Abstract
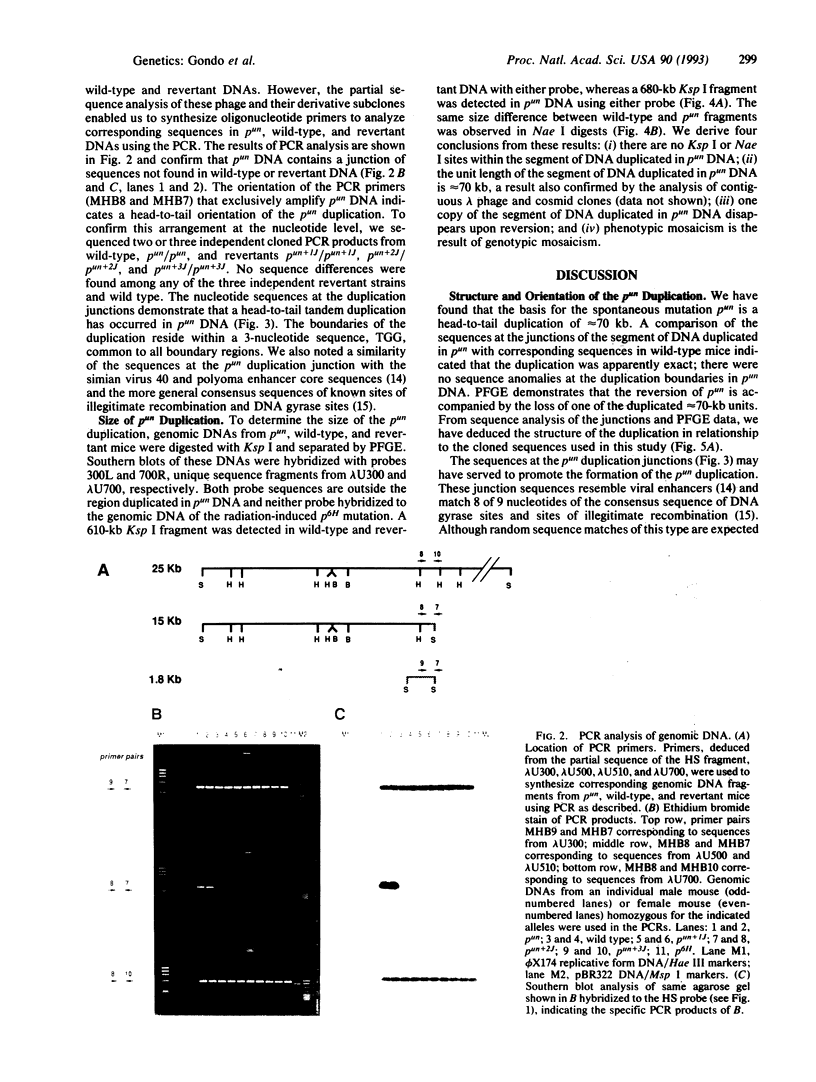
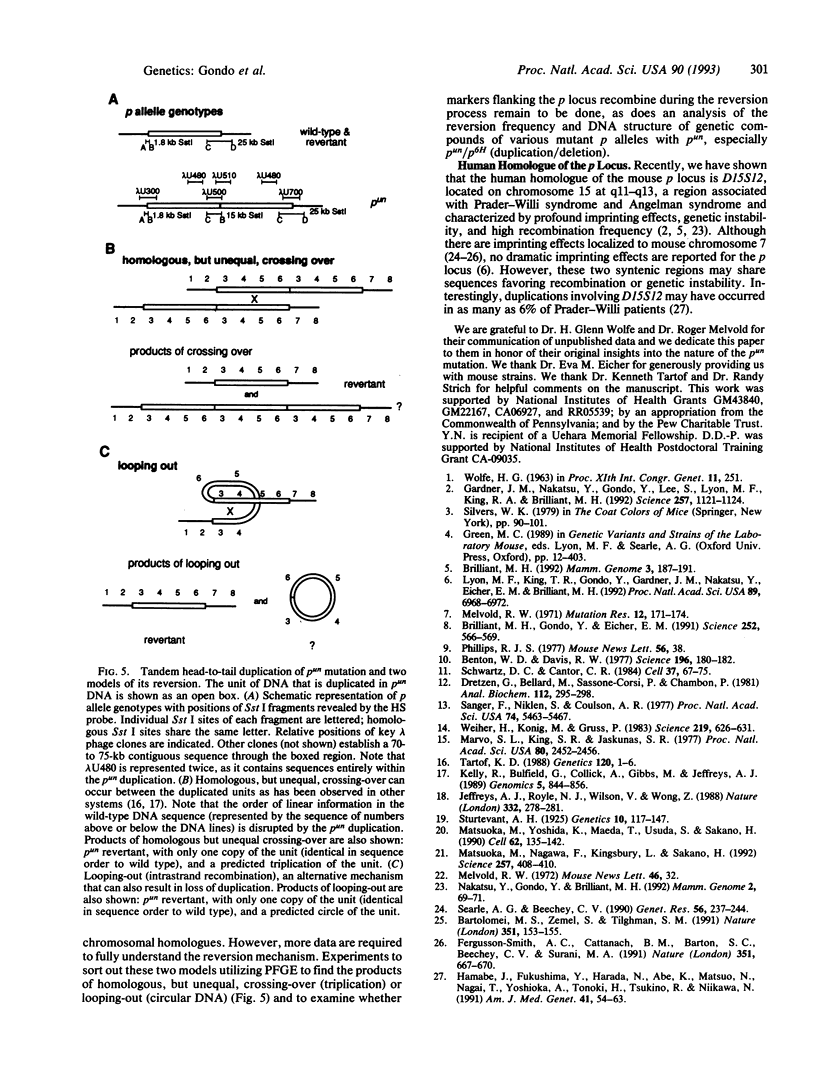
The mouse pink-eyed unstable (p(un)) mutation, affecting coat color, exhibits one of the highest reported reversion frequencies of any mammalian mutation and is associated with a duplication of genomic DNA at the p locus. In this study, genomic clones containing the boundaries of the p(un) duplication were isolated and characterized. The structure of these sequences and their wild-type and revertant counterparts were analyzed by restriction mapping, PCR product analysis, DNA sequence analysis, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. DNA from p(un) was distinguished from wild-type and revertant DNA by a head-to-tail tandem duplication of approximately 70 kilobases. No differences were detected between revertant and wild-type DNAs. Thus, the reversion in phenotype of p(un) mice is coupled with the loss of one copy of an approximately 70-kilobase duplicated segment. Testable models are presented to account for p(un) reversion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartolomei M. S., Zemel S., Tilghman S. M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):153–155. doi: 10.1038/351153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilliant M. H., Gondo Y., Eicher E. M. Direct molecular identification of the mouse pink-eyed unstable mutation by genome scanning. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.1673574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilliant M. H. The mouse pink-eyed dilution locus: a model for aspects of Prader-Willi syndrome, Angelman syndrome, and a form of hypomelanosis of Ito. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(4):187–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00355717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith A. C., Cattanach B. M., Barton S. C., Beechey C. V., Surani M. A. Embryological and molecular investigations of parental imprinting on mouse chromosome 7. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):667–670. doi: 10.1038/351667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. M., Nakatsu Y., Gondo Y., Lee S., Lyon M. F., King R. A., Brilliant M. H. The mouse pink-eyed dilution gene: association with human Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabe J., Fukushima Y., Harada N., Abe K., Matsuo N., Nagai T., Yoshioka A., Tonoki H., Tsukino R., Niikawa N. Molecular study of the Prader-Willi syndrome: deletion, RFLP, and phenotype analyses of 50 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):54–63. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Bulfield G., Collick A., Gibbs M., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a highly unstable mouse minisatellite locus: evidence for somatic mutation during early development. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):844–856. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., King T. R., Gondo Y., Gardner J. M., Nakatsu Y., Eicher E. M., Brilliant M. H. Genetic and molecular analysis of recessive alleles at the pink-eyed dilution (p) locus of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvo S. L., King S. R., Jaskunas S. R. Role of short regions of homology in intermolecular illegitimate recombination events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2452–2456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Nagawa F., Kingsbury L., Sakano H. Response. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):408–410. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5068.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Yoshida K., Maeda T., Usuda S., Sakano H. Switch circular DNA formed in cytokine-treated mouse splenocytes: evidence for intramolecular DNA deletion in immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90247-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvold R. W. Spontaneous somatic reversion in mice. Effects of parental genotype on stability at the p-locus. Mutat Res. 1971 Jun;12(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu Y., Gondo Y., Brilliant M. H. The p locus is closely linked to the mouse homolog of a gene from the Prader-Willi chromosomal region. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(1):69–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00570442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Beechey C. V. Genome imprinting phenomena on mouse chromosome 7. Genet Res. 1990 Oct-Dec;56(2-3):237–244. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant A H. The Effects of Unequal Crossing over at the Bar Locus in Drosophila. Genetics. 1925 Mar;10(2):117–147. doi: 10.1093/genetics/10.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D. Unequal crossing over then and now. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





