Abstract
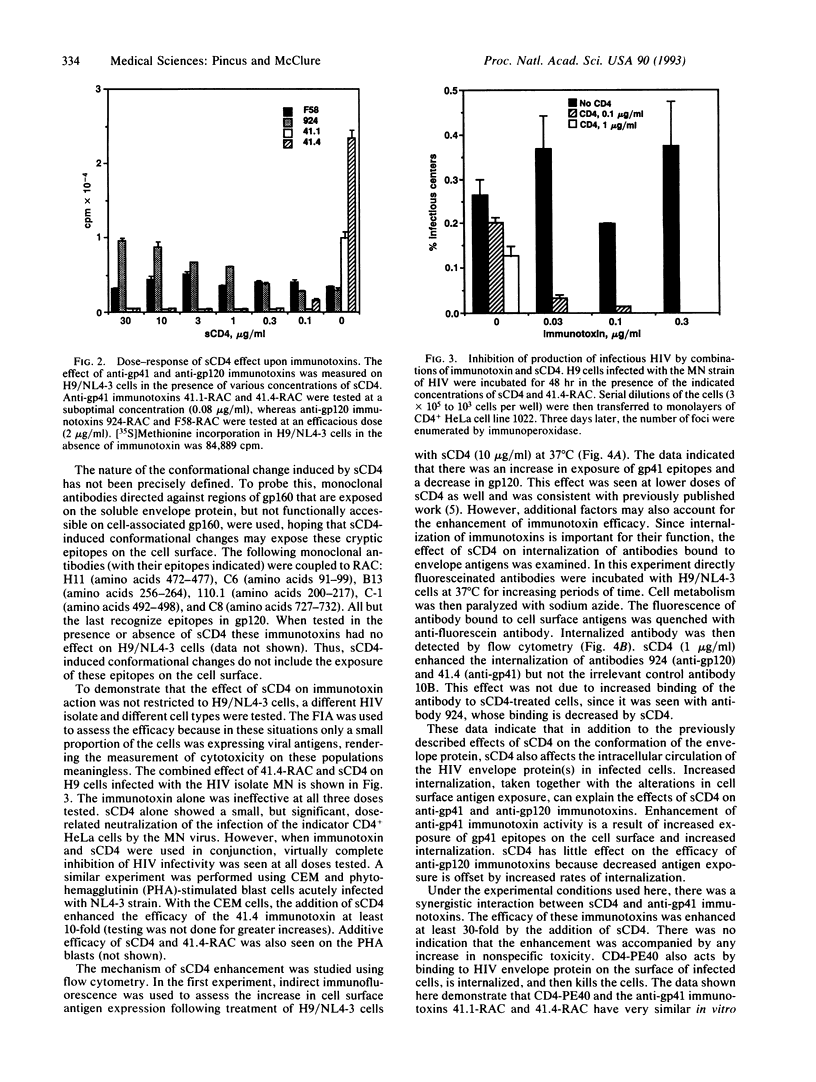
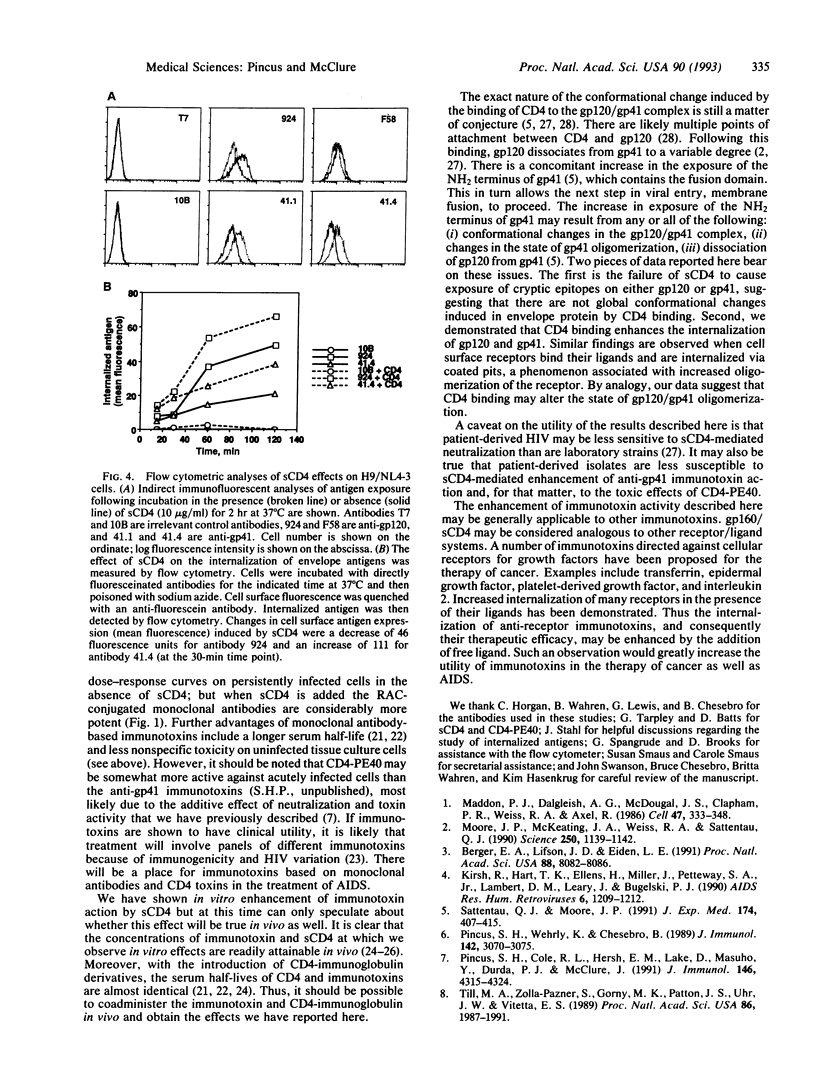
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the gp120 or gp41 portions of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) envelope protein gp160 were conjugated to ricin A chain, and their immunotoxic activities against HIV-infected cells were evaluated in the presence or absence of soluble CD4 (sCD4). Immunotoxin activity was measured in vitro as cytotoxicity and inhibition of secretion of infectious HIV. The efficacy of anti-gp41 immunotoxins was enhanced at least 30-fold in the presence of sCD4. This effect was specific for HIV-infected cells, but not for uninfected cells, and was seen at concentrations of sCD4 as low as 0.1 micrograms/ml. Anti-gp120 immunotoxins were marginally inhibited at higher concentrations of sCD4. Flow cytometry analyses showed that sCD4 increased the expression of gp41 on the surface of infected cells and increased internalization of gp120 and gp41. These data suggest that sCD4 alters the cellular trafficking of HIV envelope proteins. These findings also have important implications for the therapeutic use of anti-HIV immunotoxins and may be generalizable to other immunotoxins as well.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Clouse K. A., Chaudhary V. K., Chakrabarti S., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I., Moss B. CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein blocks the spread of human immunodeficiency virus infection in vitro and is active against cells expressing the envelope glycoproteins from diverse primate immunodeficiency retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9539–9543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. A soluble recombinant polypeptide comprising the amino-terminal half of the extracellular region of the CD4 molecule contains an active binding site for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Lifson J. D., Eiden L. E. Stimulation of glycoprotein gp120 dissociation from the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by soluble CD4 and CD4 peptide derivatives: implications for the role of the complementarity-determining region 3-like region in membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8082–8086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., Ljunggren K., Hinkula J., Norrby E., Akerblom L., Wahren B. A monoclonal antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 which mediates cellular cytotoxicity and neutralization. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.936-940.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrn R. A., Mordenti J., Lucas C., Smith D., Marsters S. A., Johnson J. S., Cossum P., Chamow S. M., Wurm F. M., Gregory T. Biological properties of a CD4 immunoadhesin. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):667–670. doi: 10.1038/344667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chamow S. M., Mordenti J., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Mitsuya H., Byrn R. A., Lucas C., Wurm F. M., Groopman J. E. Designing CD4 immunoadhesins for AIDS therapy. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):525–531. doi: 10.1038/337525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., FitzGerald D. J., Moss B., Pastan I., Berger E. A. Selective killing of HIV-infected cells by recombinant human CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):369–372. doi: 10.1038/335369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Metcalf J., Griffin D. E. Use of a new CD4-positive HeLa cell clone for direct quantitation of infectious human immunodeficiency virus from blood cells of AIDS patients. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Lifson J. D. HIV interactions with CD4: a continuum of conformations and consequences. Immunol Today. 1992 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90154-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan C., Brown K., Pincus S. H. Alteration in H chain V region affects complement activation by chimeric antibodies. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2527–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh R., Hart T. K., Ellens H., Miller J., Petteway S. A., Jr, Lambert D. M., Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Morphometric analysis of recombinant soluble CD4-mediated release of the envelope glycoprotein gp120 from HIV-1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Oct;6(10):1209–1212. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Chalifoux L. V., Reimann K. A., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Lambert J. M. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. Delivery of ribosome-inactivating proteins to spleen and lymph node T cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):666–673. doi: 10.1172/JCI112625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Goldmacher V. S., Ritz J., Yetz J. M., Schlossman S. F., Lambert J. M. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. In vivo stability of disulfide-linked immunotoxin conjugates. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):977–984. doi: 10.1172/JCI112399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Huang Y. X., Ashkenazi A., Ho D. D. Virions of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates resistant to soluble CD4 (sCD4) neutralization differ in sCD4 binding and glycoprotein gp120 retention from sCD4-sensitive isolates. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):235–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.235-243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Weiss R. A., Sattentau Q. J. Dissociation of gp120 from HIV-1 virions induced by soluble CD4. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2251501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Cole R. L., Hersh E. M., Lake D., Masuho Y., Durda P. J., McClure J. In vitro efficacy of anti-HIV immunotoxins targeted by various antibodies to the envelope protein. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4315–4324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Stocks C. J., Jr, Ewing L. P. Monoclonal anti-(T,G)-A--L antibodies: characterization of fine specificity and idiotype expression. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1551–1559. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K. AZT demonstrates anti-HIV-1 activity in persistently infected cell lines: implications for combination chemotherapy and immunotherapy. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1233–1238. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Treatment of HIV tissue culture infection with monoclonal antibody-ricin A chain conjugates. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3070–3075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Use of a focal infectivity assay for testing susceptibility of HIV to antiviral agents. Biotechniques. 1991 Mar;10(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Tschachler E., Hayes S. F., Buller R. S., Reitz M. Variants selected by treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells with an immunotoxin. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Moore J. P. Conformational changes induced in the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein by soluble CD4 binding. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):407–415. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till M. A., Ghetie V., Gregory T., Patzer E. J., Porter J. P., Uhr J. W., Capon D. J., Vitetta E. S. HIV-infected cells are killed by rCD4-ricin A chain. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1166–1168. doi: 10.1126/science.2847316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till M. A., Zolla-Pazner S., Gorny M. K., Patton J. S., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Human immunodeficiency virus-infected T cells and monocytes are killed by monoclonal human anti-gp41 antibodies coupled to ricin A chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Fulton R. J., May R. D., Till M., Uhr J. W. Redesigning nature's poisons to create anti-tumor reagents. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1098–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.3317828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


