Abstract
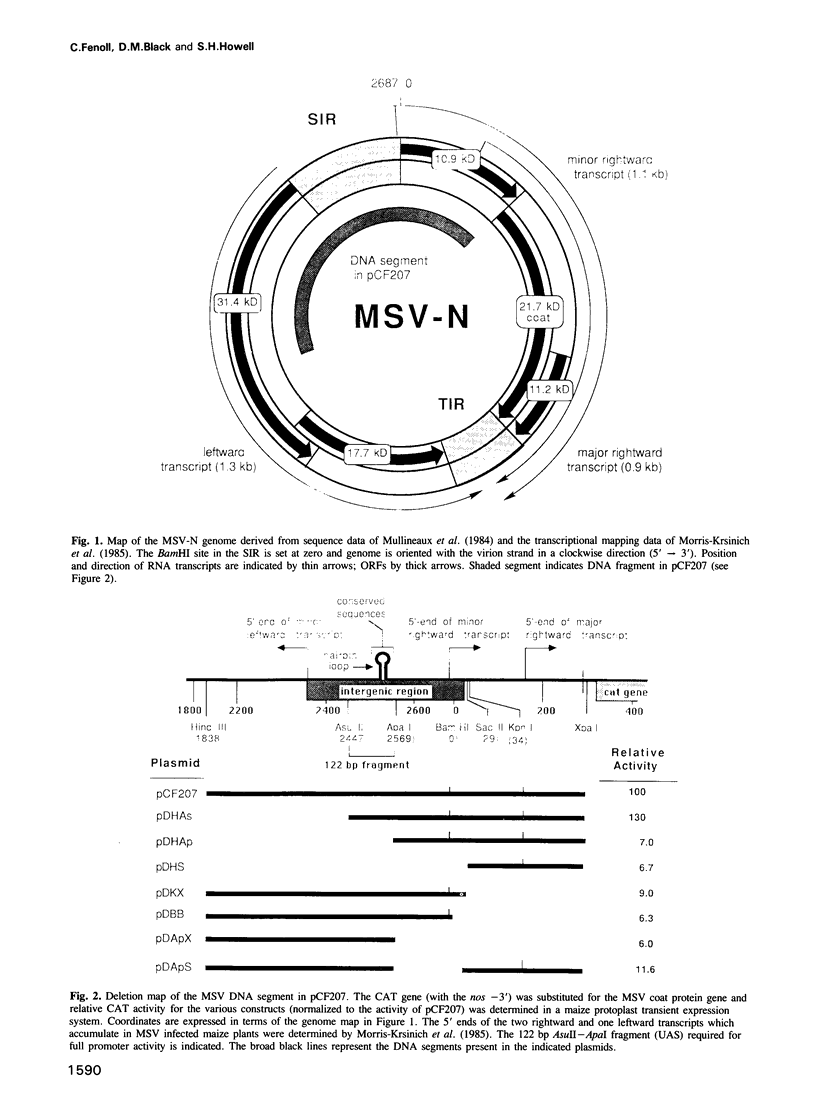
Maize streak virus (MSV), a geminivirus with a one-component genome, encodes a major coat protein RNA which accumulates in infected plants. Using a maize protoplast cell transient expression system, we have defined and studied the promoter which drives rightward transcription of the RNA encoding the coat protein. We have identified a 122 bp upstream segment that enhances promoter activity and functions as an upstream activating sequence (UAS). The UAS lies in the starting intergenic region of the viral genome and includes a region which is similar in all geminiviruses. The 122 bp UAS activates the MSV core promoter in an orientation, but not position, independent fashion. The MSV promoter UAS is interchangeable with a similar element in the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S RNA core promoter, that is the MSV UAS will activate the CaMV 35S core promoter and vice versa. However, the MSV promoter UAS specifically binds proteins in maize nuclear extracts which appear to differ from those bound by the functionally equivalent region of the CaMV 35S promoter.
Keywords: plant virus, geminivirus, promoter upstream activating sequences, transient expression system, DNA–protein complexes
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen Z. L., Schuler M. A., Beachy R. N. Functional analysis of regulatory elements in a plant embryo-specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8560–8564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donson J., Morris-Krsinich B. A., Mullineaux P. M., Boulton M. I., Davies J. W. A putative primer for second-strand DNA synthesis of maize streak virus is virion-associated. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3069–3073. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert P. R., Ha S. B., An G. Identification of an essential upstream element in the nopaline synthase promoter by stable and transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5745–5749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Maize Adh-1 promoter sequences control anaerobic regulation: addition of upstream promoter elements from constitutive genes is necessary for expression in tobacco. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Walker J. C., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. The ocs element: a 16 base pair palindrome essential for activity of the octopine synthase enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3203–3208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5824–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. Homology between human bladder carcinoma oncogene product and mitochondrial ATP-synthase. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):262–264. doi: 10.1038/301262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley W. B., Czarnecka E., Nagao R. T., Key J. L. Upstream sequences required for efficient expression of a soybean heat shock gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):559–565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. D., Stein V. E., Coutts R. H., Buck K. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the infectious cloned DNA components of tomato golden mosaic virus: potential coding regions and regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2197–2205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth A. J., Caton J., Bossert M., Goodman R. M. Nucleotide sequence of bean golden mosaic virus and a model for gene regulation in geminiviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3572–3576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H. Physical structure and genetic organisation of the genome of maize streak virus (Kenyan isolate). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7359–7375. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofuku K. D., Okamuro J. K., Goldberg R. B. Interaction of an embryo DNA binding protein with a soybean lectin gene upstream region. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):734–737. doi: 10.1038/328734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaulen Hildegard, Schell Jeff, Kreuzaler Fritz. Light-induced expression of the chimeric chalcone synthase-NPTII gene in tobacco cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Fluhr R., Green P. J., Chua N. H. Sequences in the pea rbcS-3A gene have homology to constitutive mammalian enhancers but function as negative regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDowell S. W., Macdonald H., Hamilton W. D., Coutts R. H., Buck K. W. The nucleotide sequence of cloned wheat dwarf virus DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2173–2180. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris-Krsinich B. A., Mullineaux P. M., Donson J., Boulton M. I., Markham P. G., Short M. N., Davies J. W. Bidirectional transcription of maize streak virus DNA and identification of the coat protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7237–7256. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullineaux P. M., Donson J., Morris-Krsinich B. A., Boulton M. I., Davies J. W. The nucleotide sequence of maize streak virus DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3063–3068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Wong M., Chua N. H. The 5'-proximal region of the wheat Cab-1 gene contains a 268-bp enhancer-like sequence for phytochrome response. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Functional regions of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter determined by use of the firefly luciferase gene as a reporter of promoter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4870–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. L., Vasil V., Vasil I. K., Ferl R. J. Constitutive and anaerobically induced DNase-I-hypersensitive sites in the 5' region of the maize Adh1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):799–803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D. Viral and cellular transcription enhancers. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:24–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Markham P. G., Callis R. J., Pinner M. S. The nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of the geminivirus beet curly top virus. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1761–1767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timko M. P., Kausch A. P., Castresana C., Fassler J., Herrera-Estrella L., Van den Broeck G., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Cashmore A. R. Light regulation of plant gene expression by an upstream enhancer-like element. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):579–582. doi: 10.1038/318579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]