Abstract
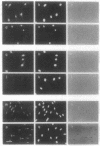
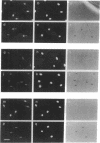
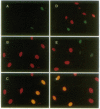
Decreased affinity of the retinoblastoma protein (RB) for the nuclear compartment has been correlated with cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the RB protein during the G1/S phase of the cell cycle. We examined the effects of microinjected protein-serine/threonine phosphatases types 1 (PP1) and 2A (PP2A) on nuclear association of RB monitored as the resistance of RB to extraction at the G1/S transition. Microinjection of PP1 into either the nucleus or the cytoplasm of cells synchronized in G1 increased the amount of RB that was resistant to extraction from the nucleus. Microinjection of PP2A, however, required direct injection into the nucleus to generate this effect. In addition, we found that nuclear injection of only the PP2A catalytic subunit (PP2AC) and not the complex containing the A and C subunits inhibited RB extraction. Microinjection of either PP1 or PP2A and the resultant increased affinity of RB for the nucleus corresponded with the inhibition of cell cycle progression into S phase. Injection of either phosphatase into cells that had entered S phase did not block DNA synthesis, suggesting that the effect of the injected phosphatases on cell cycle arrest was specific. In vitro biochemical studies with purified PP1 and PP2A showed that intact RB protein phosphorylated by cdc2 kinase served as a substrate for both protein phosphatases. Our results suggest that protein phosphatases may be important regulators of RB function and support the idea that cell cycle progression is regulated by the phosphorylation state of the RB protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of a type 1 protein phosphatase encoded by bws1+ in fission yeast mitotic control. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Scully P., Lee W. H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.2300823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGuzman A., Lee E. Y. Preparation of low-molecular-weight forms of rabbit muscle protein phosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:356–368. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Brautigan D. L., Lamb N. J. Protein phosphatase type 1 in mammalian cell mitosis: chromosomal localization and involvement in mitotic exit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1421–1430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Scheidtmann K. H., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W., Walter G. Complexes of polyoma virus medium T antigen and cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7952–7954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Hamlin J. L. An amplified chromosomal sequence that includes the gene for dihydrofolate reductase initiates replication within specific restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Park S. H., Bogenmann E., Cheng J. C., Yandell D. W., Kaye F. J., Minna J. D., Dryja T. P., Weinberg R. A. Frequent inactivation of the retinoblastoma anti-oncogene is restricted to a subset of human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2775–2779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Stewart A. A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 6. Measurement of type-1 and type-2 protein phosphatases in extracts of mammalian tissues; an assessment of their physiological roles. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakes S., Mellgren R. L., Schlender K. K. Isolation and characterization of an inhibitor-sensitive and a polycation-stimulated protein phosphatase from rat liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 29;888(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Carbone A., Walter G. Purified polyoma virus medium T antigen has tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity but no significant phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1866–1874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuret J., Bell H., Cohen P. Identification of high levels of protein phosphatase-1 in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80741-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMorte V. J., Goldsmith P. K., Spiegel A. M., Meinkoth J. L., Feramisco J. R. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in living cells by microinjection of Gi2 antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Buchkovich K. J., Marshak D. R., Anderson C. W., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated on multiple sites by human cdc2. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4279–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. T., Gruenwald S., Morla A. O., Lee W. H., Wang J. Y. Retinoblastoma cancer suppressor gene product is a substrate of the cell cycle regulator cdc2 kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):857–864. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., Shon J., Pipas J. M., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product undergoes cell cycle-dependent dephosphorylation and binding to and release from SV40 large T. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90590-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Cao X. R., Yen A., Chandler S., Driscoll B., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of phosphorylation of the human retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.2588006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Weinberg R. A. G1/S phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein is associated with an altered affinity for the nuclear compartment. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Russell K. L., Garrard L. J., Green D. D. Cardiac contractile protein phosphatases. Purification of two enzyme forms and their characterization with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6257–6265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Walter G. Protein phosphatases and DNA tumor viruses: transformation through the back door? Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):589–598. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphree A. L., Benedict W. F. Retinoblastoma: clues to human oncogenesis. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1028–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.6320372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Cherington V., Morgan W., DeAnda J., Kaplan D., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Cellular proteins that associate with the middle and small T antigens of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3934-3940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K. Complete interaction of cellular 56,000- and 32,000-Mr proteins with simian virus 40 small-t antigen in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1240–1243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1240-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Mumby M. C., Rundell K., Walter G. Dephosphorylation of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and p53 protein by protein phosphatase 2A: inhibition by small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1996–2003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Nairn A. C. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:1–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. H., Beeson M., Gordon L. Failure to phosphorylate the retinoblastoma gene product in senescent human fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.2166342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D. J. Nuclear binding of purified retinoblastoma gene product is determined by cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usui H., Imazu M., Maeta K., Tsukamoto H., Azuma K., Takeda M. Three distinct forms of type 2A protein phosphatase in human erythrocyte cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3752–3761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Carbone-Wiley A., Joshi B., Rundell K. Homologous cellular proteins associated with simian virus 40 small T antigen and polyomavirus medium T antigen. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4760–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4760-4762.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]