Abstract
The glucocorticoid receptor and the other members of the steroid receptor super-family share a highly conserved, cysteine-rich region which coincides with the DNA binding/transactivating domain. It has been postulated that this region is folded into two 'zinc finger' structures, similar to those originally reported for the transcription factor TFIIIA. The first potential finger domain contains four conserved cysteines and one conserved histidine, while the second contains five conserved cysteines. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we have analysed the consequences of altering the proposed finger-like structures. Our results show that most of the mutations affecting the conserved cysteines result in a total loss of glucocorticoid receptor function. In one important exception, however, a conserved cysteine (Cys500) is dispensable for glucocorticoid receptor activity and therefore cannot be involved in complexing a metal ion to form a finger structure. Moreover, the replacement of either Cys476 or Cys482 by His residues maintains partial in vivo activity of the glucocorticoid receptor, while their exchange for an alanine or serine residue, respectively, eliminates receptor function. These results support, at a genetic level, the involvement of cysteines of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain in metal ion complexation and define the candidate residues involved in such coordination.
Full text
PDF

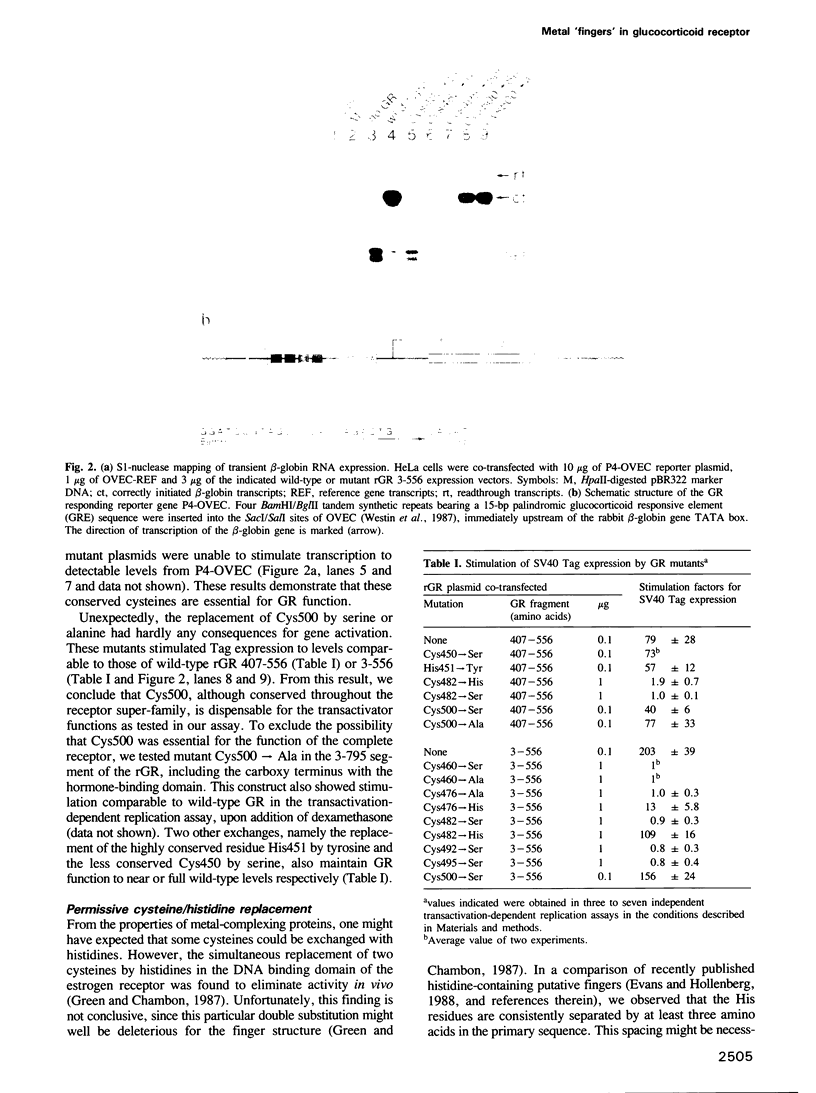



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Argos P. Fingers and helices. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):215–215. doi: 10.1038/324215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Skroch P., Weinmann J., Butkeraitis P., Ponta H. DNA sequences outside the receptor-binding sites differently modulate the responsiveness of the mouse mammary tumour virus promoter to various steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M. The mouse glucocorticoid receptor: mapping of functional domains by cloning, sequencing and expression of wild-type and mutant receptor proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2513–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Yang N., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):91–94. doi: 10.1038/331091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckaby C. S., Conneely O. M., Beattie W. G., Dobson A. D., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure of the chromosomal chicken progesterone receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Functional analysis of the glucocorticoid regulatory elements present in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. A synthetic distal binding site can replace the proximal binding domain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1214–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.3029866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Borgmeyer U., Nowock J. Interaction of the TGGCA-binding protein with upstream sequences is required for efficient transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1355–1360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Kennedy N., Skroch P., Hynes N. E., Groner B. Hormonal response region in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat can be dissociated from the proviral promoter and has enhancer properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1020–1024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Kämpe O., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Association between transplantation antigens and a viral membrane protein synthesized from a mammalian expression vector. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbah M., Redeuilh G., Secco C., Baulieu E. E. The binding activity of estrogen receptor to DNA and heat shock protein (Mr 90,000) is dependent on receptor-bound metal. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8631–8635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni A., Cattaneo R., Serfling E., Schaffner W. A novel expression selection approach allows precise mapping of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7457–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela D., Weber H., Weissmann C. Is sequence conservation in interferons due to selection for functional proteins? Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):698–700. doi: 10.1038/313698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



