Abstract
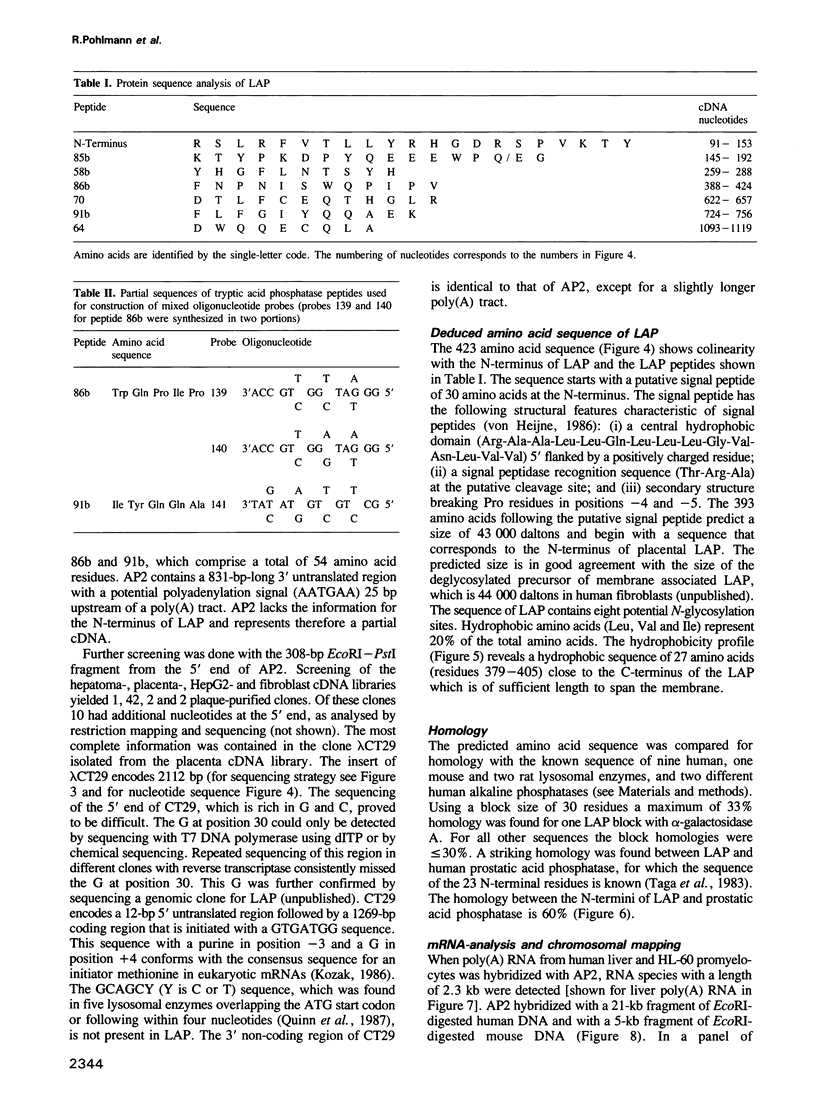
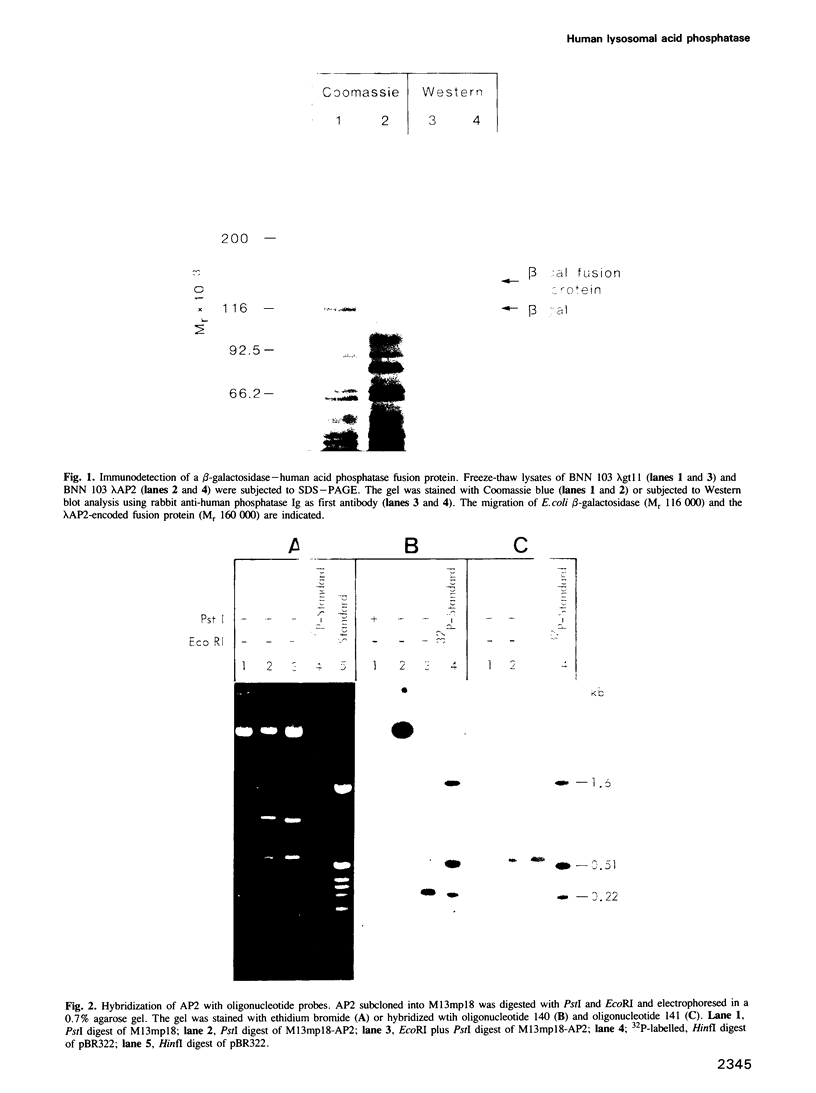
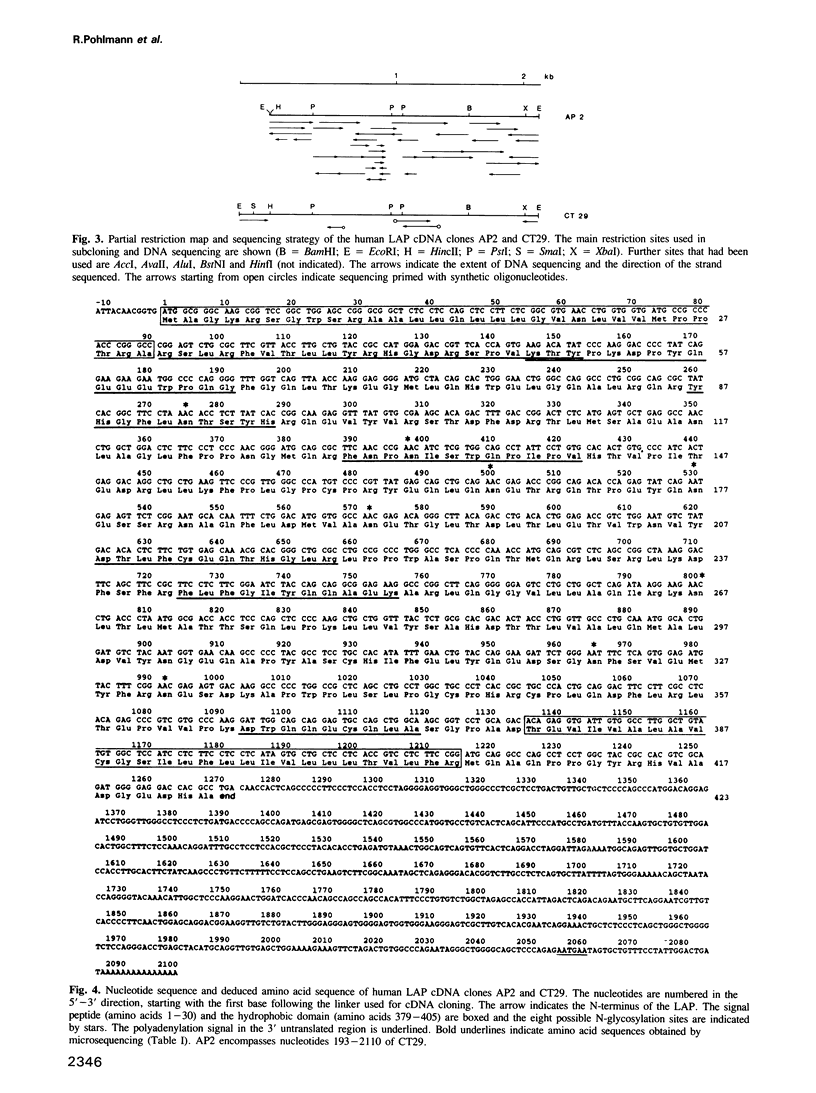
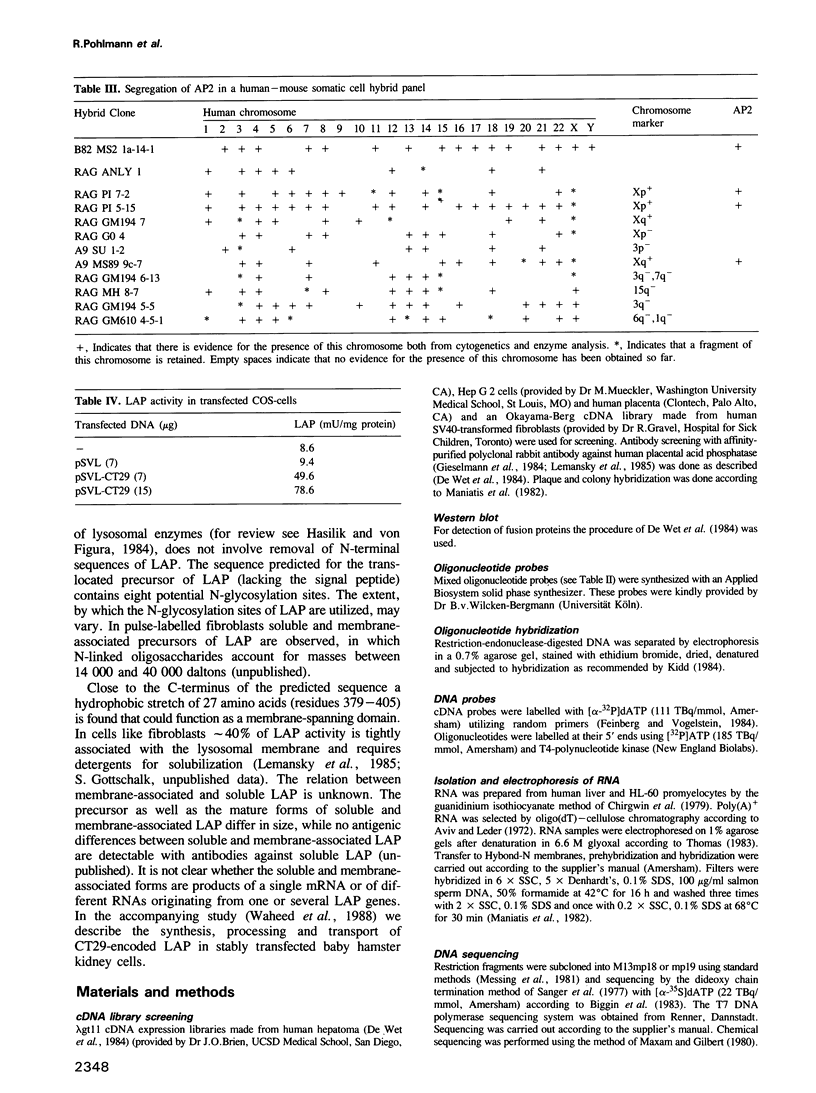
A 2112-bp cDNA clone (lambda CT29) encoding the entire sequence of the human lysosomal acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2) was isolated from a lambda gt11 human placenta cDNA library. The cDNA hybridized with a 2.3-kb mRNA from human liver and HL-60 promyelocytes. The gene for lysosomal acid phosphatase was localized to human chromosome 11. The cDNA includes a 12-bp 5' non-coding region, an open reading frame of 1269 bp and an 831-bp 3' non-coding region with a putative polyadenylation signal 25 bp upstream of a 3' poly(A) tract. The deduced amino acid sequence reveals a putative signal sequence of 30 amino acids followed by a sequence of 393 amino acids that contains eight potential glycosylation sites and a hydrophobic region, which could function as a transmembrane domain. A 60% homology between the known 23 N-terminal amino acid residues of human prostatic acid phosphatase and the N-terminal sequence of lysosomal acid phosphatase suggests an evolutionary link between these two phosphatases. Insertion of the cDNA into the expression vector pSVL yielded a construct that encoded enzymatically active acid phosphatase in transfected monkey COS cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs I., Purrello M., Kurnit D. M., Grzeschik K. H., Siniscalco M. Isolation and characterization of human random cDNA clones homologous to DNA from the X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jul;10(4):385–397. doi: 10.1007/BF01535634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Calhoun D. H., Bernstein H. S., Hantzopoulos P., Quinn M., Desnick R. J. Human alpha-galactosidase A: nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the mature enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4859–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G. A., Gerald P. S. Human acid phosphatase in somatic cell hybrids. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):480–482. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby N., Courval J., Francke U. Regional assignments of the genes for fumarate hydratase and guanylate kinase on chromosome 1 and for lysosomal acid phosphatase and esterase A4 on chromosome 11. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):105–107. doi: 10.1159/000130565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Grzeschik K. H., Jaye M., De La Salle H., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Regional localization on the human X chromosome and polymorphism of the coagulation factor IX gene (hemophilia B locus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., San Segundo B., McCormick M. B., Steiner D. F. Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of cloned human and mouse preprocathepsin B cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7721–7725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong D., Calhoun D. H., Hsieh W. T., Lee B., Wells R. D. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the human lysosomal proteinase cathepsin B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., de Wet J. R., O'Brien J. S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human alpha-L-fucosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1262–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieselmann V., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Tartrate-inhibitable acid phosphatase. Purification from placenta, characterization and subcellular distribution in fibroblasts. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Jun;365(6):651–660. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guise K. S., Korneluk R. G., Waye J., Lamhonwah A. M., Quan F., Palmer R., Ganschow R. E., Sly W. S., Gravel R. A. Isolation and expression in Escherichia coli of a cDNA clone encoding human beta-glucuronidase. Gene. 1985;34(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Kao F. T. Regional mapping of the gene for human lysosomal acid phosphatase (ACP2) using a hybrid clone panel containing segments of human chromosome 11. Hum Genet. 1978 Nov 24;45(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00277567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam W., Clauser E., Kim Y. S., Kan Y. W., Rutter W. J. Cloning, sequencing, and chromosomal localization of human term placental alkaline phosphatase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8715–8719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Jones C., Law M. L., Puck T. T. Regional assignment of genes on human chromosomes 11 and 12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):474–477. doi: 10.1159/000131001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemansky P., Gieselmann V., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Synthesis and transport of lysosomal acid phosphatase in normal and I-cell fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9023–9030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchter-Wasyl E., Ostrowski W. Subunit structure of human prostatic acid phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 9;365(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiniuk F., Mehler M., Pellicer A., Tzall S., La Badie G., Hobart C., Ellenbogen A., Hirschhorn R. Isolation of a cDNA for human acid alpha-glucosidase and detection of genetic heterogeneity for mRNA in three alpha-glucosidase-deficient patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9641–9644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrsny R. J., Meizel S. Potassium ion influx and Na+,K+-ATPase activity are required for the hamster sperm acrosome reaction. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Rosenfeld M. G., Kreibich G., Gubler U., Sabatini D. D., Adesnik M., Andy R. Nucleotide sequence of rat preputial gland beta-glucuronidase cDNA and in vitro insertion of its encoded polypeptide into microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7292–7296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Auffray C. A program for prediction of protein secondary structure from nucleotide sequence data: application to histocompatibility antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Quan F., Willard H. F., Lamhonwah A. M., Korneluk R. G., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A., Mahuran D. J. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the beta subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M., Hantzopoulos P., Fidanza V., Calhoun D. H. A genomic clone containing the promoter for the gene encoding the human lysosomal enzyme, alpha-galactosidase A. Gene. 1987;58(2-3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D., Roy S. Hydrophobic basis of packing in globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saini M. S., Van Etten R. L. A homogeneous isoenzyme of human liver acid phosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):613–624. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A., Lalley P. A. Assignment and linear order of human acid phosphatase-2, esterase A4, and lactate dehydrogenase A genes on chromosome 11. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;16(1-5):231–234. doi: 10.1159/000130598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., West C., Westwood B., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of human glucocerebrosidase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7289–7293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga E. M., Moore D. L., Van Etten R. L. Studies on the structural basis of the heterogeneity of human prostatic and seminal acid phosphatases. Prostate. 1983;4(2):141–150. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Towatari T., Katunuma N., Teller D. C., Titani K. Homology of amino acid sequences of rat liver cathepsins B and H with that of papain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Winfield S., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA containing the complete coding sequence for human lysosomal glucocerebrosidase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Martin B. M., Kaslow D. C., Migeon B. R., Choudary P. V., Stubbleflied B. K., Mayor J. A., Murray G. J., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. Signal sequence and DNA-mediated expression of human lysosomal alpha-galactosidase A. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Gottschalk S., Hille A., Krentler C., Pohlmann R., Braulke T., Hauser H., Geuze H., von Figura K. Human lysosomal acid phosphatase is transported as a transmembrane protein to lysosomes in transfected baby hamster kidney cells. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2351–2358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Van Etten R. L. Biosynthesis and processing of lysosomal acid phosphatase in cultured human cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):274–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90796-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Van Etten R. L., Gieselmann V., von Figura K. Immunological characterization of human acid phosphatase gene products. Biochem Genet. 1985 Apr;23(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00504327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Naylor S. L., Grzeschik K. H., Sakaguchi A. Y. Regional assignment of human protooncogene c-myb to 6q21----qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jan;10(1):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01534477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C. Lysosomes revisited. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):391–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Fukushima H., Dewji N. N., Wilcox E., O'Brien J. S., Helinski D. R. Chromogenic immunodetection of human serum albumin and alpha-L-fucosidase clones in a human hepatoma cDNA expression library. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):437–447. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]