Abstract
Serotonin (5-HT) is a major neurotransmitter that influences various behaviors, neuronal plasticity, learning, and memory in molluscs. Although the physiology of 5-HT transmission in molluscs is well studied, little is known about the pharmacology and diversity of the 5-HT receptor system. Based on the high homology of genes coding for guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptors, we have cloned a gene for the Lymnaea stagnalis 5-HT (5HTlym) receptor. The putative receptor protein, 509 amino acids long, has highest homology with the Drosophila 5-HT receptors and mammalian 5HT1 receptors. As revealed by RNA blot-hybridization analysis, two mRNA species of 2.3 and 3.2 kb are detected in the central nervous system of Lymnaea. Transient expression of 5HTlym in COS-7 cells showed saturable [3H]lysergic acid diethylamide binding with an estimated dissociation constant of 0.9 nM. The 5HTlym receptor exhibited a mixed 5HT-like pharmacology that cannot be precisely categorized with existing mammalian classification nomenclature. However, the 5HTlym receptor does display some characteristics that have been attributed to the putative mammalian vascular 5HT1-like receptor.
Full text
PDF

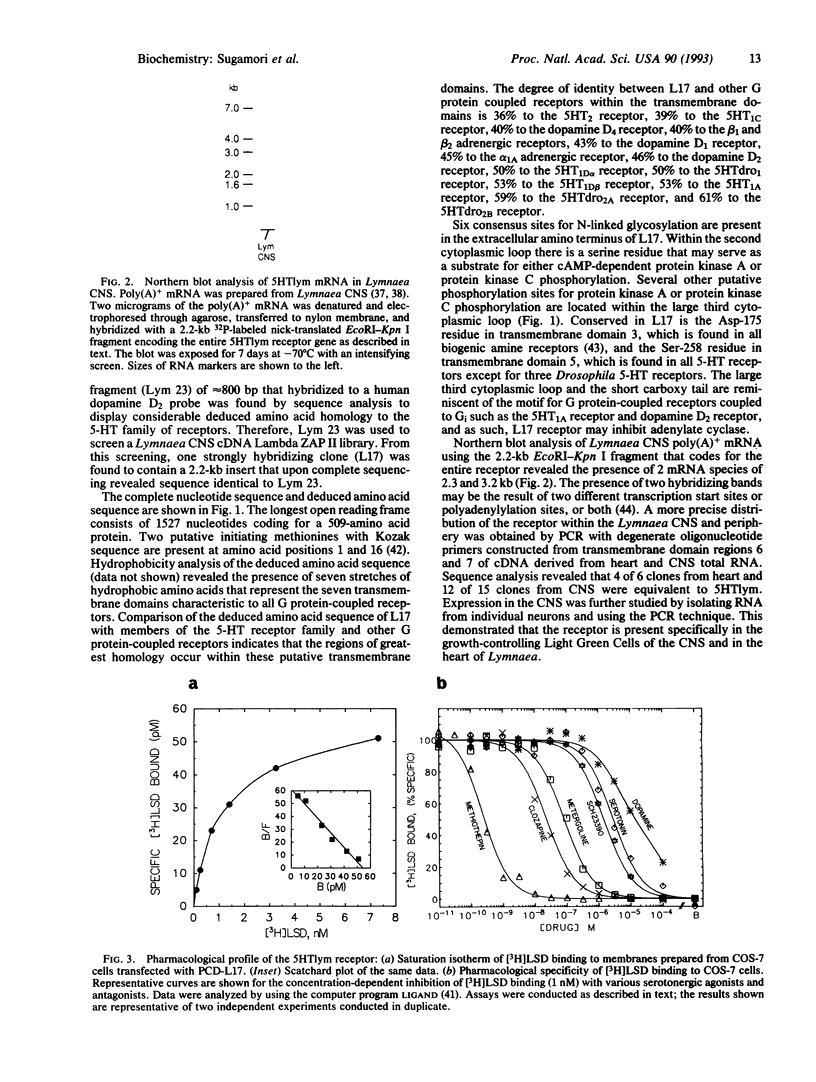
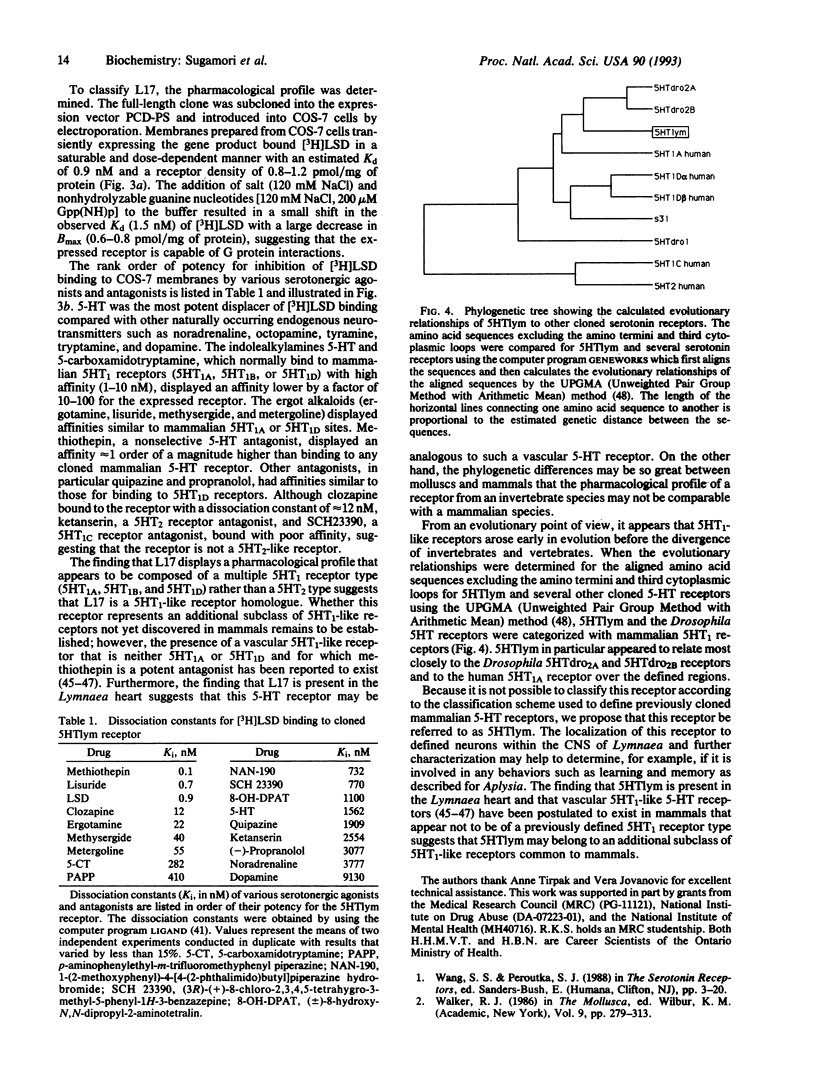

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Zhou Q. Y., Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of the rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5825–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom A. H., Villalón C. M., Verdouw P. D., Saxena P. R. The 5-HT1-like receptor mediating reduction of porcine carotid arteriovenous shunting by RU 24969 is not related to either the 5-HT1A or the 5-HT1B subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 14;171(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Young A. C., Brann M. R., Buckley N. J. Cloning and expression of the human and rat m5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D. Rapid isolation of eukaryotic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):463–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braha O., Dale N., Hochner B., Klein M., Abrams T. W., Kandel E. R. Second messengers involved in the two processes of presynaptic facilitation that contribute to sensitization and dishabituation in Aplysia sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demchyshyn L., Sunahara R. K., Miller K., Teitler M., Hoffman B. J., Kennedy J. L., Seeman P., Van Tol H. H., Niznik H. B. A human serotonin 1D receptor variant (5HT1D beta) encoded by an intronless gene on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5522–5526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Benson J. A., Levitan I. B. Serotonin-induced hyperpolarization of an indentified Aplysia neuron is mediated by cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):5013–5017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.5013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Lohse M. J., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The genomic clone G-21 which resembles a beta-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the 5-HT1A receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):358–360. doi: 10.1038/335358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A., Maayani S., Wolfe B. B. Subtypes of receptors for serotonin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:307–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld H. M., Paupardin-Tritsch D. Ionic mechanisms and receptor properties underlying the responses of molluscan neurones to 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(2):427–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. I., Kater S. B. Expression and function of the neurotransmitter serotonin during development of the Helisoma nervous system. Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;131(2):483–495. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. I., Mills L. R., Kater S. B. Novel effects of serotonin on neurite outgrowth in neurons cultured from embryos of Helisoma trivolvis. J Neurobiol. 1991 Mar;22(2):182–194. doi: 10.1002/neu.480220208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Metcalf M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a human 5-HT1D-type serotonin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon P. G., McCobb D. P., Kater S. B. Serotonin selectively inhibits growth cone motility and synaptogenesis of specific identified neurons. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):561–564. doi: 10.1126/science.6093252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Schoeffter P. 5-HT receptors: subtypes and second messengers. J Recept Res. 1991;11(1-4):197–214. doi: 10.3109/10799899109066399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H., Oksenberg D., Ashkenazi A., Peroutka S. J., Duncan A. M., Rozmahel R., Yang Y., Mengod G., Palacios J. M., O'Dowd B. F. Characterization of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5735–5738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Huang K. N., Livelli T. J., Axel R., Jessell T. M. The 5HT2 receptor defines a family of structurally distinct but functionally conserved serotonin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):928–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D. Molecular biology of serotonin receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:335–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemenes G., Elekes K., Hiripi L., Benjamin P. R. A comparison of four techniques for mapping the distribution of serotonin and serotonin-containing neurons in fixed and living ganglia of the snail, Lymnaea. J Neurocytol. 1989 Apr;18(2):193–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01206662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Mechanism of calcium current modulation underlying presynaptic facilitation and behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A profusion of controls. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):1–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy F. O., Gudermann T., Birnbaumer M., Kaumann A. J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a human gene (S31) encoding a novel serotonin receptor mediating inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 20;296(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80379-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman M. W., Ono J. K., McCaman R. E. 5-hydroxytryptamine measurements in molluscan ganglia and neurons using a modified radioenzymatic assay. J Neurochem. 1984 Jul;43(1):91–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer A. R., Emptage N. J., Carew T. J. Pharmacological dissociation of modulatory effects of serotonin in Aplysia sensory neurons. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1811–1813. doi: 10.1126/science.1662413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Nguyen T., Tirpak A., Jarvie K. R., Israel Y., Seeman P., Niznik H. B. Cloning of two additional catecholamine receptors from rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80140-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:45–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perren M. J., Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P. Vascular 5-HT1-like receptors that mediate contraction of the dog isolated saphenous vein and carotid arterial vasoconstriction in anaesthetized dogs are not of the 5-HT1A or 5-HT1D subtype. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Bach A. W., Wozny M., Taleb O., Dal Toso R., Shih J. C., Seeburg P. H. Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5HT-2 receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4135–4140. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. C., Weiss K. R., Goldstein R. S., Kupfermann I. The role of a modulatory neuron in feeding and satiation in Aplysia: effects of lesioning of the serotonergic metacerebral cells. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1562–1578. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Erdemli I., Hoyer D., Stoll A., Seiler M. P., Schoeffter P. 5-HT1-like receptors mediate 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced contraction of guinea-pig isolated iliac artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):386–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Morse B., Whitman M. M., Ivanshchenko Y., Jaye M., Felder S. Cloning of the human serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT1C receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1469–1478. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92105-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudou F., Boschert U., Amlaiky N., Plassat J. L., Hen R. A family of Drosophila serotonin receptors with distinct intracellular signalling properties and expression patterns. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10267–10271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. S., Zatz M. Regulation of circadian rhythmicity. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1104–1111. doi: 10.1126/science.6287576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Wu C. M., Guan H. C., Ohara K., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O., Kennedy J., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Jovanovic V. Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):149–152. doi: 10.1038/358149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Bach A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat brain cDNA encoding a 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4017–4023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witz P., Amlaiky N., Plassat J. L., Maroteaux L., Borrelli E., Hen R. Cloning and characterization of a Drosophila serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8940–8944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



