Abstract
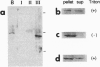
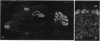
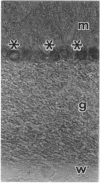
A third species of diacylglycerol kinase (EC 2.7.1.107) cDNA was cloned from a rat brain cDNA library. The isolated cDNA encoded a 788-amino acid, 88-kDa polypeptide. This isozyme shared 58% identity with the previously isolated rat 80-kDa and 90-kDa diacylglycerol kinases. EF hand motifs, cysteine-rich zinc finger-like sequences, and putative ATP-binding site were all conserved among these isozymes. The 88-kDa diacylglycerol kinase was expressed specifically in brain and localized predominantly in cerebellar Purkinje cells. This isozyme was associated equally with particulate and supernatant fractions in cDNA-transfected COS-7 cells and dominantly with the particulate fraction in the brain. After Triton X-100 extraction, this isozyme remained in the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction of the brain and transfected COS-7 cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Pollenz R. S., Booker E. L., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Diacylglycerol-induced translocation of diacylglycerol kinase: use of affinity-purified enzyme in a reconstitution system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M. Inositol-lipid-specific phospholipase C isoenzymes and their differential regulation by receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2880001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Kondo H. Molecular cloning and expression of a 90-kDa diacylglycerol kinase that predominantly localizes in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7598–7602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Watanabe M., Kondo H., Yuasa H., Sakane F., Kanoh H. Gene cloning, sequence, expression and in situ localization of 80 kDa diacylglycerol kinase specific to oligodendrocyte of rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Nov;16(1-2):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90196-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Yamada K., Sakane F. Diacylglycerol kinase: a key modulator of signal transduction? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Feb;15(2):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Yamada K., Sakane F., Imaizumi T. Phosphorylation of diacylglycerol kinase in vitro by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj2580455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Williams L. K., Rieser G. D. Association of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeleton of A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1341–1350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., MacCumber M. W., Glatt C. E., Snyder S. H. Brain phospholipase C isozymes: differential mRNA localizations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2923–2927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. M., Gittinger C. K., Landreth G. E. Characterization of the epidermal growth factor receptor associated with cytoskeletons of A431 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):295–304. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Imai S., Yamada K., Kanoh H. The regulatory role of EF-hand motifs of pig 80K diacylglycerol kinase as assessed using truncation and deletion mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1015–1021. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92038-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Yamada K., Imai S., Kanoh H. Porcine 80-kDa diacylglycerol kinase is a calcium-binding and calcium/phospholipid-dependent enzyme and undergoes calcium-dependent translocation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7096–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane F., Yamada K., Kanoh H., Yokoyama C., Tanabe T. Porcine diacylglycerol kinase sequence has zinc finger and E-F hand motifs. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):345–348. doi: 10.1038/344345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., de Widt J., van der Wal J., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Gussow D., Ploegh H. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L. Purification, cDNA-cloning and expression of human diacylglycerol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81461-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., van der Wal J., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L., Ploegh H. L. Diacylglycerol kinase is phosphorylated in vivo upon stimulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and serine/threonine kinases, including protein kinase C-epsilon. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):875–881. doi: 10.1042/bj2890875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegant F. A., Blok F. J., Defize L. H., Linnemans W. A., Verkley A. J., Boonstra J. Epidermal growth factor receptors associated to cytoskeletal elements of epidermoid carcinoma (A431) cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):87–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Kanoh H. Occurrence of immunoreactive 80 kDa and non-immunoreactive diacylglycerol kinases in different pig tissues. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):601–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]