Abstract
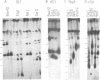
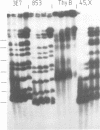
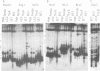
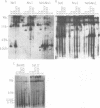
A physical map of the human pseudoautosomal region has been constructed using pulsed field gel electrophoresis and the infrequently cutting restriction enzymes BssHIII, EagI, SstII, NotI, MluI and NruI. This map extends 2.3 Mbp from the telomere to sex-chromosome-specific DNA, includes at least seven CpG islands and locates four genetically mapped loci. Five of the CpG islands are organized into two clusters. One cluster is adjacent to the telomere, the other extends into sex-chromosome-specific DNA. There is congruence between the genetic and physical maps which implies that the frequency of recombination is approximately uniform throughout the DNA.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Frommer M., Miller O. J., Macleod D. A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated, CpG-rich DNA. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne P. S. Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of Mammals. Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00274192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. D., Ma P., Smith K. D. Characterization and evolution of a single-copy sequence from the human Y chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):576–581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Brown W. R., Rappold G. A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):687–692. doi: 10.1038/317687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON-SMITH M. A. KARYOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS IN GONADAL DYSGENESIS AND THEIR BEARING ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF MALFORMATIONS. J Med Genet. 1965 Jun;2(2):142–155. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD C. E., JONES K. W., POLANI P. E., DE ALMEIDA J. C., BRIGGS J. H. A sex-chromosome anomaly in a case of gonadal dysgenesis (Turner's syndrome). Lancet. 1959 Apr 4;1(7075):711–713. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91893-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischel-Ghodsian N., Nicholls R. D., Higgs D. R. Unusual features of CpG-rich (HTF) islands in the human alpha globin complex: association with non-functional pseudogenes and presence within the 3' portion of the zeta gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9215–9225. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Darling S. M., Thomas N. S., Goodfellow P. N. A pseudoautosomal gene in man. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2877492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Pritchard C., Tippett P., Goodfellow P. N. Recombination between the X and Y chromosomes: implications for the relationship between MIC2, XG and YG. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 May;51(Pt 2):161–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Soriano P., Müller U., Jaenisch R. High frequency of unequal recombination in pseudoautosomal region shown by proviral insertion in transgenic mouse. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):682–685. doi: 10.1038/324682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E. A., Schorderet D. F., Gartler S. M. Linkage of the steroid sulfatase gene to the sex-reversed mutation in the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):465–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Bostock C., Robertson M., Christie S., Mitchen J. L., Dahlberg J. E. U1 small nuclear RNA genes are located on human chromosome 1 and are expressed in mouse-human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2211–2220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Human-mouse cell hybrid with human multiple Y chromosomes. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):63–65. doi: 10.1038/262063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. A., Goodfellow P. J., Goodfellow P. N. Mapping the limits of the human pseudoautosomal region and a candidate sequence for the male-determining gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):273–275. doi: 10.1038/328273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Vergnaud G., Cooke H. J., Weissenbach J. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):291–295. doi: 10.1038/319291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWARTZ M. N., TRAUTNER T. A., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XI. Further studies on nearest neighbor base sequences in deoxyribonucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmler M. C., Rouyer F., Vergnaud G., Nyström-Lahti M., Ngo K. Y., de la Chapelle A., Weissenbach J. Pseudoautosomal DNA sequences in the pairing region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):692–697. doi: 10.1038/317692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. I., Golembieski W., Gilbert J. D., Kizyma L., Miller O. J. Overabundance of rare-cutting restriction endonuclease sites in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1173–1184. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Levilliers J., Petit C., Rouyer F., Simmler M. C. Normal and abnormal interchanges between the human X and Y chromosomes. Development. 1987;101 (Suppl):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]