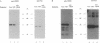Abstract
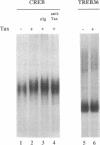
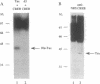
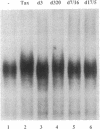
The trans-activator protein Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) activates the viral 21-base-pair (bp) enhancer in the long terminal repeat and has been suggested to associate indirectly with the enhancer DNA. To demonstrate this, we used DNA-affinity precipitation assay and detected the Tax protein in 21-bp DNA-protein complexes isolated from HTLV-1-infected cells. To identify cellular components in the complexes, we tested various 21-bp DNA-binding proteins by gel electrophoretic mobility-shift assay. Each binding protein gave a shifted band of each 21-bp DNA-protein complex, and exogenously added Tax protein further shifted these bands of cAMP-responsive element (CRE) binding protein (CREB) and CRE modulator but did not shift other bands. Anti-Tax antibodies blocked formation of the complex, indicating complex formations of [Tax-CREB(or CRE modulator)-21-bp DNA]. The formations of these complexes paralleled the functional activities of Tax mutants. Furthermore, the Tax-CREB complex was detected in a nuclear extract of HTLV-1-infected cells, and the Tax-CREB-21-bp-DNA complex was demonstrated as a major component of Tax complexes containing the 21-bp DNA probe. These observations indicate that Tax protein binds to CREB and CRE modulator and the complexes then bind to the 21-bp enhancer, suggesting that the complex binding to the enhancer mediates trans-activation of transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Béraud C., Lombard-Platet G., Michal Y., Jalinot P. Binding of the HTLV-I Tax1 transactivator to the inducible 21 bp enhancer is mediated by the cellular factor HEB1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3795–3803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Paskalis H., Kleinman-Ewing C., Wong-Staal F., Pavlakis G. N. The pX protein of HTLV-I is a transcriptional activator of its long terminal repeats. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.2992082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Niki T., Mori T., Matsuda T., Matsui M., Nomura N., Seiki M. HTLV-1 Tax induces expression of various immediate early serum responsive genes. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. c-fos promoter trans-activation by the tax1 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Seiki M., Kiyokawa T., Yoshida M. Functional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I by a trans-acting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2277–2281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Seiki M., Sato M., Yoshida M. A transcriptional enhancer sequence of HTLV-I is responsible for trans-activation mediated by p40 chi HTLV-I. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):713–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshida M. A unique enhancer element for the trans activator (p40tax) of human T-cell leukemia virus type I that is distinct from cyclic AMP- and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-responsive elements. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3234–3239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3234-3239.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshimura T., Yoshida M. The indirect association of human T-cell leukemia virus tax protein with DNA results in transcriptional activation. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4525–4528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4525-4528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Nagata K., Hanaoka M., Nakai M., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K. I., Shirakawa S., Miyoshi I. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Fujisawa J., Suzuki T., Ueda K., Muramatsu M., Tsuboi A., Arai N., Yoshida M. Transcriptional activator Tax of HTLV-1 binds to the NF-kappa B precursor p105. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1737–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Purification of his-tagged proteins in non-denaturing conditions suggests a convenient method for protein interaction studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6337–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Taniguchi T., Tsuru S., Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2883–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman V. S., Sarngadharan M. G., Nakao Y., Ito Y., Aoki T., Gallo R. C. Natural antibodies to the structural core protein (p24) of the human T-cell leukemia (lymphoma) retrovirus found in sera of leukemia patients in Japan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1653–1657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Kawaguchi T., Seiki M., Yoshida M. Association of the pX gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus type-I with nucleus. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):462–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Böhnlein E., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor alpha subunit (Tac or CD25 antigen) gene expression: binding of inducible nuclear proteins to discrete promoter sequences correlates with transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4468–4472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Shibuya H., Harada H., Hatakeyama M., Seiki M., Fujita T., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Taniguchi T. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Seiki M., Malefijt R. D., Heike T., Fujisawa J., Takebe Y., Nishida J., Shlomai J., Yokota T., Yoshida M. Activation of T cell-derived lymphokine genes in T cells and fibroblasts: effects of human T cell leukemia virus type I p40x protein and bovine papilloma virus encoded E2 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6547–6566. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Dynan W. S., Chen I. S., Wachsman W. Binding of host-cell factors to DNA sequences in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I: implications for viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1457–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Igata A., Matsumoto M., Tara M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1031–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R. E., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. A nuclear factor is required for transactivation of HTLV-I gene expression. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paskalis H., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Cis-acting sequences responsible for the transcriptional activation of human T-cell leukemia virus type I constitute a conditional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6558–6562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hikikoshi A., Taniguchi T., Yoshida M. Expression of the pX gene of HTLV-I: general splicing mechanism in the HTLV family. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2990031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Takano M., Teruuchi T., Miwa M. Requirement of multiple copies of a 21-nucleotide sequence in the U3 regions of human T-cell leukemia virus type I and type II long terminal repeats for trans-acting activation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8112–8116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Identification of HTLV-I tax trans-activator mutants exhibiting novel transcriptional phenotypes. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1875–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Nyunoya H., Morita T., Sato T., Shimotohno K. Isolation of cDNAs for DNA-binding proteins which specifically bind to a tax-responsive enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1420–1426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1420-1426.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsman W., Shimotohno K., Clark S. C., Golde D. W., Chen I. S. Expression of the 3' terminal region of human T-cell leukemia viruses. Science. 1984 Oct 12;226(4671):177–179. doi: 10.1126/science.6091270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M. Expression of the HTLV-1 genome and its association with a unique T-cell malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 8;907(2):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Seiki M., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2534–2537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Giam C. Z. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator, Tax, enhances CREB binding to HTLV-I 21-base-pair repeats by protein-protein interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7070–7074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L. J., Giam C. Z. Interaction of the human T-cell lymphotrophic virus type I (HTLV-I) transcriptional activator Tax with cellular factors that bind specifically to the 21-base-pair repeats in the HTLV-I enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11445–11449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]