/- 0.05 mM) were isolated from a starting pool of approximately 10(14) sequences by affinity chromatography. After the initial rise and plateau of the amount of RNA that eluted with soluble analog, a step gradient elution was used to further enrich the pool for sequences with higher affinities for the target. To our knowledge, the isolation of RNA molecules that bind either a nonplanar or a hydrophobic ligand has not been reported previously. A conserved nucleotide sequence and secondary structure present in many of the RNA molecules are necessary but not sufficient for binding the analog. No catalysts of the targeted Diels-Alder reaction were found among the binders. The absence of catalysis contrasts with previous successful experiments with antibodies and suggests that other strategies may be needed to identify oligonucleotides with diverse catalytic activities.
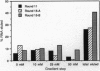
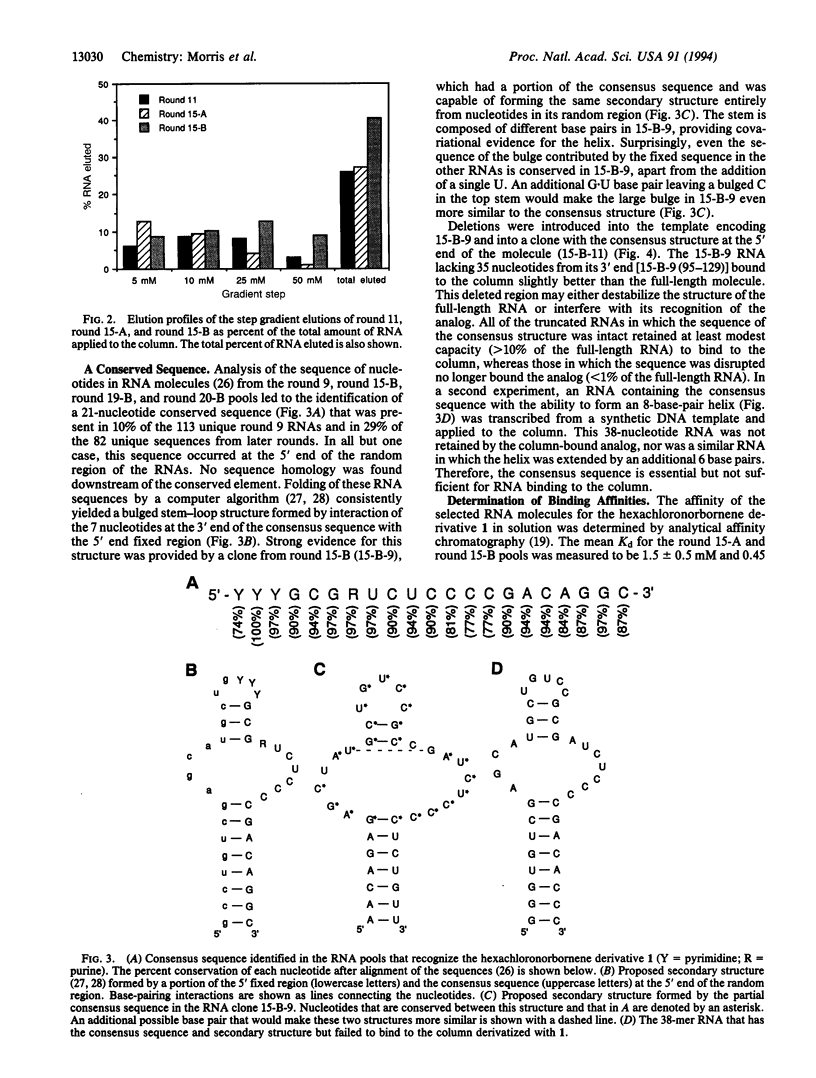
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurup H., Williams D. M., Eckstein F. 2'-Fluoro- and 2'-amino-2'-deoxynucleoside 5'-triphosphates as substrates for T7 RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9636–9641. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. Isolation of new ribozymes from a large pool of random sequences [see comment]. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1411–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.7690155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Zapp M. L., Green M. R., Szostak J. W. HIV-1 Rev regulation involves recognition of non-Watson-Crick base pairs in viral RNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudry A. A., Joyce G. F. Directed evolution of an RNA enzyme. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):635–641. doi: 10.1126/science.1496376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell G. J., Illangesekare M., Yarus M. Three small ribooligonucleotides with specific arginine sites. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5497–5502. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Szostak J. W. Selection of a ribozyme that functions as a superior template in a self-copying reaction. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1910–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.1470913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogeweg P., Konings D. A. U1 snRNA: the evolution of its primary and secondary structure. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):323–333. doi: 10.1007/BF02115650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek D., Lynott C. K., Rifkin D. B., Janjić N. High-affinity RNA ligands to basic fibroblast growth factor inhibit receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11227–11231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison R. D., Gill S. C., Pardi A., Polisky B. High-resolution molecular discrimination by RNA. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1425–1429. doi: 10.1126/science.7510417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman N., Joyce G. F. Evolution in vitro of an RNA enzyme with altered metal dependence. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):182–185. doi: 10.1038/361182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorsch J. R., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA aptamers specific for cyanocobalamin. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 1;33(4):973–982. doi: 10.1021/bi00170a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Hoffarth V., Zimniak L. Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1416–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1604315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. A small metalloribozyme with a two-step mechanism. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):560–563. doi: 10.1038/358560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. In vitro selection of RNAs that undergo autolytic cleavage with Pb2+. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3887–3895. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli J. A., Krauch T., Moroney S. E., Benner S. A. Enzymatic incorporation of a new base pair into DNA and RNA extends the genetic alphabet. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):33–37. doi: 10.1038/343033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli J. A., McConnell T. S., Zaug A. J., Noller H. F., Cech T. R. Aminoacyl esterase activity of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1420–1424. doi: 10.1126/science.1604316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudent J. R., Uno T., Schultz P. G. Expanding the scope of RNA catalysis. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1924–1927. doi: 10.1126/science.8009223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Gold L., Platt T. Selective enrichment of RNA species for tight binding to Escherichia coli rho factor. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):201–207. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Tuerk C., Gold L. Selection of high affinity RNA ligands to the bacteriophage R17 coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):862–869. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90870-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik D. S., Green B. S., Chap R., Sela M., Eshhar Z. catELISA: a facile general route to catalytic antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., MacDougal S., Gold L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]